Patent application title: SELF-LEARNING SYSTEM FOR WATER SPORT USERS
Inventors:
Hsiu-Ying Sung (Taipei City, TW)
IPC8 Class: AA63B7106FI
USPC Class:
700 91
Class name: Data processing: generic control systems or specific applications specific application, apparatus or process contest or contestant analysis, management, or monitoring (e.g., statistical analysis, handicapping, scoring)
Publication date: 2014-06-26
Patent application number: 20140180449
Abstract:
The present disclosure relates to a self-learning system for water sport
users which comprises a wearable camera device, a computer and a learning
data base. The carrying camera comprises a fixing element, a bearing
element and a waterproof camera. The fixing element is disposed on a
human body. The bearing element is disposed on the fixing element. The
bearing element is bendable and has adjustable length. The waterproof
camera is disposed on the bearing element. The waterproof camera shoots
human postures of water sport. The waterproof camera transforms image
signal to digital signal. The computer receives and processes the digital
signal, and then through a water-sport learning module assesses human
posture as well as provides swimming information. The present disclosure
also relates to a self-learning system for water sport users which
comprises a carrying camera, a computer and a learning network platform.Claims:
1. A self-learning system for water sport users, comprising: a wearable
camera device, which includes: a fixing element wearable on a human body;
a bearing element coupled to the fixing element and having a bendable
form and adjustable length; and a waterproof camera disposed on the
bearing element such that the waterproof camera is configured to have an
adjustable angle for filming postures of a body doing water sport and
converting the filmed image signals to digital signals for output; a
computer receiving and processing the digital signals of the wearable
camera device; and a learning data base read by the computer, having a
water-sport learning module, and assessing water-sport postures via the
water-sport learning module.
2. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 1, wherein the fixing element is a pair of goggles.
3. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 1, wherein the waterproof camera includes a casing, a lens disposed on one end of the casing, and an image sensor unit, a processor, a power supply unit and a storage unit disposed in the casing.
4. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 1, wherein the water-sport learning module further includes information on standard swimming instruction.
5. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 1, wherein the water-sport learning module further includes a function of image comparison to display incorrect aspects of water-sport postures.
6. A self-learning system for water sport users, comprising: a wearable camera device, which includes: a fixing element wearable on a human body; a bearing element coupled to the fixing element and having a bendable form and adjustable length; and a waterproof camera disposed on the bearing element such that the waterproof camera is configured to have an adjustable angle for forming postures of a body doing water sport and converting the filmed image signals to digital signals for output; a computer receiving and processing the digital signals of the wearable camera device; and a network learning platform, wherein the computer connects to the network learning platform through the internet, the network learning platform has an interactive water-sport learning module, and the network learning platform interactively assesses water-sport postures by using the interactive water-sport learning module.
7. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 6, wherein the fixing element is a pair of goggles.
8. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 6, wherein the waterproof camera includes a casing, a lens disposed on one end of the casing, and an image sensor unit, a processor, a power supply unit and a storage unit disposed in the casing.
9. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 6, wherein the interactive water-sport learning module further includes information on standard swimming instruction.
10. The self-learning system for water sport users according to claim 6, wherein the interactive water-sport learning module further includes a function of image comparison to display incorrect aspects of water-sport postures.
Description:
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0001] 1. Field of the Invention
[0002] The present disclosure relates to an assisting tool for learning water sport; in particular, to a self-learning system for water sport users.
[0003] 2. Description of Related Art
[0004] Swimming is a popular sport enjoyed by the public. Typically in swimming, correct postures and movements have key effect on raising swimming technique and swimming speed. If the swimming movements are incorrect, the postures are poorly coordinated, leading to an increase in resistance during swimming and inefficiency of the exerted force to push forward, not only wasting unnecessary energy but also limiting the speed of the swimmer.
