Patent application title: INFORMATION STORAGE MEDIUM INCLUDING EVENT OCCURRENCE INFORMATION, APPARATUS AND METHOD FOR REPRODUCING THE SAME
Inventors:
Kil-Soo Jung (Hwaseong-Gun, KR)
Kil-Soo Jung (Hwaseong-Gun, KR)
Sung-Wook Park (Seoul, KR)
Assignees:
SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO., LTD.
IPC8 Class: AG06F3048FI
USPC Class:
715716
Class name: Data processing: presentation processing of document, operator interface processing, and screen saver display processing operator interface (e.g., graphical user interface) on screen video or audio system interface
Publication date: 2010-11-04
Patent application number: 20100281368
dium storing event information for generating an
event with reference to an audio/video data structure and an apparatus
and method thereof. The information storage medium includes: core data,
that includes audio/video data and navigation data for reproducing the
audio/video data; and program data that is used for interaction with a
user, wherein the program data includes event occurrence information for
generating an event with reference to a structure of the audio/video
data.Claims:
1. An information storage medium having computer readable data recorded
thereon, the computer readable data comprising:core data, comprising
audio/video data; andprogram data configured to be used for interaction
with a user, the program data comprising event occurrence information
that, when executed by a reproducing apparatus, causes the reproducing
apparatus to generate an event with reference to a structure of the
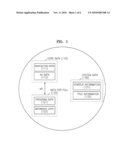
audio/video data when the reproducing apparatus reproduces audio/video
data at a corresponding time point according to the event occurrence
information, the program data being executed by the reproducing apparatus
in synchronization with the audio/video data based on the event, a video
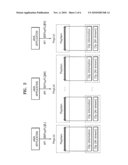
portion of the audio/video data being displayed through a display window
defined in the program data.
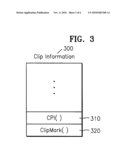
2. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the program data comprises application data written according to a JAVA language.
3. The information storage medium of claim 2, wherein the application data written by the JAVA language is configured to control the audio/video data through an application program interface.
4. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the event occurrence information comprises information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a specific Presentation Time Stamp of an audio/video clip constructing the audio/video data, and is provided within a clip information file that includes characteristic information for the audio/video clip, is reproduced.
5. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the event occurrence information comprises information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a predetermined mark of an audio/video clip constructing the audio/video data, and is provided within a clip information file that includes characteristic information for the audio/video clip, is reproduced.
6. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the event occurrence information comprises information that requires an event to be generated when a packet corresponding to a predetermined specific location of an audio/video clip constructing the audio/video data is reproduced.
7. The information storage medium of claim 4, wherein the event occurrence information comprises an event identifier as a parameter for generating the event.
8. A reproduction method to reproduce data from an information storage medium in which core data including audio/video data and navigation data for reproducing the audio/video data and program data used for interaction with a user which is separate from the core data are recorded, the method comprising:reading and registering information stored in an event occurrence table;generating an event included in the registered information at a time point corresponding to the event while the audio/video data is reproduced in synchronization with the program data based on the event;reproducing a video portion of the audio/video data through a display window defined in the program data; andexecuting the program data in synchronization with the audio/video data based on the event.
9. The reproduction method of claim 8, further comprising:reading a JAVA application that performs an operation corresponding to the generated event and a parameter needed to be transferred to the JAVA application, from the event occurrence table, using an event identifier;transferring the read parameter and the generated event to the JAVA application; andperforming, with the JAVA application, an operation corresponding to the received generated event in synchronization to audio/video data.
10. The reproduction method of claim 8, wherein the event occurrence table stores event occurrence information for generating an event at a predetermined reproduction time of audio/video data, in a binary table format.
11. The reproduction method of claim 10, wherein the event occurrence table comprises:an event identifier identifying an event; andevent occurrence time information, comprising a value of reproduction time information;wherein the event occurrence time information comprises an elapsed time or a value of unique information of the audio/video data.Description:
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001]This application is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/916,403, filed on Aug. 12, 2004, which claims the benefit of Korean Patent Application No. 2003-70751, filed on Oct. 10, 2003, Korean Patent Application No. 2004-26643, filed on Apr. 19, 2004, in the Korean Intellectual Property Office, and U.S. provisional Patent Application No. 60/508,315, filed on Oct. 6, 2003, in the US Patent and Trademark Office, the disclosures of which are incorporated herein in their entirety by reference.
BACKGROUND
[0002]1. Field
[0003]The following description relates to an information storage medium including event occurrence information and an apparatus and method of reproducing the same, and more particularly, to an information storage medium storing event information for generating an event with reference to an AV data structure and an apparatus and method of reproducing the same.
[0004]2. Description of the Related Art
[0005]A moving-image data is classified into audio-video (AV) data for a high definition movie and navigation data for controlling reproduction of the AV data. Demand for applications with programming and browsing functions for reinforcing interaction with a user regarding the above-mentioned moving-image data is increasing. However, in order to provide these functions, an application using program data should be executed in synchronization to AV data.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0006]The invention provides an information storage medium including event occurrence information, which is capable of executing an application in synchronization with AV data by including event occurrence information designated based on an AV data structure in program data, and a reproduction apparatus and method thereof.
[0007]The invention also includes a reproduction method and apparatus, which record event occurrence information in a format of a binary table to generate and reproduce an event.
[0008]According to an aspect of the invention, there is provided an information storage medium, including: core data, which includes AV data and navigation data for reproducing the AV data; and program data which is used for interaction with a user, wherein the program data includes event occurrence information for generating an event with reference to a structure of the AV data.
[0009]The program data may be application data written by a JAVA language.
[0010]The event occurrence information may be information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a specific Presentation Time Stamp (PTS) of an AV clip constructing the AV data, within clip information file including characteristic information for the AV clip, is reproduced.
[0011]The event occurrence information may be information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a predetermined mark of an AV clip constructing the AV data, which is within a clip information file that includes characteristic information for the AV clip, is reproduced.
