Patent application title: STREAMING MEDIA FOR PORTABLE DEVICES
Inventors:
Gilbert Springer (Fremont, CA, US)
IPC8 Class: AH04L2906FI
USPC Class:
726 12
Class name: Network firewall proxy server or gateway
Publication date: 2016-05-19
Patent application number: 20160142376
Abstract:
A system and method for allowing hand-held/wireless device devices to (1)
provide audio/video conferencing; (2) access AV content through streaming
and cloud transfer; and (3) offer hand-held and computer access to
cameras and sensors for surveillance using ordinary personal computers as
proxy servers is described. In a first aspect, a remote view streaming
system which comprises a webcam server which enables streaming video over
a network is disclosed. The system includes a portable device. The
portable device includes a client application. The portable device is
configured to receive the streaming video from the network and display it
on a screen. The system includes a proxy server for authenticating a
connection between the webcam server and the portable device. In a second
aspect, a portable device is disclosed. The portable device comprises a
client application; wherein the client application includes
authentication information to allow connection to the proxy server and in
turn can be connected directly to a webcam server if the webcam server
has proper authentication.Claims:
1. A remote view streaming system which comprises: at least one webcam
server which enables streaming video over a network; a portable device
including a client application, the portable device configured to receive
the streaming video from the network and display it on a screen; and a
proxy server for authenticating a connection between the at least one
webcam server and the portable device.
2. The remote view streaming system of claim 1, wherein the at least one webcam server comprises a plurality of webcam servers which are paired to the client application.
3. The remote view streaming system of claim 1, wherein the at least one webcam server registers itself with proxy server, wherein the proxy server stores the at least one webcam server information in a relational database.
4. The remote view streaming system of claim 3, wherein the proxy server acquires one or more keys from the relational database and provides the at least one webcam server's information to the client application to establish the direct connection with the client application.
5. The remote view streaming system of claim 1, wherein the client application receives an active list of webcam servers after the proxy server authenticates the connection.
6. The remote view streaming system of claim 1, wherein the portable device comprises a smartphone and the client application comprises a smartphone client.
7. The remote view streaming system of claim 1, wherein the portable device comprises any of a smartphone, PDA, and tablet computer.
8. A portable device comprising: a client application; wherein the client application includes authentication information to allow connection to a proxy server and in turn can be connected directly to at least one webcam server if the at least one webcam server has proper authentication.
9. The portable device of claim 8, wherein the at least one webcam server comprises a plurality of webcam servers which are paired to the client application.
10. The portable device of claim 8, wherein the at least one webcam server registers itself with proxy server, wherein the proxy server stores the at least one webcam server information in a relational database.
11. The portable device of claim 8, wherein the proxy server acquires one or more keys from the relational database and provides the at least one webcam server's information to the client application to establish the direct connection with the client application.
12. The portable device of claim 8, wherein the client application receives an active list of webcam servers after the proxy server authenticates the connection.
13. A smartphone comprising: a smartphone client application; wherein the smartphone application includes authentication information to allow connection to a proxy server and in turn can be connected directly to at least one webcam server if the at least one webcam server has proper authentication; wherein the proxy server acquires one or more keys from the relational database and provides the at least one webcam server's information to the smartphone client to establish the direct connection with the smartphone client; and wherein the smartphone client receives an active list of webcam servers after the proxy server authenticates the connection.
14. The smartphone of claim 13, wherein the at least one webcam server comprises a plurality of webcam servers which are paired to the smartphone client.
15. The smartphone of claim 13, wherein the at least one webcam server registers itself with proxy server, wherein the proxy server stores the at least one webcam server information in a relational database.
Description:
CROSS REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATION
[0001] Under 35 U.S.C. 120, this application is a Continuation Application and claims priority to U.S. application Ser. No. 13/053,077, filed Mar. 21, 2011, entitled "STREAMING MEDIA FOR PORTABLE DEVICES", which claims the benefit of U.S. Patent Application Ser. No. 61/315,848, entitled "STREAMING MEDIA FOR HAND-HELD/WIRELESS DEVICES," filed on Mar. 19, 2010, all of which are incorporated herein by reference in their entireties.