[0005] In order to improve swimming techniques, a swimmer typically hires a swimming instructor to raise the swimming technique and swimming speed. During the instruction by the swimming instructor, the swimming instructor can instruct the swimmer on correct swimming postures and techniques, and correct the incorrect parts of the swimmer so that the swimmer can obtain the correct swimming postures. Afterward, when the swimmer practices by himself or herself without the instruction of a professional instruction on the side, the swimmer cannot tell if his or her postures are correct or not during swimming. Therefore, an assisting tool for swimmers to observe whether his or her own swimming postures are correct or not, in order to assist the user to immediately correct the postures when practicing swimming by himself or herself, is an area that can be enhanced in swimming.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0006] The self-learning system for water sport users of the present disclosure films the postures of the user during swimming. Afterward, the user can assess his or her own swimming movements along a learning software for water sport, to find out what to improve on, and obtain correct information on swimming from the learning software for water sport.
[0007] The present disclosure provides a self-learning system for water sport users, which includes a wearable camera device, a computer, and a learning data base. The wearable camera device includes a fixing element, a bearing element, and a waterproof camera. The fixing element is disposed on a human body. The bearing element is disposed on the fixing element. The bearing element is flexible and has adjustable length. The waterproof camera is disposed on the bearing element for filming the human postures during water sport. The recorded images are transformed by the waterproof camera into digital signals before being outputted. The computer receives and processes the digital signals, and then assesses the human postures in the water and provides information on learning swimming by using a water-sport learning module.
[0008] The present disclosure provides a self-learning system for water sport users, which includes a wearable camera device, a computer and a network learning platform. The wearable camera device includes a fixing element, a bearing element, and a waterproof camera. The fixing element is disposed on a human body. The bearing element is disposed on the fixing element. The bearing element is flexible and has adjustable length. The waterproof camera is disposed on the bearing element for filming the human postures during water sport. The recorded images are transformed by the waterproof camera into digital signals before being outputted. The computer receives and processes the digital signals, and is connected by network to the network learning platform, which can be a cloud platform. The network learning platform has an interactive water-sport learning module, which interactively assesses the human postures in the water.
[0009] In summary of the above, the wearable camera device allows the user to film his or her own posture in water sports, such that the user can view his or her own movements and postures after practice to assess whether they are correct, and use the information as reference for further self-adjustments. Additionally, the user can film the movements and postures during water sport and send them to the computer, and compare and analyze the postures with the correct postures from the learning data base, thereby obtaining a grade and level for his or her own postures and enabling himself or herself to correct the incorrect parts. Moreover, the user can also connect to the internet and use the network learning platform to compare with and analyze the correct postures from the interactive water-sport learning module provided by the manufacturer, thereby obtaining a grade and level for his or her own postures and learning more professional swimming information.
[0010] In order to further the understanding regarding the present disclosure, the following embodiments are provided along with illustrations to facilitate the disclosure of the present disclosure.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0011] FIG. 1 shows a schematic diagram of a user wearing a wearable camera device according to the present disclosure;
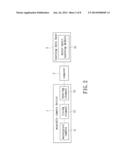
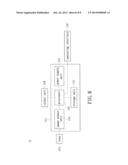
[0012] FIG. 2 shows a block diagram of a self-learning system for water sport users according to a first embodiment of the present disclosure;
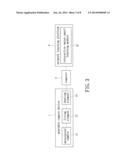
[0013] FIG. 3 shows a block diagram of a self-learning system for water sport users according to another embodiment of the present disclosure;
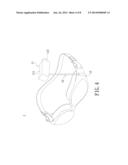
[0014] FIG. 4 shows a schematic diagram of a wearable camera device according to a first embodiment of the present disclosure;
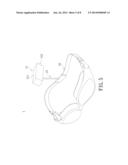
[0015] FIG. 5 shows a schematic diagram of a wearable camera device according to a second embodiment of the present disclosure;
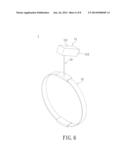
[0016] FIG. 6 shows a schematic diagram of a wearable camera device according to a third embodiment of the present disclosure;
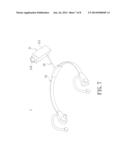
[0017] FIG. 7 shows a schematic diagram of a wearable camera device according to a fourth embodiment of the present disclosure;
[0018] FIG. 8 shows a block diagram of a waterproof camera according to the present disclosure.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0019] The object of the self-learning system for water sport users of the present disclosure is to film the postures during water sport by a camera worn on the body of the user, e.g. filming the postures of swimming, water ballet, or surfing. However the water sports are not limited to the above. Afterward, the user can view his or her own motion in the water, compare the recorded images with a software program of a water-sport learning module of the present disclosure, and obtain correct information for movement and posture by the assessment and suggested improvements given by the water-sport learning module.