[0012]The event occurrence information may be information that requires an event to be generated when a packet corresponding to a predetermined specific location of an AV clip constructing the AV data is reproduced.
[0013]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a reproduction apparatus including: a reader, which reads AV data and program data including event occurrence information; a program engine, which executes the program data and outputs the event occurrence information; and a presentation engine, which reproduces the AV data and generates an event when AV data at a corresponding time point according to the event occurrence information is reproduced.
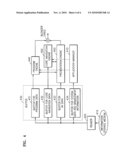
[0014]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a reproduction method including: reading AV data and program data including event occurrence information; executing the program data and interpreting and outputting the event occurrence information; and reproducing the AV data, and generating an event when AV data at a corresponding time point according to the event occurrence information is reproduced.
[0015]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a reproduction method including: reading and registering information stored in an event occurrence table; and generating an event included in the registered information at a time point corresponding to the error while AV data is reproduced.
[0016]The event occurrence table may store event occurrence information for generating an event at a predetermined reproduction time point of AV/video data, in a form of a binary table.
[0017]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a computer-readable medium having embodied thereon a computer program for executing the method.
[0018]Additional aspects and/or advantages of the invention will be set forth in part in the description which follows and, in part, will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by practice of the invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0019]FIG. 1 shows data types to be stored in an information storage medium according to an embodiment.
[0020]FIG. 2 shows correlations of PlayList, PlayItem, Clip Information, and Clip, constructing AV data.
[0021]FIG. 3 shows the configuration of the Clip Information.
[0022]FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a reproduction apparatus, according to an embodiment.
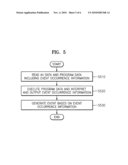
[0023]FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a reproduction method according to an embodiment.
[0024]FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a process that generates an event and reproduces AV data.
[0025]Throughout the drawings and the detailed description, unless otherwise described, the same drawing reference numerals will be understood to refer to the same elements, features, and structures. The relative size and depiction of these elements may be exaggerated for clarity, illustration, and convenience.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0026]The following detailed description is provided to assist the reader in gaining a comprehensive understanding of the methods, apparatuses, and/or systems described herein. Accordingly, various changes, modifications, and equivalents of the systems, apparatuses and/or methods described herein will be suggested to those of ordinary skill in the art. The progression of processing steps and/or operations described is an example; however, the sequence of steps and/or operations is not limited to that set forth herein and may be changed as is known in the art, with the exception of steps and/or operations necessarily occurring in a certain order. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions may be omitted for increased clarity and conciseness.
[0027]FIG. 1 shows data types to be stored in an information storage medium according an embodiment. Referring to FIG. 1, core data 110 includes AV data 111 and navigation data 112. The navigation data 112 is a collection of navigation commands for reproducing the AV data. The core data is also referred to as core mode data. The core data 110 is data that is used in a video application such as DVD and is required for showing a video, such as a movie. A mode that reproduces such core data 110 is referred to as a movie mode.
[0028]Data for reinforcing various interactions with a user is generally known as Data for Full 120. The Data for Full 120 is also referred to as Data for Full mode. The Data for Full mode includes program data 121 for providing various interactions with a user and browsing data 122 to allow network browsing, such as Internet browsing. The program data 121 is, for example, a java application that provides various user interaction functions. The browsing data 122 includes markup documents written with a markup language, such as XML, markup documents including or linking script codes, such as ECMA script, script files, at least one image referenced by the markup documents, and resource files such as graphics and sounds. The core data 110 is able to communicate with the Data for Full 120 through application program interface (API). The program data 121 includes event occurrence information for generating event at a time and/or location designated by the AV data 112.
[0029]System data 130 includes at least startup information 131 and title information 132. The system data 130 is read when the information storage medium is booted or inserted. The system data that is read when the storage medium is booted or inserted does not belong to a specific mode.
[0030]The AV data recorded on the information storage medium is able to be reproduced in a plurality of modes, including: a core mode that reproduces data in a movie mode using the navigation data as the data for code mode, as described above, and a full mode that allows AV data to be displayed through a display window defined in an application made by a program language as Data for Full mode. When the full mode is selected by a user or by a navigation flow, a display window for displaying moving-image data is created by a function programmed in an application (for example, Java application using a Java language as a programming language) made by a programming language, AV data is controlled and displayed through the API, and simultaneously JAVA-based contents or various resources (for example, image, audio, etc.) referred in the JAVA application are displayed in synchronization of reproduction of the AV data. However, to display the AV data through the display window defined in the JAVA application in the above-described full mode, synchronization of the AV data and the JAVA application is necessary.
[0031]FIG. 2 shows correlations of PlayList, PlayItem, Clip Information, and Clip, constructing AV data. Referring to FIG. 2, the JAVA application controls the AV data through API, such as "BDPIayPL" (PlayList Number), as Data for Full mode. The PlayList is a fundamental unit of reproduction and the information storage medium stores a plurality of PlayLists. The PlayList includes a plurality of PlayItems that are connected to one another. The PlayItem designates one part of a Clip, particularly, the PlayItem is used to designate a reproduction start time and a reproduction end time of the Clip. Accordingly, the corresponding part in a Clip is searched using Clip information. An AV stream is recorded using a Clip as a fundamental unit. Clips are typically recorded on a continuous space, respectively, and are compressed to reduce theirs capacities.
[0032]To reproduce the recorded Clips, it is necessary to detect characteristic information of the compressed presentation data. Clip information is recorded for each Clip. The Clip information includes audio and video properties of each Clip, Entry Point Map storing location information of Entry Point allowing random access per a predetermined interval, etc. In a case of MPEG as a general moving-image compression technique, Entry Point is an I picture or a GOP header used as a random access point. The Entry point Map is used in a time search for detecting a time point elapsed by a predetermined time after the reproduction begins.