FIELD OF THE INVENTION
[0002] The present invention relates generally to portable devices and more particularly to a method and system for streaming media thereto.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0003] Substantial interest for extending the usefulness of hand-held/wireless device devices for the acquisition of live and stored content through streaming media to hand-held devices is desirable. The present invention addresses such a need.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0004] A system and method for allowing hand-held/wireless device devices to (1) provide audio/video conferencing; (2) access AV content through streaming and cloud transfer; and (3) offer hand-held and computer access to cameras and sensors for surveillance using ordinary personal computers as proxy servers is described.
[0005] In a first aspect, a remote view streaming system which comprises a webcam server which enables streaming video over a network is disclosed. The system includes a portable device. The portable device includes a client application. The portable device is configured to receive the streaming video from the network and display it on a screen. The system includes a proxy server for authenticating a connection between the webcam server and the portable device.
[0006] In a second aspect, a portable device is disclosed. The portable device comprises a client application; wherein the client application includes authentication information to allow connection to the proxy server and in turn can be connected directly to a webcam server if the webcam server has proper authentication.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF DRAWINGS
[0007] The accompanying drawings illustrate an embodiment of the present invention and, together with the description, serve to explain the principle of the invention. One skilled in the art will recognize that the particular embodiments illustrated in the drawings are merely exemplary, and are not intended to limit the scope of the present invention.
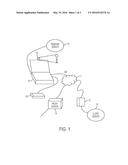
[0008] FIG. 1 is a diagram of a remote view streaming system in accordance with an embodiment.
[0009] FIG. 2 is a flow chart of a process for setting up the remote view streaming system in accordance with the present invention.
[0010] FIG. 3 is a flow chart of a process for utilizing the remote control streaming system in accordance with the present invention.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0011] The present invention relates generally to portable devices and more particularly to a method and system for streaming media thereto. The following description is presented to enable one of ordinary skill in the art to make and use the invention and is provided in the context of a patent application and its requirements. Various modifications to the preferred embodiment and the generic principles and features described herein will be readily apparent to those skilled in the art. Thus, the present invention is not intended to be limited to the embodiment shown but is to be accorded the widest scope consistent with the principles and features described herein.
Definitions
[0012] 1. Universal Plug and Play (UPnP).
[0013] The UPnP architecture allows device-to-device networking of personal computers, networked home appliances, consumer electronics devices and wireless devices. It is a distributed, open architecture protocol based on established standards such as the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP), HTTP, XML, and SOAP. UPnP control points are devices which use UPnP protocols to control UPnP devices.
[0014] The UPnP architecture supports zero configuration networking. A UPnP compatible device from any vendor can dynamically join a network, obtain an IP address, announce its name, convey its capabilities upon request, and learn about the presence and capabilities of other devices. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) servers are optional and are only used if they are available on the network. Devices can disconnect from the network automatically without leaving state information.
[0015] 2. NAT Transversal NAT-T (NAT Traversal in the IKE) is a method of enabling IPsec-protected IP datagram's to pass through a network address translator (NAT). It is also a technique for TCP-IP and or VOP connections.
[0016] 3. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP).
[0017] TCP provides a communication service at an intermediate level between an application program and the Internet Protocol (IP). That is, when an application program desires to send a large chunk of data across the Internet using IP, instead of breaking the data into IP-sized pieces and issuing a series of IP requests, the software can issue a single request to TCP and let TCP handle the IP details.
[0018] IP works by exchanging pieces of information called packets. A packet is a sequence of octets and consists of a header followed by a body. The header describes the packet's destination and, optionally, the routers to use for forwarding until it arrives at its destination. The body contains the data IP is transmitting.