[0020] Referring to FIG. 1 and FIG. 2, the present disclosure provides a self-learning system for water sport users, which includes a wearable camera device 1, a computer 2 and a learning data base 3. As shown in FIG. 1, the user wears the wearable camera device 1 during swimming. The wearable camera device 1 is disposed on the human body. The wearable camera device 1 of the present disclosure includes a water proof camera 11, a fixing element 12, and a bearing element 13. The wearable camera device 1 can film the postures of the motion in the water, and transform the recorded image signals into digital signals for output.
[0021] As shown in FIG. 2, after practicing the sport the user can transmit the digital signals of the image file recorded by the wearable camera device 1 to the computer 2, by using transmission device such as USB, data transmission cable, wireless transmission device or Bluetooth device, etc. The computer 2 can receive the digital signal transmitted by the wearable camera device 1 and process the digital signals so that the user can read the recorded images.
[0022] The learning data base 3 can be saved on CDs or other storage devices such as flash drives or discs. The learning data base is then read by the computer 2. The learning data base 3 has a water-sport learning module 31, which is a software program capable of assessing movement postures and providing related instructions and suggestions. The water-sport learning module 31 assesses the posture of a human body doing water sport and provides instructional information for swimming.
[0023] More specifically, the user can film the postures of water sport and transmit the image files to the computer 2, and then enter an assessment or comparison command, such that the water-sport learning module 31 grades the water-sport postures of the user doing water sport. For example, the water-sport learning module 31 can grade the postures of the swimmer from A to F, wherein A is a posture fully meeting the desired standards, B is a posture of an advanced swimmer, C is a posture of an intermediate swimmer, D is a posture of a basic-level swimmer, E is a posture of an introductory-level swimmer, and F is a posture of an entry-level swimmer. The postures of the swimmer can be graded from A to F by using the program of the water-sport learning module 31 to compare the image files of the water-sport postures.
[0024] Additionally, the water-sport learning module 31 can compare images to display incorrect aspects of the posture of a swimmer, e.g. the angle of motion of the arm is too large, the pedaling form of the leg is incorrect, etc., thereby promptly correcting the incorrect postures of the swimmer such that the swimmer can learn aspects of his swimming that needs to be improved upon. Moreover, the swimmer can input instructional commands, so that the water-sport learning module 31 provides relevant swimming instructions and a plurality of correct swimming postures. Also, incorrect postures of the swimmer can be addressed by playing the corresponding animation or image files with the correct swimming postures, thereby facilitating the user to learn the correct swimming postures.
[0025] Referring to FIG. 1 and FIG. 3, the present disclosure also provides a self-learning system for water sport users, which includes a wearable camera device 1, a computer 2, and a network learning platform 4.
[0026] As shown in FIG. 3, after the user wears the wearable camera device 1 during swimming, the digital signals of the image files recorded by the wearable camera device 1 is transmitted to the computer 2 by a transmission device. The computer 2 can receive the digital signals transmitted by the wearable camera device 1 and process the digital signals, such that the recorded images can be read by the user.
[0027] The user can use the computer 2 to connect to the internet and access the network learning platform 4 provided by the manufacturer. Namely, the user can access the website of the manufacturer and use the network learning platform 4 provided by the manufacturer. The network learning platform 4 can be a cloud platform and has an interactive water-sport learning module 41, also a network application, which can assess and analyze movement postures. The user can upload or download files through the interactive water-sport learning module 41 to interactively assess movement postures of water sport and obtain instructional information on swimming provided by the interactive water-sport learning module 41.