[0033]FIG. 3 shows a configuration of the Clip Information. Referring to FIG. 3, the Clip Information 300 includes at least Characteristic Point Information (CPI) 310 and ClipMark( ) 320. CPI 310 includes EP_map (Entry Point Map) information. The EP_map information is information for indicating an entry point of a corresponding clip. Entry Point in the MPEG video coding standard indicates a start point of an image coded as an I picture. The EP_map information provides a relationship between a Presentation Time Stamp (PTS) value and its address in an AV stream file. An entry point of the PTS value is represented as "PTS_EP_start", and the address of the entry point is represented as "SPN_EP_start". Meanwhile, ClipMark( ) 320 is used as information for embedding Mark at a specific location in the AV stream file.
[0034]Accordingly, CPI( ) or ClipMark( ) are used as parameters for generating a trigger event as will be described later. Further, the API used in the JAVA application and required parameters will be described in more detail.
[0035]1. BDVideo.SetTrigger (trigger_id, Clip_Information_file_name, PTS_EP_start, ref) [0036]meaning: generate a trigger event when a clip is reproduced at a PTS value in designated clip information [0037]parameters: [0038]trigger_id: trigger event identifier [0039]Clip_Information_file_name: name of clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0040]PTS_EP_start: entry point of a PTS value in clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0041]ref: value to be included in an event variable when an event is called up
[0042]2. BDVideo.SetTrigger (trigger_id, Clip_AV_stream_file_name, SPN_EP_start, ref) [0043]meaning: generate a trigger event when a source packet number of a designated clip AV stream is reproduced [0044]2) parameters: [0045]trigger_id: trigger event identifier
[0046]Clip_AV_stream_file_name: name of an AV stream in which a trigger event will be generated [0047]SPN_EP_start: start point of a source packet in a clip AV stream in which a trigger event will be generated [0048]ref: value to be included in an event variable when an event is called up
[0049]3. BDVideo.SetTrigger (trigger_id, Clip_AV_stream_file_name, ClipMark( ) ref) [0050]1) meaning: generate a trigger event when ClipMark in designated clip information is reproduced [0051]2) parameters: [0052]trigger_id: trigger event identifier [0053]Clip_Information_file_name: name of clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0054]ClipMark( ): ClipMark in clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0055]ref: value to be included in an event variable when an event is called up BDVideo.ClearTrigger(trigger_id) [0056]1) meaning: release a request trigger event [0057]2) parameters [0058]trigger_id: trigger event identifier (for example, if "-1" is designated as trigger_id, this can be used as meaning of commanding the release of all generated trigger events)
[0059]FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a reproduction apparatus, according to an embodiment. The reproduction apparatus displays AV data recorded on an information storage medium using data for a specific mode according to a display method. Referring to FIG. 4, the reproduction apparatus comprises a reader 420, a buffer 430, a program engine 440, a core navigation engine 450, a presentation engine 460, a application engine 470, and a blender 480.
[0060]The reader 420 reads AV data, program data, core navigation data, and system data from the information storage medium 410 and transfers the read data to the respective corresponding buffers 431, 432, 433 and 434. The respective buffers (buffer 431 for program data, buffer 432 for core navigation data, buffer 433 for AV data, and buffer 433 for system data and management information) buffer the received data, respectively. The buffered results are transmitted to the respective corresponding engines for reproduction and are reproduced by the respective engines. The respective engines include, for example, a program engine, a core navigation engine, a presentation engine, and an application manager. At this time, the system data is transferred to the application manager 470. The application manager 470 determines a mode and data to be first reproduced based on an entry point of start-up data in the system data.
[0061]While the respective AV data is reproduced, entry points of respective objects generated due to conversion between modes or title search are transferred to corresponding reproduction engines capable of reproducing the corresponding objects, with reference to the system data, thereby reproducing the respective objects. The application manager 470 may also include a user input receiving unit and a user input processing unit in order to transfer a user input to an engine for corresponding mode. The presentation engine 460 decodes and reproduces moving-image data and still-image streams and/or data files. The program engine 440 controls the presentation engine 460 through the API, like the core navigation engine 450.
[0062]The program engine 440 executes the JAVA application including the above described various event occurrence information and transfers the event occurrence information to the presentation engine 460. The presentation engine 460 generates an event at the time point that it reproduces a time point or location corresponding to the event occurrence information (i.e., PTS value or ClipMark of a specific clip information, or specific location in a clip AV stream), while reproducing AV data.
[0063]As such, if an event is generated at a specific time point or location according to the event occurrence information, the program engine 440 recognizes the generation and executes a corresponding operation according to a program function programmed by the JAVA application. The event occurrence information can be recorded in an event occurrence table 495, and a process for generating an event using the event occurrence table 495 and an event manager 490 will be described later.
[0064]FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a reproduction method according to an embodiment. Referring to FIG. 5, if a specific JAVA application is executed by a user input or a navigation command, etc., the program engine 440 interprets event occurrence information (for example, APIs) included in the JAVA application and transfers a corresponding parameter value to the presentation engine 460 in step S510. The corresponding parameter of the API has been described above. The presentation engine 460 detects a designated time point or location of a clip corresponding to the transferred parameter value in operation 520 and generates a corresponding event when a clip at the detected event occurrence time point or location is reproduced in operation 530. When the event is generated, the program engine 440 recognizes the event occurrence, calls up an event handler function programmed in the JAVA application, and executes a specific operation in synchronization of the reproduction time-point of the corresponding clip.
[0065]As described above, the presentation engine 460 may generate an event at an event occurrence location while the presentation engine 460 reproduces AV data, by inserting event occurrence information in the AV data. Hereinafter, a method that stores event information synchronized to AV data in a separate location without changing the AV data and transfers the event information to the presentation engine 460, is described.
[0066]An event is generated using an event occurrence table in which event occurrence information is placed in the table in a form of binary data in order for the event to be generated at a specific reproduction location of AV data, separately from program data such as a JAVA application (referred to as "tablizing" information). Such an event generation table is interpreted and managed by an application manager 470 or an event manager. Tablizing information in a form of binary data refers to a method that stores information needed for event occurrence by providing meanings to each of predetermined bits of a series of binary data.