[0019] Due to network congestion, traffic load balancing, or other unpredictable network behavior, IP packets can be lost, duplicated, or delivered out of order. TCP detects these problems, requests retransmission of lost data, rearranges out-of-order data, and even helps minimize network congestion to reduce the occurrence of the other problems. Once the TCP receiver has reassembled the sequence of octets originally transmitted, it passes them to the application program. Thus, TCP abstracts the application's communication from the underlying networking details.
[0020] 4. NAT Transversal. A Web Exclusive from Windows IT Pro . . . NAT-T uses UDP port 4500 and is quickly being adopted by many organizations.
Features
[0021] A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment provides a means for direct connections with the user's proxy server for remote connectivity, eliminating the streaming load on the host central server. A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment also provides a means for proxy to hand-held/wireless device client to exchange authentication keys enabling hand-held/wireless device/proxy server connection.
[0022] A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment provides a means for managing media video integrity through frame rate controls. It also provides a streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment which provides a means for recording proxy server source video remotely using a hand-held/wireless device. Moreover, a streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment provides a means for eliminating blocking artifacts on the playback stream from proxy server to hand-held/wireless device.
[0023] A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment provides a means for zooming video images on a hand-held/wireless device. A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment also provides a means for eliminating media streams to multiple destinations through direct connection between client and server.
[0024] A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment provides a means for improving media stream detection through direct connect simplicity. A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment also automatically detects a camera (proxy) server using one central (host) proxy server allowing for a direct connection. In addition, a streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment supports Windows 2000/XP/Vista, as well as the Mac OS.
[0025] A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment will send SMS text alerts upon a change in proxy server's video content. Moreover, a streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment will record and time stamp shifts in video content and enable SMS Alert to hand-held/wireless devices.
[0026] A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment supports connectivity with IP Camera with JPEG/MJPEG and H.264 Protocols. A streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment also provides a method for piercing firewall/proxy piercing. In addition, a streaming media process in accordance with an embodiment provides a method for remotely saving/recording screen shots.
[0027] A system that utilizes a streaming media process in accordance with the present invention can take the form of an entirely hardware implementation, an entirely software implementation, or an implementation containing both hardware and software elements. In one implementation, this detection procedure is implemented in software, which includes, but is not limited to, application software, firmware, resident software, microcode, etc.
[0028] Furthermore, the streaming media process can take the form of a computer program product accessible from a computer-usable or computer-readable medium providing program code for use by or in connection with a computer or any instruction execution system. For the purposes of this description, a computer-usable or computer-readable medium can be any apparatus that can contain, store, communicate, propagate, or transport the program for use by or in connection with the instruction execution system, apparatus, or device.
[0029] The medium can be an electronic, magnetic, optical, electromagnetic, infrared, or semiconductor system (or apparatus or device) or a propagation medium. Examples of a computer-readable medium include a semiconductor or solid state memory, magnetic tape, a removable computer diskette, a random access memory (RAM), a read-only memory (ROM), a rigid magnetic disk, and an optical disk. Current examples of optical disks include DVD, compact disk-read-only memory (CD-ROM), and compact disk-read/write (CD-R/W). To describe the features of the present invention in more detail, refer now to the following description in conjunction with the accompanying Figures.
Remote View Application
[0030] An implementation of the present invention utilizes a remote view streaming system. FIG. 1 is a diagram of a remote view streaming system in accordance with an embodiment. The remote view streaming system has three modules.
[0031] 1) A webcam server 12 within a computer 15 which enables streams of live or recorded video over a public network 17 via a video player 19 or a camera 21 coupled to the computer 15.
[0032] 2) A portable device 13, such as a smartphone, PDA, tablet computer such as the IPAD or other handheld device. The portable device 13 includes a client application 14. The client application 14 receives the live or recorded video from the network 17 and displays the video on a screen of the portable device 13.
[0033] 3) A proxy server 16 coupled to the network 17, which is the mediator between the webcam server 12 and the client application 14 for establishment of a direct connection therebetween.
Operation
[0034] FIG. 2 is a flow chart of a process for setting up the remote view streaming system in accordance with the present invention. First, the user downloads the client application, such as a smartphone client, onto their portable device such as a smartphone, via step 102. Next, the user downloads the webcam server onto their computer system such as a PC or Apple computer, via step 104. Then, a proxy server is deployed on a public network, such as the Internet. Both the client application and the webcam server are configured with the URL of the proxy server before deployment, via step 106.
[0035] The user can pair as many webcam servers as desired to their client application by being connected to the same network. The user can manually pair by typing in a key on the webcam server. The user can then go anywhere and login to servers they had previously paired with UPNP without being on the same network (it does not matter whether it is a private or public IP).
[0036] FIG. 3 is a flow chart of a process for utilizing the remote control streaming system in accordance with the present invention. The user starts the webcam server. First, the webcam server registers itself with the proxy server, via step 202. The proxy server then stores the webcam server's provided information in a relational database, via step 204. The webcam server re-registers itself from time to time to remain active in the relational database.
[0037] The user starts the client application by acquiring any key from the proxy server to an active webcam server list, via step 206. The proxy server acquires one or more keys from a relational database and provides all the information to the client application to establish a direct connection with the webcam server, via step 208.
[0038] The client application receives the active list of webcam servers and displays it on portable device for the user to select, via step 210. The user selects any webcam server listed on the portable device and the portable device then makes a direct connection with a webcam server, via step 212.
[0039] When the webcam server gets a request from the client application for a connection, it then authenticates the client application using the key shared during the previous pairing process, via step 214. If a match is confirmed, the webcam server permits the connection to be established. Otherwise it disallows the connection, via step 216.
Advantages
[0040] The user can manually select from the proxy server live (video/images) from the camera. The user can also select and record from the proxy server's camera upon detection of motion (shift in content). Therefore, a push notification can be sent to the smartphone that motion has been detected. Then the user of the smartphone can review the recording and its history.
[0041] The user may select frame rates increasing/decreasing live streaming smoothness (correction for bandwidth variances). The user can also choose to receive SMS push notifications when movement is detected and or recorded. The user can remotely load archived videos on their PC and play them on their portable device, such as a smartphone. The user can also apply all previously proven hand-held hand gestures (pinch in/out, double tapping, etc).
[0042] The user can refresh the active webcam server list at any time. A universal plug and play (UPnP) is supported for network address translation (NAT) traversal. Motion detection settings can be changed for either the client application or the webcam server.
[0043] Although the present invention has been described in accordance with the embodiments shown, one of ordinary skill in the art will readily recognize that there could be variations to the embodiments and those variations would be within the spirit and scope of the present invention. Accordingly, many modifications may be made by one of ordinary skill in the art without departing from the spirit and scope of the appended claims.
User Contributions:
Comment about this patent or add new information about this topic:
| People who visited this patent also read: | |
| Patent application number | Title |
|---|---|
| 20200298971 | SYSTEM FORMING A TWO DEGREES OF FREEDOM ACTUATOR, FOR EXAMPLE FOR VARYING THE PITCH ANGLE OF THE BLADES OF A PROPELLER DURING ROTATION |
| 20200298970 | ROTATING ELECTRIC DISTRIBUTED ANTI-TORQUE FIN |
| 20200298969 | STRUCTURALLY TUNABLE CORES |
| 20200298968 | ROTOR FOR A HOVER-CAPABLE AIRCRAFT AND METHOD FOR CONTAINMENT OF VIBRATIONS TRANSMITTED TO THE MAST OF A ROTOR OF A HOVER-CAPABLE AIRCRAFT |
| 20200298967 | VIBRATION ATTENUATION SYSTEM FOR ELECTRIC AND HYBRID ELECTRIC VEHICLES |