[0028] More specifically, the user can transmit the recorded image files of water sport postures to the computer 2, and then the user can connect to the network learning platform 4, upload the video or picture files of movement postures, and then enter the comparison or assessment command to prompt the interactive water-sport learning module 41 to grade the water sport posture of the user and assign a grade to the swimming posture of the user. Additionally, the interactive water-sport learning module 41 can display the incorrect aspects of the postures of the swimmer by comparing images, e.g. the angle of motion of the arm is too large, the pedaling form of the leg is incorrect, etc., thereby promptly correcting the incorrect postures of the swimmer such that the swimmer can learn aspects of his swimming that needs to be improved upon.
[0029] Moreover, the user can enter instructional commands, so that the interactive water-sport learning module 41 provides relevant swimming instruction, and plays the corresponding animation or image files with the correct swimming postures to address the incorrect postures of the swimmer, thereby facilitating the user to learn the correct swimming postures. Alternatively, professional swimming instructions can be conducted via the network learning platform 4, e.g. coaches on the national team level can provide swimming instructions so that the user can obtain more information on swimming.
[0030] Referring to FIG. 4 to FIG. 8, the wearable camera device 1 of the present disclosure is described in detail. The waterproof camera 11 is disposed on a body part by the fixing element 12 and the bearing element 13. The part of disposal can vary according to practical needs. In other words, the fixing element 12 can be disposed on the head, neck, back, waist, or other parts of the body, for filming the postures during water sport. For example, the waterproof camera 11 can be disposed on the head to film the swimming postures, and the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11 can aim towards the arm, the legs, or the back to achieve the effect of filming.
[0031] The main purpose of the fixing element 12 is to fix the waterproof camera 11 on the body, therefore the fixing element 12 is an accessory which can be worn on the body. The fixing element 12 can be swimming goggles, head band, clip, headband, belt, or an accessory wearable on the body. However the type of fixing element 12 is not limited to the above. The bearing element 13 is disposed on the fixing element 12. The bearing element 13 is an element on which the waterproof camera 11 can adjust angles, so the bearing element 13 has flexibility, adjustable length, deformability or any adjustable quality, thereby allowing the bearing element 13 to bear and adjust the filming angle of the waterproof camera 11. The bearing element 13 can be an adjustable rod, a plastic unit, an elastic unit, a contracting unit, a soft metal tube or axis, etc. However, the type of bearing element 13 is not limited to the above. The combination of the fixing element 12 and the bearing element 13 allows the waterproof camera 11 to be disposed on any parts of the body, and the waterproof camera 11 can adjust its filming angle up, left, down and right.
[0032] FIG. 4 and FIG. 5 are schematic diagrams of respectively the first embodiment and the second embodiment of the wearable camera device 1. In the first embodiment, the fixing element 12 is a pair of swimming goggles, and the bearing element 13 is disposed on the forward portion of the goggles. The waterproof camera 11 is disposed on the other end of the bearing element 13. The method of coupling between the bearing element 13 and the goggles can be screw, welding, adhesive, latching, mating, or the bearing element 13 and the swimming goggles are integrally formed as one body. However, the method of connection between the bearing element 13 and the goggles is not limited to the above. Likewise, the method of connection between the bearing element 13 and the waterproof camera 11 can be screw, welding, adhesive, latching, mating, or the bearing element 13 and the waterproof camera 11 are integrally formed as one body. However, the method of connection between the bearing element 13 and the waterproof camera 11 is not limited to the above.
[0033] Therefore, when the user puts on the goggles, the waterproof camera 11 is also worn on the head. However, the present disclosure does not limit the location of attachment of the waterproof camera 11 on the human body, and the waterproof camera 11 can also be disposed on the neck, back, waist or other parts of the human body. At this moment, the waterproof camera 11 is positioned on top of the head, or at either side of the head, in order to allow the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11 to film in the direction of the back of the body. At this moment, depending on which body parts need to be filmed, the user can adjust the shape and length of the bearing element 13, or directly adjust the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11, to film behind the body or specific parts of the body.