[0067]The event occurrence table includes identifiers for identifying events, event occurrence time information, information for a JAVA application operated by an event, parameter information to be transferred to a JAVA application operated by an event, and additional information.
[0068]The event identifier is information for identifying an event, such as an identifier trigger_id of a trigger event used in an event occurrence function, and is for example Event_ID. The event occurrence time can be a value of reproduction time information, such as an elapsed time, or a value of unique information of an AV stream such as PTS, SPN, ClipMark. The JAVA application information is information used for identifying a JAVA application to be executed. The JAVA application information can be an ID or name of an application. The parameter information is parameter information that must be transferred to a JAVA application to be executed according to a type of an event. The parameter information can have various values according to a type of an event and characteristics of a JAVA application that operates in correspondence to the event. The additional information is used to additionally store information, such as meta data, and can be omitted. Table 1 is an example of the event occurrence table.
TABLE-US-00001 TABLE 1 Event Event occurrence Application Additional Parameter identifier time information information information Event_ID PTS, SPN, Application JAVA Parameter 1 = a ClipMark( ), 1 application Parameter 2 = b reproduction for deleted elapsed time pictures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
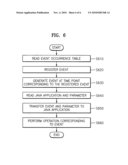
[0069]FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a process that generates an event and reproduces AV data, using an event occurrence table, such as Table 1.
[0070]When a disc is inserted into a reproduction apparatus, the application manager 470 or the event manager 490 reads information stored in the event occurrence table in operation 610. Then, the application manager 470 or the event manager registers an event in the program engine 440 using an event identifier and event occurrence time information in operation 620. Thereafter, while AV data is reproduced, the program engine 440 generates the event at a time point corresponding to the registered event in operation 630. The program engine 440 reads a JAVA application for performing a predetermined operation in response to the corresponding event, and parameters, which must be transferred to the JAVA application, from the application manager 470 or event manager that has read the event occurrence table, using the generated event identifier, in operation 640. The parameters and the generated event are transferred to the JAVA application in operation 650. Thus, the JAVA application that has received the event performs the predetermined operation corresponding to the generated event in synchronization to the AV data in operation 660.
[0071]When a new event is generated while the JAVA application operates, the JAVA application receives new parameter values defined in the event occurrence table according to the contents of the generated event and performs a different operation in synchronization to AV data. When a JAVA application indicated by the generated event is not being executed when the event occurrence table is searched for through the application manager or event manager in order to perform the corresponding operation according to the event occurrence, the program engine can ignore the generated event, or can execute the corresponding JAVA application and then transfer the generated event to the JAVA application.
[0072]In the event occurrence and AV data reproduction method described above with reference to FIG. 5, an event with a specific reproduction time is registered in a specific JAVA application through programming and also operations to be executed when the event is generated, are programmed in the corresponding JAVA application. However, in the event occurrence and AV data reproduction method described above with reference to FIG. 6, even parameter information that must be transferred and/or information for a JAVA application that must operate when an event is generated, are written in a form of a table, so that the event is generated using these information.
[0073]As shown in Table 1, the event occurrence table can include event identifiers, event occurrence time information, JAVA application information, and additional information; however, the event occurrence table is able to include only event identifiers and event occurrence time information as basic information. When the event occurrence table only includes the basic information, it is difficult or impossible to know that JAVA application receives an event and operates a corresponding operation when the program engine generates the event.
[0074]Therefore, a JAVA application that must receive a generated event and perform a predetermined operation includes "event listener" for recognizing an event identifier of the generated event. The JAVA application is preferably made at the same time that a storage medium in which AV data is recorded is manufactured. Event listener is a type of function and is defined in a JAVA application that includes the corresponding function. Information included in the JAVA application is various; however, the JAVA application may include specific operation functions that must be performed when an event is generated, for each of event identifiers. Such an event listener is defined in a JAVA application to be operated when an event with a specific event identifier is generated. Accordingly, when the program engine generates an event with a specific event identifier while the presentation engine performs a reproduction operation, all JAVA applications that include event listeners in the program engine and are currently being reproduced, receive the event identifier of the currently generated event as a parameter through the event listeners.
[0075]When each of the JAVA applications is programmed in a manner to operate a specific operation while a corresponding event identifier is generated in its own event listener, the JAVA application performs the specific operation while receiving the event identifier. Otherwise, the JAVA application operates according to a separate program sequence or ignores the received event identifier.
[0076]The processes, functions, methods and/or software described above may be recorded, stored, or fixed in one or more computer-readable storage media that includes program instructions to be implemented by a computer to cause a processor to execute or perform the program instructions. The media may also include, alone or in combination with the program instructions, data files, data structures, and the like. The media and program instructions may be those specially designed and constructed, or they may be of the kind well-known and available to those having skill in the computer software arts. Examples of computer-readable media include magnetic media, such as hard disks, floppy disks, and magnetic tape; optical media such as CD-ROM disks and DVDs; magneto-optical media, such as optical disks; and hardware devices that are specially configured to store and perform program instructions, such as read-only memory (ROM), random access memory (RAM), flash memory, and the like. Examples of program instructions include machine code, such as produced by a compiler, and files containing higher level code that may be executed by the computer using an interpreter. The described hardware devices may be configured to act as one or more software modules in order to perform the operations and methods described above, or vice versa. In addition, a computer-readable storage medium may be distributed among computer systems connected through a network and computer-readable codes or program instructions may be stored and executed in a decentralized manner.
[0077]As described above, the invention can set an event occurrence time using an AV data structure and generate a specific event at the set time. Accordingly, it is possible to output an application picture in synchronization with an AV picture.
[0078]Operations may be performed according to event occurrence without changing an AV data structure, by storing event occurrence information in a table format, without including the event occurrence information in AV data.
[0079]A number of examples have been described above. Nevertheless, it will be understood that various modifications may be made. For example, suitable results may be achieved if the described techniques are performed in a different order and/or if components in a described system, architecture, device, or circuit are combined in a different manner and/or replaced or supplemented by other components or their equivalents. Accordingly, other implementations are within the scope of the following claims.
Claims:
1. An information storage medium having computer readable data recorded
thereon, the computer readable data comprising:core data, comprising
audio/video data; andprogram data configured to be used for interaction
with a user, the program data comprising event occurrence information
that, when executed by a reproducing apparatus, causes the reproducing
apparatus to generate an event with reference to a structure of the
audio/video data when the reproducing apparatus reproduces audio/video
data at a corresponding time point according to the event occurrence
information, the program data being executed by the reproducing apparatus
in synchronization with the audio/video data based on the event, a video
portion of the audio/video data being displayed through a display window
defined in the program data.
2. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the program data comprises application data written according to a JAVA language.
3. The information storage medium of claim 2, wherein the application data written by the JAVA language is configured to control the audio/video data through an application program interface.
4. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the event occurrence information comprises information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a specific Presentation Time Stamp of an audio/video clip constructing the audio/video data, and is provided within a clip information file that includes characteristic information for the audio/video clip, is reproduced.
5. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the event occurrence information comprises information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a predetermined mark of an audio/video clip constructing the audio/video data, and is provided within a clip information file that includes characteristic information for the audio/video clip, is reproduced.
6. The information storage medium of claim 1, wherein the event occurrence information comprises information that requires an event to be generated when a packet corresponding to a predetermined specific location of an audio/video clip constructing the audio/video data is reproduced.
7. The information storage medium of claim 4, wherein the event occurrence information comprises an event identifier as a parameter for generating the event.
8. A reproduction method to reproduce data from an information storage medium in which core data including audio/video data and navigation data for reproducing the audio/video data and program data used for interaction with a user which is separate from the core data are recorded, the method comprising:reading and registering information stored in an event occurrence table;generating an event included in the registered information at a time point corresponding to the event while the audio/video data is reproduced in synchronization with the program data based on the event;reproducing a video portion of the audio/video data through a display window defined in the program data; andexecuting the program data in synchronization with the audio/video data based on the event.
9. The reproduction method of claim 8, further comprising:reading a JAVA application that performs an operation corresponding to the generated event and a parameter needed to be transferred to the JAVA application, from the event occurrence table, using an event identifier;transferring the read parameter and the generated event to the JAVA application; andperforming, with the JAVA application, an operation corresponding to the received generated event in synchronization to audio/video data.
10. The reproduction method of claim 8, wherein the event occurrence table stores event occurrence information for generating an event at a predetermined reproduction time of audio/video data, in a binary table format.
11. The reproduction method of claim 10, wherein the event occurrence table comprises:an event identifier identifying an event; andevent occurrence time information, comprising a value of reproduction time information;wherein the event occurrence time information comprises an elapsed time or a value of unique information of the audio/video data.
Description:
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001]This application is a continuation of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10/916,403, filed on Aug. 12, 2004, which claims the benefit of Korean Patent Application No. 2003-70751, filed on Oct. 10, 2003, Korean Patent Application No. 2004-26643, filed on Apr. 19, 2004, in the Korean Intellectual Property Office, and U.S. provisional Patent Application No. 60/508,315, filed on Oct. 6, 2003, in the US Patent and Trademark Office, the disclosures of which are incorporated herein in their entirety by reference.
BACKGROUND
[0002]1. Field
[0003]The following description relates to an information storage medium including event occurrence information and an apparatus and method of reproducing the same, and more particularly, to an information storage medium storing event information for generating an event with reference to an AV data structure and an apparatus and method of reproducing the same.
[0004]2. Description of the Related Art
[0005]A moving-image data is classified into audio-video (AV) data for a high definition movie and navigation data for controlling reproduction of the AV data. Demand for applications with programming and browsing functions for reinforcing interaction with a user regarding the above-mentioned moving-image data is increasing. However, in order to provide these functions, an application using program data should be executed in synchronization to AV data.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0006]The invention provides an information storage medium including event occurrence information, which is capable of executing an application in synchronization with AV data by including event occurrence information designated based on an AV data structure in program data, and a reproduction apparatus and method thereof.
[0007]The invention also includes a reproduction method and apparatus, which record event occurrence information in a format of a binary table to generate and reproduce an event.
[0008]According to an aspect of the invention, there is provided an information storage medium, including: core data, which includes AV data and navigation data for reproducing the AV data; and program data which is used for interaction with a user, wherein the program data includes event occurrence information for generating an event with reference to a structure of the AV data.
[0009]The program data may be application data written by a JAVA language.
[0010]The event occurrence information may be information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a specific Presentation Time Stamp (PTS) of an AV clip constructing the AV data, within clip information file including characteristic information for the AV clip, is reproduced.
[0011]The event occurrence information may be information that requires an event to be generated when a time point corresponding to a predetermined mark of an AV clip constructing the AV data, which is within a clip information file that includes characteristic information for the AV clip, is reproduced.
[0012]The event occurrence information may be information that requires an event to be generated when a packet corresponding to a predetermined specific location of an AV clip constructing the AV data is reproduced.
[0013]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a reproduction apparatus including: a reader, which reads AV data and program data including event occurrence information; a program engine, which executes the program data and outputs the event occurrence information; and a presentation engine, which reproduces the AV data and generates an event when AV data at a corresponding time point according to the event occurrence information is reproduced.
[0014]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a reproduction method including: reading AV data and program data including event occurrence information; executing the program data and interpreting and outputting the event occurrence information; and reproducing the AV data, and generating an event when AV data at a corresponding time point according to the event occurrence information is reproduced.
[0015]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a reproduction method including: reading and registering information stored in an event occurrence table; and generating an event included in the registered information at a time point corresponding to the error while AV data is reproduced.
[0016]The event occurrence table may store event occurrence information for generating an event at a predetermined reproduction time point of AV/video data, in a form of a binary table.
[0017]According to another aspect of the invention, there is provided a computer-readable medium having embodied thereon a computer program for executing the method.
[0018]Additional aspects and/or advantages of the invention will be set forth in part in the description which follows and, in part, will be obvious from the description, or may be learned by practice of the invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
[0019]FIG. 1 shows data types to be stored in an information storage medium according to an embodiment.
[0020]FIG. 2 shows correlations of PlayList, PlayItem, Clip Information, and Clip, constructing AV data.
[0021]FIG. 3 shows the configuration of the Clip Information.
[0022]FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a reproduction apparatus, according to an embodiment.
[0023]FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a reproduction method according to an embodiment.
[0024]FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a process that generates an event and reproduces AV data.
[0025]Throughout the drawings and the detailed description, unless otherwise described, the same drawing reference numerals will be understood to refer to the same elements, features, and structures. The relative size and depiction of these elements may be exaggerated for clarity, illustration, and convenience.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE PREFERRED EMBODIMENTS
[0026]The following detailed description is provided to assist the reader in gaining a comprehensive understanding of the methods, apparatuses, and/or systems described herein. Accordingly, various changes, modifications, and equivalents of the systems, apparatuses and/or methods described herein will be suggested to those of ordinary skill in the art. The progression of processing steps and/or operations described is an example; however, the sequence of steps and/or operations is not limited to that set forth herein and may be changed as is known in the art, with the exception of steps and/or operations necessarily occurring in a certain order. Also, descriptions of well-known functions and constructions may be omitted for increased clarity and conciseness.
[0027]FIG. 1 shows data types to be stored in an information storage medium according an embodiment. Referring to FIG. 1, core data 110 includes AV data 111 and navigation data 112. The navigation data 112 is a collection of navigation commands for reproducing the AV data. The core data is also referred to as core mode data. The core data 110 is data that is used in a video application such as DVD and is required for showing a video, such as a movie. A mode that reproduces such core data 110 is referred to as a movie mode.
[0028]Data for reinforcing various interactions with a user is generally known as Data for Full 120. The Data for Full 120 is also referred to as Data for Full mode. The Data for Full mode includes program data 121 for providing various interactions with a user and browsing data 122 to allow network browsing, such as Internet browsing. The program data 121 is, for example, a java application that provides various user interaction functions. The browsing data 122 includes markup documents written with a markup language, such as XML, markup documents including or linking script codes, such as ECMA script, script files, at least one image referenced by the markup documents, and resource files such as graphics and sounds. The core data 110 is able to communicate with the Data for Full 120 through application program interface (API). The program data 121 includes event occurrence information for generating event at a time and/or location designated by the AV data 112.
[0029]System data 130 includes at least startup information 131 and title information 132. The system data 130 is read when the information storage medium is booted or inserted. The system data that is read when the storage medium is booted or inserted does not belong to a specific mode.
[0030]The AV data recorded on the information storage medium is able to be reproduced in a plurality of modes, including: a core mode that reproduces data in a movie mode using the navigation data as the data for code mode, as described above, and a full mode that allows AV data to be displayed through a display window defined in an application made by a program language as Data for Full mode. When the full mode is selected by a user or by a navigation flow, a display window for displaying moving-image data is created by a function programmed in an application (for example, Java application using a Java language as a programming language) made by a programming language, AV data is controlled and displayed through the API, and simultaneously JAVA-based contents or various resources (for example, image, audio, etc.) referred in the JAVA application are displayed in synchronization of reproduction of the AV data. However, to display the AV data through the display window defined in the JAVA application in the above-described full mode, synchronization of the AV data and the JAVA application is necessary.
[0031]FIG. 2 shows correlations of PlayList, PlayItem, Clip Information, and Clip, constructing AV data. Referring to FIG. 2, the JAVA application controls the AV data through API, such as "BDPIayPL" (PlayList Number), as Data for Full mode. The PlayList is a fundamental unit of reproduction and the information storage medium stores a plurality of PlayLists. The PlayList includes a plurality of PlayItems that are connected to one another. The PlayItem designates one part of a Clip, particularly, the PlayItem is used to designate a reproduction start time and a reproduction end time of the Clip. Accordingly, the corresponding part in a Clip is searched using Clip information. An AV stream is recorded using a Clip as a fundamental unit. Clips are typically recorded on a continuous space, respectively, and are compressed to reduce theirs capacities.
[0032]To reproduce the recorded Clips, it is necessary to detect characteristic information of the compressed presentation data. Clip information is recorded for each Clip. The Clip information includes audio and video properties of each Clip, Entry Point Map storing location information of Entry Point allowing random access per a predetermined interval, etc. In a case of MPEG as a general moving-image compression technique, Entry Point is an I picture or a GOP header used as a random access point. The Entry point Map is used in a time search for detecting a time point elapsed by a predetermined time after the reproduction begins.
[0033]FIG. 3 shows a configuration of the Clip Information. Referring to FIG. 3, the Clip Information 300 includes at least Characteristic Point Information (CPI) 310 and ClipMark( ) 320. CPI 310 includes EP_map (Entry Point Map) information. The EP_map information is information for indicating an entry point of a corresponding clip. Entry Point in the MPEG video coding standard indicates a start point of an image coded as an I picture. The EP_map information provides a relationship between a Presentation Time Stamp (PTS) value and its address in an AV stream file. An entry point of the PTS value is represented as "PTS_EP_start", and the address of the entry point is represented as "SPN_EP_start". Meanwhile, ClipMark( ) 320 is used as information for embedding Mark at a specific location in the AV stream file.
[0034]Accordingly, CPI( ) or ClipMark( ) are used as parameters for generating a trigger event as will be described later. Further, the API used in the JAVA application and required parameters will be described in more detail.
[0035]1. BDVideo.SetTrigger (trigger_id, Clip_Information_file_name, PTS_EP_start, ref) [0036]meaning: generate a trigger event when a clip is reproduced at a PTS value in designated clip information [0037]parameters: [0038]trigger_id: trigger event identifier [0039]Clip_Information_file_name: name of clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0040]PTS_EP_start: entry point of a PTS value in clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0041]ref: value to be included in an event variable when an event is called up
[0042]2. BDVideo.SetTrigger (trigger_id, Clip_AV_stream_file_name, SPN_EP_start, ref) [0043]meaning: generate a trigger event when a source packet number of a designated clip AV stream is reproduced [0044]2) parameters: [0045]trigger_id: trigger event identifier
[0046]Clip_AV_stream_file_name: name of an AV stream in which a trigger event will be generated [0047]SPN_EP_start: start point of a source packet in a clip AV stream in which a trigger event will be generated [0048]ref: value to be included in an event variable when an event is called up
[0049]3. BDVideo.SetTrigger (trigger_id, Clip_AV_stream_file_name, ClipMark( ) ref) [0050]1) meaning: generate a trigger event when ClipMark in designated clip information is reproduced [0051]2) parameters: [0052]trigger_id: trigger event identifier [0053]Clip_Information_file_name: name of clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0054]ClipMark( ): ClipMark in clip information for a clip in which a trigger event will be generated [0055]ref: value to be included in an event variable when an event is called up BDVideo.ClearTrigger(trigger_id) [0056]1) meaning: release a request trigger event [0057]2) parameters [0058]trigger_id: trigger event identifier (for example, if "-1" is designated as trigger_id, this can be used as meaning of commanding the release of all generated trigger events)
[0059]FIG. 4 is a block diagram of a reproduction apparatus, according to an embodiment. The reproduction apparatus displays AV data recorded on an information storage medium using data for a specific mode according to a display method. Referring to FIG. 4, the reproduction apparatus comprises a reader 420, a buffer 430, a program engine 440, a core navigation engine 450, a presentation engine 460, a application engine 470, and a blender 480.
[0060]The reader 420 reads AV data, program data, core navigation data, and system data from the information storage medium 410 and transfers the read data to the respective corresponding buffers 431, 432, 433 and 434. The respective buffers (buffer 431 for program data, buffer 432 for core navigation data, buffer 433 for AV data, and buffer 433 for system data and management information) buffer the received data, respectively. The buffered results are transmitted to the respective corresponding engines for reproduction and are reproduced by the respective engines. The respective engines include, for example, a program engine, a core navigation engine, a presentation engine, and an application manager. At this time, the system data is transferred to the application manager 470. The application manager 470 determines a mode and data to be first reproduced based on an entry point of start-up data in the system data.
[0061]While the respective AV data is reproduced, entry points of respective objects generated due to conversion between modes or title search are transferred to corresponding reproduction engines capable of reproducing the corresponding objects, with reference to the system data, thereby reproducing the respective objects. The application manager 470 may also include a user input receiving unit and a user input processing unit in order to transfer a user input to an engine for corresponding mode. The presentation engine 460 decodes and reproduces moving-image data and still-image streams and/or data files. The program engine 440 controls the presentation engine 460 through the API, like the core navigation engine 450.
[0062]The program engine 440 executes the JAVA application including the above described various event occurrence information and transfers the event occurrence information to the presentation engine 460. The presentation engine 460 generates an event at the time point that it reproduces a time point or location corresponding to the event occurrence information (i.e., PTS value or ClipMark of a specific clip information, or specific location in a clip AV stream), while reproducing AV data.
[0063]As such, if an event is generated at a specific time point or location according to the event occurrence information, the program engine 440 recognizes the generation and executes a corresponding operation according to a program function programmed by the JAVA application. The event occurrence information can be recorded in an event occurrence table 495, and a process for generating an event using the event occurrence table 495 and an event manager 490 will be described later.
[0064]FIG. 5 is a flowchart illustrating a reproduction method according to an embodiment. Referring to FIG. 5, if a specific JAVA application is executed by a user input or a navigation command, etc., the program engine 440 interprets event occurrence information (for example, APIs) included in the JAVA application and transfers a corresponding parameter value to the presentation engine 460 in step S510. The corresponding parameter of the API has been described above. The presentation engine 460 detects a designated time point or location of a clip corresponding to the transferred parameter value in operation 520 and generates a corresponding event when a clip at the detected event occurrence time point or location is reproduced in operation 530. When the event is generated, the program engine 440 recognizes the event occurrence, calls up an event handler function programmed in the JAVA application, and executes a specific operation in synchronization of the reproduction time-point of the corresponding clip.
[0065]As described above, the presentation engine 460 may generate an event at an event occurrence location while the presentation engine 460 reproduces AV data, by inserting event occurrence information in the AV data. Hereinafter, a method that stores event information synchronized to AV data in a separate location without changing the AV data and transfers the event information to the presentation engine 460, is described.
[0066]An event is generated using an event occurrence table in which event occurrence information is placed in the table in a form of binary data in order for the event to be generated at a specific reproduction location of AV data, separately from program data such as a JAVA application (referred to as "tablizing" information). Such an event generation table is interpreted and managed by an application manager 470 or an event manager. Tablizing information in a form of binary data refers to a method that stores information needed for event occurrence by providing meanings to each of predetermined bits of a series of binary data.
[0067]The event occurrence table includes identifiers for identifying events, event occurrence time information, information for a JAVA application operated by an event, parameter information to be transferred to a JAVA application operated by an event, and additional information.
[0068]The event identifier is information for identifying an event, such as an identifier trigger_id of a trigger event used in an event occurrence function, and is for example Event_ID. The event occurrence time can be a value of reproduction time information, such as an elapsed time, or a value of unique information of an AV stream such as PTS, SPN, ClipMark. The JAVA application information is information used for identifying a JAVA application to be executed. The JAVA application information can be an ID or name of an application. The parameter information is parameter information that must be transferred to a JAVA application to be executed according to a type of an event. The parameter information can have various values according to a type of an event and characteristics of a JAVA application that operates in correspondence to the event. The additional information is used to additionally store information, such as meta data, and can be omitted. Table 1 is an example of the event occurrence table.
TABLE-US-00001 TABLE 1 Event Event occurrence Application Additional Parameter identifier time information information information Event_ID PTS, SPN, Application JAVA Parameter 1 = a ClipMark( ), 1 application Parameter 2 = b reproduction for deleted elapsed time pictures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
[0069]FIG. 6 is a flowchart illustrating a process that generates an event and reproduces AV data, using an event occurrence table, such as Table 1.
[0070]When a disc is inserted into a reproduction apparatus, the application manager 470 or the event manager 490 reads information stored in the event occurrence table in operation 610. Then, the application manager 470 or the event manager registers an event in the program engine 440 using an event identifier and event occurrence time information in operation 620. Thereafter, while AV data is reproduced, the program engine 440 generates the event at a time point corresponding to the registered event in operation 630. The program engine 440 reads a JAVA application for performing a predetermined operation in response to the corresponding event, and parameters, which must be transferred to the JAVA application, from the application manager 470 or event manager that has read the event occurrence table, using the generated event identifier, in operation 640. The parameters and the generated event are transferred to the JAVA application in operation 650. Thus, the JAVA application that has received the event performs the predetermined operation corresponding to the generated event in synchronization to the AV data in operation 660.
[0071]When a new event is generated while the JAVA application operates, the JAVA application receives new parameter values defined in the event occurrence table according to the contents of the generated event and performs a different operation in synchronization to AV data. When a JAVA application indicated by the generated event is not being executed when the event occurrence table is searched for through the application manager or event manager in order to perform the corresponding operation according to the event occurrence, the program engine can ignore the generated event, or can execute the corresponding JAVA application and then transfer the generated event to the JAVA application.
[0072]In the event occurrence and AV data reproduction method described above with reference to FIG. 5, an event with a specific reproduction time is registered in a specific JAVA application through programming and also operations to be executed when the event is generated, are programmed in the corresponding JAVA application. However, in the event occurrence and AV data reproduction method described above with reference to FIG. 6, even parameter information that must be transferred and/or information for a JAVA application that must operate when an event is generated, are written in a form of a table, so that the event is generated using these information.
[0073]As shown in Table 1, the event occurrence table can include event identifiers, event occurrence time information, JAVA application information, and additional information; however, the event occurrence table is able to include only event identifiers and event occurrence time information as basic information. When the event occurrence table only includes the basic information, it is difficult or impossible to know that JAVA application receives an event and operates a corresponding operation when the program engine generates the event.
[0074]Therefore, a JAVA application that must receive a generated event and perform a predetermined operation includes "event listener" for recognizing an event identifier of the generated event. The JAVA application is preferably made at the same time that a storage medium in which AV data is recorded is manufactured. Event listener is a type of function and is defined in a JAVA application that includes the corresponding function. Information included in the JAVA application is various; however, the JAVA application may include specific operation functions that must be performed when an event is generated, for each of event identifiers. Such an event listener is defined in a JAVA application to be operated when an event with a specific event identifier is generated. Accordingly, when the program engine generates an event with a specific event identifier while the presentation engine performs a reproduction operation, all JAVA applications that include event listeners in the program engine and are currently being reproduced, receive the event identifier of the currently generated event as a parameter through the event listeners.
[0075]When each of the JAVA applications is programmed in a manner to operate a specific operation while a corresponding event identifier is generated in its own event listener, the JAVA application performs the specific operation while receiving the event identifier. Otherwise, the JAVA application operates according to a separate program sequence or ignores the received event identifier.
[0076]The processes, functions, methods and/or software described above may be recorded, stored, or fixed in one or more computer-readable storage media that includes program instructions to be implemented by a computer to cause a processor to execute or perform the program instructions. The media may also include, alone or in combination with the program instructions, data files, data structures, and the like. The media and program instructions may be those specially designed and constructed, or they may be of the kind well-known and available to those having skill in the computer software arts. Examples of computer-readable media include magnetic media, such as hard disks, floppy disks, and magnetic tape; optical media such as CD-ROM disks and DVDs; magneto-optical media, such as optical disks; and hardware devices that are specially configured to store and perform program instructions, such as read-only memory (ROM), random access memory (RAM), flash memory, and the like. Examples of program instructions include machine code, such as produced by a compiler, and files containing higher level code that may be executed by the computer using an interpreter. The described hardware devices may be configured to act as one or more software modules in order to perform the operations and methods described above, or vice versa. In addition, a computer-readable storage medium may be distributed among computer systems connected through a network and computer-readable codes or program instructions may be stored and executed in a decentralized manner.
[0077]As described above, the invention can set an event occurrence time using an AV data structure and generate a specific event at the set time. Accordingly, it is possible to output an application picture in synchronization with an AV picture.
[0078]Operations may be performed according to event occurrence without changing an AV data structure, by storing event occurrence information in a table format, without including the event occurrence information in AV data.
[0079]A number of examples have been described above. Nevertheless, it will be understood that various modifications may be made. For example, suitable results may be achieved if the described techniques are performed in a different order and/or if components in a described system, architecture, device, or circuit are combined in a different manner and/or replaced or supplemented by other components or their equivalents. Accordingly, other implementations are within the scope of the following claims.
User Contributions:
Comment about this patent or add new information about this topic:
| People who visited this patent also read: | |
| Patent application number | Title |
|---|---|
| 20100280341 | POLYMER MEMBRANES FOR CONTINUOUS ANALYTE SENSORS |
| 20100280340 | MEDICAL SYSTEM AND METHOD OF SWITCHING ANTENNA |
| 20100280339 | AUTOMATIC WIRELESS PAN/LAN SWITCHING |
| 20100280338 | EAR-WORN BIOFEEDBACK DEVICE |
| 20100280337 | SIMULTANEOUS AMBULATORY PULSE OXIMETRY AND PH MONITORING FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF GERD-RELATED RESPIRATORY DISEASE |