[0034] In the second embodiment, the fixing element 12 can also be a pair of swimming goggles, and the bearing element 13 is disposed on the head band of the goggle. Namely, the bearing element 13 is connected to the headband of the goggles. The waterproof camera 11 is disposed on the other end of the bearing element 13. Therefore, when the user puts on the goggles, the waterproof camera 11 is directly worn on the back of the head, and the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11 faces toward the back of the body. As a result, the user can adjust the bearing element 13 or the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11 to film behind the body or specific parts of the body. However, the present disclosure does not limit the location of attachment of the waterproof camera 11 on the human body, and the waterproof camera 11 can also be disposed on the neck, back, waist or other parts of the human body.
[0035] FIG. 6 shows a schematic diagram of a third embodiment of the wearable camera device 1. The fixing element 12 can be a head band with elasticity, and the bearing element 13 is disposed on the head band with elasticity. Namely the bearing element 13 is connected to the head band with elasticity. The user can put the head band on the head, allowing the waterproof camera 11 to be worn on the head and film behind the body or specific parts of the body by adjusting the bearing element 13 or the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11.
[0036] FIG. 7 shows a schematic diagram of a fourth embodiment of the wearable camera device 1. The fixing element 12 can be an ear-loop type device, and the bearing element 13 is disposed on the ear-loop type device. Namely the bearing element 13 is combined with the ear-loop type device. The user can wear the ear-loop type device on the head, to film behind the body or specific parts of the body by adjusting the bearing element 13 or the lens 112 of the waterproof camera 11.
[0037] Moreover, the fixing element 12 can be a belt. Namely, the waterproof camera 11 is disposed on the waist. At this moment, the filming angle of the waterproof camera 11 can be adjusted via the bearing element 13, and film the posture of the swinging arms in front or the kicking legs behind, to achieve the effect of filming specific parts of the body.
[0038] Therefore, the object of wearing the fixing element 12 and the bearing element 13 of the wearable camera device 1 is to dispose the waterproof camera 11 on any part of the body. Using the waterproof camera 11 to film the movement postures allows the user to see whether his or her own postures are correct, further serving as a reference for self-adjustments.
[0039] FIG. 8 shows a block diagram of a waterproof camera 11. The waterproof camera 11 includes a casing 111, one end of which has a lens 112 which can auto-adjust the focus. An image sensor unit 113, a processor 114, a power supply unit 115, and a storage unit 117 are disposed in the casing 111 and are electrically connected to each other. The power supply unit 115 provides electrical power and is preferably a rechargeable battery which can be used repeatedly, such as lithium battery or a common battery.
[0040] After the lens 112 captures an image, the image sensor unit 113 captures image signals which are converted by the processor 114 and other electronic units into digital signals, which are in turn saved by the storage unit 117. The image sensor unit 113 can be a conventional charge-coupled device (CCD) or a CMOS image sensor. In order to reduce the storage space required and facilitate storage, the processor 114 can have a digital signal processor with a specified specification such as MPG, WMV, WMA, etc. The storage device is preferably secure digital memory card with a small volume, or other types of flash memory, or a Microdrive.
[0041] Moreover, an operating interface 116 can be disposed on the casing 111. The operating interface 116 has on-off and function-operating keys, so that the user can operate the waterproof camera 11. The waterproof camera 11 can further include an output unit 118 through which the recorded images can be outputted.
[0042] In summary, the present disclosure has the following advantages. The wearable camera device can film the postures of the user during water sport, such that the user can determine whether his or her own movement postures are correct or not after viewing them, serving as reference for self-adjustment of movement postures. The user can film the movement postures during water sport and transmit them to a computer. The learning data base can compare and analyze the filmed movement postures with correct movement postures, and grade the movement postures of the user and facilitate correction of the incorrect parts. The user can connect to the internet and access the cloud resources and the interactive water-sport learning module provided by the manufacturer through the network learning platform to compare and analyze with the correct postures, thereby obtaining a grade and level for the postures, improving incorrect postures, and also obtaining more professional swimming information.
[0043] The descriptions illustrated supra set forth simply the preferred embodiments of the present disclosure; however, the characteristics of the present disclosure are by no means restricted thereto. All changes, alternations, or modifications conveniently considered by those skilled in the art are deemed to be encompassed within the scope of the present disclosure delineated by the following claims.
User Contributions:
Comment about this patent or add new information about this topic: