Patent application title: Means and methods for regulating gene expression
Inventors:
Arie P. Otte (Amersfoort, NL)
Arthur L. Kruckeberg (Shoreline, WA, US)
David P. E. Satijn (Nieuwegein, NL)
Assignees:
Chromagenics B.V.
IPC8 Class: AC12P2100FI
USPC Class:
435 691
Class name: Chemistry: molecular biology and microbiology micro-organism, tissue cell culture or enzyme using process to synthesize a desired chemical compound or composition recombinant dna technique included in method of making a protein or polypeptide
Publication date: 2008-08-28
Patent application number: 20080206813
Claims:
1. A method for producing a proteinaceous molecule in a cell, the method
comprising:providing a cell selected from the group consisting of a cell
having an adenovirus Early Region 1 (E1) sequence, a HuNS-1 myeloma cell,
a 293 cell, a CHO cell, a Vero cell, a WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma cell, a
BHK cell, a non-secreting mouse myeloma Sp2/0-Ag 14 cell, a non-secreting
mouse myeloma NSO cell, and an NCI-H295R adrenal gland carcinoma
cell;wherein the cell comprises an anti-repressor activity sequence
operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a heterologous
proteinaceous molecule, wherein the anti-repressor activity sequence
comprises SEQ ID NO: 17;expressing the proteinaceous molecule in the
cell; andharvesting material comprising the thus expressed proteinaceous
molecule.
2. The method according to claim 1, wherein the anti-repressor activity sequence consists of SEQ ID NO: 17.
3. The method according to claim 1, wherein the cell comprises an adenovirus Early Region 1 (E1) sequence.
4. The method according to claim 1, wherein the proteinaceous molecule is secreted by the cell.
5. The method according to claim 2, wherein the proteinaceous molecule is secreted by the cell.
6. The method according to claim 1, wherein the cell comprises a plurality of said anti-repressor activity sequence operably linked to the nucleic acid sequence encoding the heterologous proteinaceous molecule.
7. The method according to claim 6, wherein at least one anti-repressor activity sequence is positioned 5' of the sequence encoding the proteinaceous molecule and at least one anti-repressor activity sequence is positioned 3' of the sequence encoding the proteinaceous molecule.
8. The method according to claim 1, wherein the cell is a CHO cell.
9. The method according to claim 6, wherein the cell is a CHO cell.
10. The method according to claim 7, wherein the cell is a CHO cell.
11. A method for producing a proteinaceous molecule in a cell, the method comprising:providing a cell selected from the group consisting of a cell having an adenovirus Early Region 1 (E1) sequence, a HuNS-1 myeloma cell, a 293 cell, a CHO cell, a Vero cell, a WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma cell, a BHK cell, a non-secreting mouse myeloma Sp2/0-Ag 14 cell, a non-secreting mouse myeloma NSO cell, and an NCI-H295R adrenal gland carcinoma cell; wherein the cell comprises an anti-repressor activity sequence operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a heterologous proteinaceous molecule, wherein the anti-repressor activity sequence comprises at least 50 bases of SEQ ID NO: 17;expressing the proteinaceous molecule in the cell; andharvesting material comprising the thus expressed proteinaceous molecule.
12. A recombinant host cell line comprising:a cell selected from the group consisting of a cell line comprising an adenovirus Early Region 1 (E1) sequence, a HuNS-1 myeloma cell line, a 293 cell line, a CHO cell line, a Vero cell line, a WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma cell line, a BHK cell line, a non-secreting mouse myeloma Sp2/0-Ag 14 cell line, a non-secreting mouse myeloma NSO cell line, and an NCI-H295R adrenal gland carcinoma cell line;the cell comprising an anti-repressor activity sequence operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a heterologous proteinaceous molecule, wherein the anti-repressor activity sequence comprises SEQ ID NO: 17.
13. The cell line of claim 12, wherein the anti-repressor activity sequence consists of SEQ ID NO: 17.
14. The cell line of claim 12, wherein the cell line comprises an adenovirus Early Region 1 sequence.
15. The cell line of claim 12, wherein the cell comprises a plurality of the anti-repressor activity sequence operably linked to said nucleic acid sequence encoding the heterologous proteinaceous molecule.
16. The cell line of claim 12, wherein at least one anti-repressor activity sequence is positioned 5' of the sequence encoding the proteinaceous molecule and at least one anti-repressor activity sequence is positioned 3' of the sequence encoding the proteinaceous molecule.
17. The cell line of claim 12, wherein the cell line is a CHO cell line.
18. The cell line of claim 15, wherein the cell line is a CHO cell line.
19. The cell line of claim 16, wherein the cell line is a CHO cell line.
20. A recombinant host cell line comprising:a cell selected from the group consisting of a cell line comprising an adenovirus Early Region 1 (E1) sequence, a HuNS-1 myeloma cell line, a 293 cell line, a CHO cell line, a Vero cell line, a WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma cell line, a BHK cell line, a non-secreting mouse myeloma Sp2/0-Ag 14 cell line, a non-secreting mouse myeloma NSO cell line, and an NCI-H295R adrenal gland carcinoma cell line;wherein the cell comprises an anti-repressor activity sequence operably linked to a nucleic acid sequence encoding a heterologous proteinaceous molecule, wherein the anti-repressor activity sequence comprises at least 50 bases of SEQ ID NO: 17.
Description:
CROSS-REFERENCE TO RELATED APPLICATIONS
[0001]This application is a divisional of co-pending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11/888,568, filed Jul. 31, 2007, now U.S. Pat. No. ______, which application is a divisional of U.S. patent application Ser. No. 11/012,546, filed Dec. 14, 2004, now U.S. Pat. No. 7,267,965, issued Sep. 11, 2007, which application is a continuation of International Patent Application No. PCT/NL03/00410, filed May 30, 2003, published in English as International Patent Publication No. WO 03/106674 on Dec. 24, 2003, which claims the benefit under 35 U.S.C. § 119 of European Patent Application No. EP 02077344.6, filed Jun. 14, 2002, the entirety of each of which are hereby incorporated by reference
STATEMENT ACCORDING TO 37 C.F.R § 1.52(e)(5)-SEQUENCE LISTING SUBMITTED ON COMPACT DISC
[0002]Pursuant to 37 C.F.R. § 1.52(e)(1)(iii), a compact disc containing an electronic version of the Sequence Listing has been submitted concomitant with this application, the contents of which are hereby incorporated by reference. The compact disc contains the file "P60555PC00 final.txt" which is 496 KB, and created on Dec. 14, 2004. A second compact disk is submitted and is an identical copy of the first compact disc (labeled, "copy 1" and "copy 2," respectively).
TECHNICAL FIELD
[0003]The invention relates to the fields of medicine and cellular biology. More specifically, the invention relates to means and methods for regulating gene expression, and production of proteinaceous molecules.
BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION
[0004]Polypeptide production at industrial scale currently provides many biologically active polypeptides for a variety of uses, including diagnostic and therapeutic pharmaceuticals, industrial catalysts and nourishment. Polypeptides are produced in a variety of host systems, including transgenic animals and plants, microbes, and cultured mammalian cells. In most cases, the host system is modified by recombinant DNA techniques, for instance resulting in introduction into the host cell of a transgene which encodes a polypeptide of interest. Such a transgene typically includes elements that influence the transcription, translation, and/or processing of the transgene's polypeptide coding sequence. A recombinant host is then identified and isolated which has a suitable yield of a polypeptide of interest, and the cell population of this recombinant host is increased to an extent that it can produce the required amount of polypeptide.
[0005]The choice of the host system depends on a number of factors including: (1) the nature and intended use of a polypeptide, and (2) the cost of production. For production of biopharmaceuticals, e.g., therapeutic proteins such as hormones, cytokines, and antibodies, the host system of choice is usually cultured mammalian cells. Considerations with respect to product use and production cost with host cells will be discussed below.
[0006](1) For in vivo therapeutic use, a therapeutic protein must not only have the correct biological activity to alter the course of a disease. It must also do no harm. Most therapeutic proteins are exported from the cell by the secretory pathway. Secreted proteins are modified by a series of post-translational events, including glycosylation, disulfide bond formation, and proteolytic processing. The post-translational modification systems vary among different species and cell types in their detailed mechanisms of action. As a result, the same polypeptide chain can be detectably different when it is produced in different host cells. These differences can be analytical, such as differences in physical properties such as molecular mass, net electrical charge, carbohydrate composition, or structure. The differences can also be functional, affecting for instance the biological activity of the protein itself (catalytic activity, ligand binding characteristics, etc.), and/or its in vivo properties (immunogenicity, biological half life, biodistribution, etc.). Functional differences can, therefore, affect both function and possible side effect(s) of a therapeutic protein. Host cell lines that produce proteins with low efficacy are not suitable for commercial exploitation. Furthermore, host cells which produce modified protein that involves significant side effects in a patient should not be used. These factors are becoming increasingly important considerations during selection of a host cell line for production of a therapeutic protein.
[0007](2) Therapeutic protein production in host cells is an intrinsically costly process. Current methods for industrial production of such proteins often perform poorly, resulting in products that are prohibitively expensive. Poor performance can be due to limitations of protein expression systems and host cell lines currently in use. These limitations mostly have a few specific causes, including (a) failure to identify and isolate recombinant host cell lines that have suitable productivity of proteins (poor predictability), (b) silencing, during the industrial production cycle, of the transgenes that encode proteins (poor stability), and (c) low or incorrect post-translational processing and secretory capacity of the host cell line. These limitations will be considered separately below.
[0008](a) Conventional methods furnish only low frequencies of recombinant host cells that have suitable yields of proteins. Identifying and isolating these rare recombinant cell lines is a laborious and expensive process. The poor predictability of conventional methods means that often a recombinant host cell line is selected for production that has sub-optimal productivity characteristics, simply because a superior recombinant cell line was not identified and isolated during the selection process.
[0009](b) Transgenes are often subject to silencing during cultivation of recombinant host cells. Silencing acts by suppressing transcription of a transgene. Detailed mechanisms of silencing are still not known, and different conventional methods are prone to different kinds of silencing phenomena. With one phenomenon, an individual transgene is silenced by formation of transcriptionally refractory heterochromatin at the transgenic locus. Heterochromatin formation is influenced by the position of genomic integration of a transgene ("position effects" (Boivin and Dura, 1998)). Transgene integration occurs more or less at random. Since most of the genome is heterochromatin, most transgene loci are prone to silencing due to position effects.
[0010]A second transgene-silencing phenomenon can occur when two or more copies of a transgene are integrated into a genome during construction of a recombinant cell line. Formation of tandem transgene repeats often occurs during the initial integration step. Furthermore, in order to increase product yield, many recombinant host cell lines are engineered after the integration step to amplify the copy number of a transgene, which also results in tandem transgene repeats (Kaufman, 1990). Tandem repeats and other configurations of multiple transgene copies are particularly prone to silencing ("repeat-induced gene silencing" (Garrick et al., 1998)).
[0011]In case that a genome contains multiple copies of a transgene, the yield can also decline via another phenomenon than transcriptional silencing. The number of copies of the transgene can decline during cultivation of a recombinant host cell line. The productivity of such cell lines at the time of selection for use is correlated with a transgene copy number, and consequently as copies of a transgene are lost, the yield declines (Kaufman, 1990).
[0012](c) Different cell types in a mammalian organism have different capacities for post-translational modification and secretion of proteins. The functions of some cell types include production of large quantities of secreted proteins; examples include lymphocytes (producing immunoglobulins), hepatocytes (producing serum proteins), and fibroblasts (producing extracellular matrix proteins). These cell types are favorable sources for deriving host cell lines for production of secreted heterologous proteins. More favorable is the use of a cell line whose progenitor organismal cell type secretes a protein or class of proteins of interest. For example, it is particularly favorable to express recombinant monoclonal antibodies in lymphocytes (or host cells derived from lymphocytes), erythropoietin in hepatocytes (or host cells derived from hepatocytes), and blood clotting factors (e.g., Factor VIII and van Willebrand's factor) in endothelial cells (or host cells derived from endothelial cells).
[0013]The use of specific cell types (or cell lines derived therefrom) for production of their affiliated proteins is favorable because such specific cell types will carry out proper post-translational modifications of produced proteins. However, specific cell types often do not have high secretory capacities. For example, cells of the central nervous system, such as neurons, have low intrinsic protein secretion capacities. These cells do secrete proteins, however, including neurotrophins. Neurotrophins regulate the fate and shape of neuronal cells during fetal and juvenile development. Moreover, they influence patterns of neuronal degeneration and regeneration in adults (Bibel and Barde, 2000). Production of neurotrophins for therapeutic applications has considerable biopharmaceutical value (e.g., Axokine®, recombinant cilliary neurotrophic factor from Regeneron). In order to produce heterologous neurotrophins with post-translational modifications (and hence functional properties) that match the naturally-occurring proteins, expression in host cells derived from the central nervous system is favorable. However, production of polypeptides such as neurotrophins in host cell lines such as those derived from neural tissue is inefficient using conventional methods. The predictability of identifying high-expressor isolates from these types of cell lines is often poor; the yield of proteins from such cell lines is generally low, and production levels are characteristically unstable.
[0014]Another drawback to a use of specific host cells for production of affiliated proteins is that it is usually difficult to isolate cell lines with favorable biotechnological characteristics. These characteristics for instance include the mode and rate of growth, and the ease of introduction of a transgene. Consequently, various general host cell lines have been established. Examples of these include CHO cells from Chinese hamster ovary (ATCC (American Type Culture Collection) CCL-61), BHK cells from baby hamster kidney (ATCC CCL-10), and Vero cells from African green monkey kidney (ATCC CCL-81). These "general purpose" host cell lines are widely used for production of a number of heterologous proteins. A disadvantage of general purpose cell lines is that the post-translational modifications of heterologous proteins produced by them often differ from the post-translational modifications of the naturally occurring proteins. These differences can have functional consequences resulting in side effects, as discussed above.
[0015]Table 1 lists a number of proteins that are currently in use or under development for biopharmaceutical applications. It also lists the tissue or cell type in which each protein is normally produced in the human body. These 24 proteins (or protein classes) come from a wide range of cells and tissue, ranging from highly secretory cells (hepatocytes, endothelial cells) to cells with low secretory capacity (e.g., neural tissue). Currently, neither general-purpose host cells nor specific host cells have qualities that enable optimal expression of the broad spectrum of biopharmaceutically important secreted proteins.
[0016]Hence, protein production by conventional host cell lines involves a lot of disadvantages and complications, for instance with respect to yield and post-translational modifications. There is a need in the art for improved protein production in recombinant host cell lines.
SUMMARY OF THE INVENTION
[0017]The invention provides a method for producing a proteinaceous molecule in a cell comprising selecting a cell for its suitability for producing the proteinaceous molecule, providing a nucleic acid encoding the proteinaceous molecule with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR (STabilizing Anti-Repression) sequence, expressing the resulting nucleic acid in the cell and collecting the proteinaceous molecule.
[0018]The STAR sequence has to be operably linked to the nucleic acid encoding the proteinaceous molecule in order to be effective. In one embodiment of the invention, one STAR element is used. Preferably however, more than one STAR element is used. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the nucleic acid encoding the proteinaceous molecule is provided with two STAR sequences; one STAR sequence at the 5' side of the coding sequence of the nucleic acid and one STAR sequence at the 3' side of the coding sequence of the nucleic acid.
Description of STAR Elements
[0019]New transcription regulatory elements were disclosed by the present inventors, which are named STAR sequences (See EP 01202581.3). STAR sequences are nucleic acid sequences that comprise a capacity to influence transcription of genes in cis. Typically, although not necessarily, the STAR sequences do not code by themselves for a functional protein.
[0020]A STAR sequence has a gene transcription modulating quality in at least one type of cell. A STAR sequence is capable of enhancing gene transcription resulting in a higher yield, increasing the proportion of transgene-comprising host cells with acceptable expression levels, and/or increasing stability of transgenes in recombinant cell lines.
[0021]In EP 01202581.3 a method of detecting, and optionally selecting, a STAR sequence is provided, comprising providing a transcription system with a variety of a fragment-comprising vectors, the vectors comprising i) an element with a gene-transcription repressing quality, and ii) a promoter directing transcription of a reporter gene, the method further comprising performing a selection step in the transcription system in order to identify the STAR sequence. In a preferred embodiment, the fragments are located between i) the element with a gene-transcription repressing quality, and ii) the promoter directing transcription of the reporter gene. RNA polymerase initiates the transcription process after binding to a specific sequence, called the promoter, that signals where RNA synthesis should begin. A STAR sequence can enhance transcription from the promoter in cis, in a given cell type and/or a given promoter.
[0022]Methods disclosed in EP 01202581.3 have been used to isolate STAR elements from the human genome. Isolated human STAR elements have been placed in DNA vectors so as to flank transgene expression units, and the vectors have subsequently been integrated into host cell genomes. Transgene expression in these recombinant host cells has been compared to expression in similar host cells in which the expression units are not flanked by STAR elements. The results show that STAR elements have at least one of three consequences for production of (heterologous) proteinaceous molecule (also referred to as (heterologous) protein): (1) they increase the predictability of identifying host cell lines that express a proteinaceous molecule at industrially acceptable levels; (2) they result in host cell lines with increased protein yields; and/or (3) they result in host cell lines that exhibit more stable protein production during prolonged cultivation. Each of these attributes is discussed in more detail below:
[0023](1) Increased predictability: Integration of transgene expression units can occur at random positions throughout the host cell genome. However, much of the genome is transcriptionally silent heterochromatin. When the expression units include STAR elements flanking the transgene, the position of integration has a reduced effect on expression. The STAR elements impair the ability of adjacent heterochromatin to silence the transgene. Consequently, the proportion of transgene-containing host cells with acceptable expression levels is increased.
[0024](2) Yield: The levels of protein expression in primary populations of recombinant host cells, directly after transgene integration, have been surveyed. The expression level of individuals in the populations varies. However, when the transgenes are protected by STAR elements, the variability is reduced. This reduced variability is most conspicuous in that fewer clones are recovered that have low levels of expression. Furthermore, the populations with STAR elements commonly have individuals with strikingly high expression. These high-yielding individuals are favorable for production of proteinaceous molecules.
[0025](3) Increased stability: STAR elements increase the stability of transgenes in recombinant host cell lines by ensuring that the transgenes are not transcriptionally silenced during prolonged cultivation. Comparative trials show that, under conditions in which transgenes that are not protected by STAR elements are progressively silenced (5 to 25 passages in cultivation), STAR element-protected transgenes continue to be expressed at high levels. This is an advantage during industrial production of proteinaceous molecules, during which cell cultivation continues for prolonged periods, from a few weeks to many months.
[0026]Hence, a STAR sequence can enhance expression of a heterologous proteinaceous molecule. In addition, a STAR sequence can enhance expression of a naturally produced proteinaceous molecule.
[0027]Transcription can be influenced through a direct effect of the STAR sequence (or the protein(s) binding to it) on the transcription of a particular promoter. Transcription can however, also be influenced by an indirect effect, for instance because the STAR sequence affects the function of one or more other regulatory elements. A STAR sequence can also comprise a stable gene transcription quality. Frequently, expression levels drop dramatically with increasing numbers of cell divisions. With the methods disclosed in EP 01202581.3 it is possible to detect and optionally select a DNA sequence that is capable of at least in part preventing the dramatic drop in transcription levels with increasing numbers of cell divisions. Strikingly, fragments comprising a STAR sequence can be detected and optionally selected with a method EP 01202581.3, in spite of the fact that the method does not necessarily measure long term stability of transcription.
[0028]A STAR sequence is suitable for enhancing the level of transcription of a gene of interest in a host cell. If, together with a gene of interest, a STAR sequence is also introduced into host cells, more clones can be detected that express more than a certain amount of the gene of interest. As used herein, such host cells are termed "host cells with acceptable expression levels."
[0029]Furthermore, if, together with a gene of interest, a STAR sequence is also introduced into host cells, a higher yield of produced proteinaceous molecules can be obtained, while gene expression level is also more stable than in the absence of such STAR sequences. Preferably, a STAR sequence derived from a plant and/or vertebrate is used. More preferably a human STAR sequence is used.
[0030]Sequences comprising a STAR sequence can be found by using a functional assay, as described above. However, once a collection of such sequences has been identified, bioinformatics can be used to find other STAR sequences. Several methods are available in the art to extract sequence identifiers from a family of DNA sequences sharing a certain common feature. Such sequence identifiers can subsequently be used to identify sequences that share one or more identifiers. Sequences sharing such one or more identifiers are likely to be a member of the same family of sequences, i.e., are likely to share the common feature of the family. By the present inventors a large number of sequences comprising STAR activity (so-called STAR sequences) were used to obtain sequence identifiers (patterns) which are characteristic for sequences comprising STAR activity. These patterns can be used to determine whether a test sequence is likely to contain STAR activity. A method for detecting the presence of a STAR sequence within a nucleic acid sequence of about 50-5000 base pairs is thus provided, comprising determining the frequency of occurrence in the sequence of at least one sequence pattern and determining that the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence. In principle any method is suited for determining whether a sequence pattern is representative of a STAR sequence. Many different methods are available in the art. Preferably, the step of determining that the occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence comprises, determining that the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern significantly differs between at least one STAR sequence and at least one control sequence. In principle any significant difference is discriminative for the presence of a STAR sequence. However, in a particularly preferred embodiment, the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern is significantly higher in at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence compared to at least one control sequence.
[0031]A considerable number of sequences comprising a STAR sequence have been identified by the present inventors. It is possible to use these sequences to test how efficient a pattern is in discriminating between a control sequence and a sequence comprising a STAR sequence. Using so-called discriminant analysis it is possible to determine on the basis of any set of STAR sequences in a species, the most optimal discriminative sequence patterns or combination thereof. Thus, preferably, at least one of the patterns is selected on the basis of optimal discrimination between at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence and a control sequence.
[0032]In a preferred embodiment, the frequency of occurrence of a sequence pattern in a test nucleic acid is compared with the frequency of occurrence in a sequence known to contain a STAR sequence. In this case, a pattern is considered representative for a sequence comprising a STAR sequence if the frequencies of occurrence are similar. In a preferred embodiment, another criterion is used. The frequency of occurrence of a pattern in a sequence comprising a STAR sequence is compared to the frequency of occurrence of the pattern in a control sequence. By comparing the two frequencies it is possible to determine for each pattern thus analyzed, whether the frequency in the sequence comprising the STAR sequence is significantly different from the frequency in the control sequence. In this embodiment, a sequence pattern is considered to be representative of a sequence comprising a STAR sequence, if the frequency of occurrence of the pattern in at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence is significantly different from the frequency of occurrence of the same pattern in a control sequence. By using larger numbers of sequences comprising a STAR sequence the number of patterns for which a statistical difference can be established increases, thus enlarging the number of patterns for which the frequency of occurrence is representative for a sequence comprising a STAR sequence. Preferably, the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least two sequences comprising a STAR sequence; more preferably, in at least five sequences comprising a STAR sequence; and, even more preferably, in at least ten sequences comprising a STAR sequence. More preferably, the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least 20 sequences comprising a STAR sequence. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least 50 sequences comprising a STAR.
[0033]The patterns that are indicative for a sequence comprising a STAR sequence are also dependent on the type of control nucleic acid used. The type of control sequence used is preferably selected on the basis of the sequence in which the presence of a STAR sequence is to be detected. In a preferred embodiment, the control sequence comprises a random sequence comprising a similar AT/CG content as at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence. In another preferred embodiment, the control sequence is derived from the same species as the sequence comprising the STAR sequence. For instance, if a test sequence is scrutinized for the presence of a STAR sequence, active in a plant cell, then preferably the control sequence is also derived from a plant cell. Similarly, for testing for STAR activity in a human cell, the control nucleic acid is preferably also derived from a human genome. In a preferred embodiment, the control sequence comprises between 50% and 150% of the bases of at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the control sequence comprises between 90% and 110% of the bases of at least one sequence comprising a STAR sequence. More preferably, between 95% and 105%.
[0034]A pattern can comprise any number of bases larger than two. Preferably, at least one sequence pattern comprises at least five, more preferably at least six, bases. In another embodiment, at least one sequence pattern comprises at least eight bases. In a preferred embodiment, the at least one sequence pattern comprises a pattern listed in Table 6 and/or Table 7. A pattern may consist of a consecutive list of bases. However, the pattern may also comprise bases that are interrupted one or more times by a number of bases that are not or only partly discriminative. A partly discriminative base is, for instance, indicated as a purine.
[0035]Preferably, the presence of STAR activity is verified using a functional assay. Several methods are presented herein to determine whether a sequence comprises STAR activity. STAR activity is confirmed if the sequence is capable of performing at least one of the following functions: (i) at least in part inhibiting the effect of sequence comprising a gene transcription repressing element of the invention, (ii) at least in part blocking chromatin-associated repression, (iii) at least in part blocking activity of an enhancer, (iv) conferring upon an operably linked nucleic acid encoding a transcription unit compared to the same nucleic acid alone, (iv-a) a higher predictability of transcription, (iv-b) a higher transcription, and/or (iv-c) a higher stability of transcription over time.
[0036]The large number of sequences comprising STAR activity identified by the present inventors open up a wide variety of possibilities to generate and identify sequences comprising the same activity in kind not necessarily in amount. For instance, it is well within the reach of a skilled person to alter the sequences identified in the invention and test the altered sequence for STAR activity. Such altered sequences are, therefore, also part of the invention. Alteration can include deletion, insertion and mutation of one or more bases in the sequences.
[0037]Sequences comprising STAR activity were identified in stretches of 400 bases. However, it is expected that not all of these 400 bases are required to retain STAR activity. Methods to delimit the sequences that confer a certain property to a fragment of between 400 and 5000 bases are well known. The minimal sequence length of a fragment comprising STAR activity is estimated to be about 50 bases.
[0038]Table 6 (SEQ ID NOS:177-342) and Table 7 (SEQ ID NOS:343-1072) list patterns of six bases that have been found to be over represented in nucleic acid molecules comprising STAR activity. This over representation is considered to be representative for a STAR sequence. The tables were generated for a family of 65 STAR sequences (SEQ ID NOS:1-65). Similar tables can be generated starting from a different set of STAR sequences, or from a smaller or larger set of STAR sequences. A pattern is representative for a STAR sequence if it is over represented in the STAR sequence compared to a sequence not comprising a STAR element. This can be a random sequence. However, to exclude a non relevant bias, the sequence comprising a STAR sequence is preferably compared to a genome or a significant part thereof. Preferably, a genome of a vertebrate or plant, more preferably, a human genome. A significant part of a genome is, for instance, a chromosome. Preferably the sequence comprising a STAR sequence and the control sequence are derived from nucleic acid of the same species.
[0039]The more STAR sequences are used for the determination of the frequency of occurrence of sequence patterns, the more representative for STARs the patterns are that are over- or under-represented. Considering that many of the functional features that can be expressed by nucleic acids are mediated by proteinaceous molecules binding to them, it is preferred that the representative pattern is over-represented in the STAR sequences. Such over-represented pattern can be part of a binding site for such a proteinaceous molecule. Preferably, the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least two sequences comprising a STAR sequence; more preferably, in at least five sequences comprising a STAR sequence; and, even more preferably, in at least ten sequences comprising a STAR sequence. More preferably, the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least 20 sequences comprising a STAR sequence. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the frequency of occurrence is representative of the frequency of occurrence of at least one sequence pattern in at least 50 sequences comprising a STAR. Preferably, the sequences comprising a STAR sequence comprises at least one of the sequences depicted in the sequences comprising STAR1-STAR65 (SEQ ID NOS:1-65), sequences comprising STAR66 and testing set (SEQ ID NOS:66-84), and sequences comprising Arabidopsis STAR A1-A35 (SEQ ID NOS:85-119) (hereinafter SEQ ID NOS:1-119).
[0040]STAR activity is a feature shared by the sequences listed in SEQ ID NOS:1-119. However, this does not mean that they must all share the same identifier sequence. It is very well possible that different identifiers exist. Identifiers may confer this common feature onto a fragment containing it, though this is not necessarily so.
[0041]By using more sequences comprising STAR activity for determining the frequency of occurrence of a sequence pattern or patterns, it is possible to select patterns that are more often than others present or absent in such a STAR sequence. In this way it is possible to find patterns that are very frequently over- or under-represented in STAR sequences. Frequently, over- or under-represented patterns are more likely to identify candidate STAR sequences in test sets. Another way of using a set of over- or under-represented patterns is to determine which pattern or combination of patterns is best suited to identify a STAR in a sequence. Using so-called discriminative statistics, we have identified a set of patterns that performs best in identifying a sequence comprising a STAR element. In a preferred embodiment, at least one of the sequence patterns for detecting a STAR sequence comprises a sequence pattern GGACCC (SEQ ID NO:464), CCCTGC (SEQ ID NO:816), AAGCCC (SEQ ID NO:270), CCCCCA (SEQ ID NO:298) and/or AGCACC (SEQ ID NO:336). In another embodiment, at least one of the sequence patterns for detecting a STAR sequence comprises a sequence pattern CCCN{16}AGC (SEQ ID NO:415), GGCN{9}GAC (SEQ ID NO:536), CACN{13}AGG (SEQ ID NO:761), and/or CTGN{4}GCC (SEQ ID NO:839).
[0042]A list of STAR sequences can also be used to determine one or more consensus sequences therein. The invention, therefore, also provides a consensus sequence for a STAR element. This consensus sequence can of course be used to identify candidate STAR elements in a test sequence.
[0043]Moreover, once a sequence comprising a STAR element has been identified in a vertebrate it can be used by means of sequence homology to identify sequences comprising a STAR element in other species belonging to vertebrate. Preferably a mammalian STAR sequence is used to screen for STAR sequences in other mammalian species. Similarly, once a STAR sequence has been identified in a plant species, it can be used to screen for homologous sequences with similar function in other plant species. The invention in one aspect provides a STAR sequence obtainable by a method according to the invention. Further provided is a collection of STAR sequences. Preferably, the STAR sequence is a vertebrate or plant STAR sequence. More preferably, the STAR sequence is a mammalian STAR sequence or an angiosperm (monocot, such as rice or dicot, such as Arabidopsis). More preferably, the STAR sequence is a primate and/or human STAR sequence.
[0044]A list of sequences comprising STAR activity can be used to determine whether a test sequence comprises a STAR element. There are, as mentioned above, many different methods for using such a list for this purpose. In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a method for determining whether a nucleic acid sequence of about 50-5000 base pairs comprises a STAR sequence, the method comprising: generating a first table of sequence patterns comprising the frequency of occurrence of the patterns in a collection of STAR sequences of the invention; generating a second table of the patterns comprising the frequency of occurrence of the patterns in at least one reference sequence; selecting at least one pattern of which the frequency of occurrence differs between the two tables; determining, within the nucleic acid sequence of about 50-5000 base pairs, the frequency of occurrence of at least one of the selected patterns; and determining whether the occurrence in the test nucleic acid is representative of the occurrence of the selected pattern in the collection of STAR sequences. Alternatively, determining comprises determining whether the frequency of occurrence in the test nucleic acid is representative of the frequency occurrence of the selected pattern in the collection of STAR sequences. Preferably, the method further comprises determining whether the candidate STAR comprises a gene transcription modulating quality using a method of the invention. Preferably, the collection of STARS comprises sequence as depicted in SEQ ID NOS:1-119. In another aspect, the invention provides an isolated and/or recombinant nucleic acid sequence comprising a STAR sequence obtainable by a method of the invention.
[0045]As mentioned above, a STAR sequence can exert its activity in a directional way, i.e., more to one side of the fragment containing it than to the other. Moreover, STAR activity can be amplified in amount by multiplying the number of STAR elements. The latter suggests that a STAR element may comprise one or more elements comprising STAR activity. Another way of identifying a sequence capable of conferring STAR activity on a fragment containing it comprises selecting from a vertebrate or plant sequence, a sequence comprising STAR activity and identifying whether the selected sequence and sequences flanking the selected sequence are conserved in another species. Such conserved flanking sequences are likely to be functional sequences. In one aspect, the invention, therefore, provides a method for identifying a sequence comprising a STAR element comprising selecting a sequence of about 50 to 5000 base pairs from a vertebrate or plant species comprising a STAR element and identifying whether sequences flanking the selected sequence in the species are conserved in at least one other species. The invention, therefore, further provides a method for detecting the presence of a STAR sequence within a nucleic acid sequence of about 50-5000 base pairs, comprising identifying a sequence comprising a STAR sequence in a part of a chromosome of a cell of a species and detecting significant homology between the sequence and a sequence of a chromosome of a different species. Preferably, the species comprises a plant or vertebrate species, ideally a mammalian species. The invention also provides a method for detecting the presence of a STAR element within a nucleic acid sequence of about 50-5000 base pairs of a vertebrate or plant species, comprising identifying whether a flanking sequence of the nucleic acid sequence is conserved in at least one other species.
[0046]It is important to note that methods of the invention for detecting the presence of a sequence comprising a STAR sequence using bioinformatical information are iterative in nature. The more sequences comprising a STAR sequence are identified with a method of the invention, the more patterns are found to be discriminative between a sequence comprising a STAR sequence and a control sequence. Using these newly found discriminative patterns, more sequences comprising a STAR sequence can be identified, which, in turn, enlarges the set of patterns that can discriminate and so on. This iterative aspect is an important aspect of methods provided in the invention.
BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE DRAWINGS
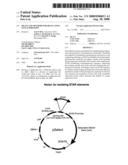
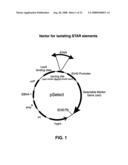
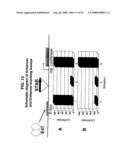
[0047]FIG. 1 is a diagram illustrating the pSelect plasmid used for isolating STAR elements. The zeocin resistance gene is under control of the SV40 promoter, and is upstream of the SV40 polyadenylation site. Upstream of the SV40 promoter is a tandem array of lexA operator sites. Between the lexA operators and the SV40 promoter is a cloning site; test DNAs (e.g., size-fractionated genomic DNA) are cloned into the BamHI site. The plasmid also has the hygromycin resistance gene (hygro) for selection of transformed cells, the EBNA-1 and oriP sequences for plasmid replication in mammalian cells, and the ampicillin resistance gene (ampR) and ori sequence for propagation in Escherichia coli.
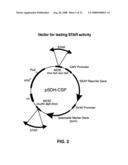
[0048]FIG. 2 is a diagram depicting the pSDH-CSP plasmid used for testing STAR activity. The Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase (SEAP) reporter gene is under control of the CMV promoter, and the puromycin resistance selectable marker (puro) is under control of the SV40 promoter. Flanking these two genes are multiple cloning sites (MCSI and MCSII) into which STAR elements can be cloned. The plasmid also has an origin of replication (ori) and ampicillin resistance gene (ampR) for propagation in Escherichia coli.
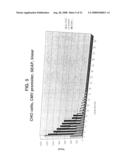
[0049]FIG. 3 is a graph showing that STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) and STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) improve predictability and yield of transgene expression in U-2 OS cells. Expression of luciferase from the CMV promoter by U-2 OS cells transfected with pSDH-CMV, pSDH-CMV-STAR6, or pSDH-CMV-STAR8 was determined. The STAR-containing constructs confer greater predictability and elevated yield relative to the pSDH-CMV construct alone.
[0050]FIG. 4 is a graph illustrating that STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6), but not STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8), improves predictability and yield of transgene expression in CHO cells. Expression of SEAP from the CMV promoter by CHO cells transfected with pSDH-CSP, pSDH-CSP-STAR6, or pSDH-CSP-STAR8 was determined. The STAR6-containing constructs confer greater predictability and elevated yield relative to the pSDH-CSP construct alone, identifying STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) as a promiscuous STAR element. In contrast, the STAR8-containing constructs do not consistently increase yield or predictability relative to the pSDH-CSP construct, suggesting that STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) is a cell line-specific STAR element.
[0051]FIG. 5 is a graph depicting that STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) and STAR49 (SEQ ID NO:49) improve predictability and yield of transgene expression. Expression of SEAP from the CMV promoter by CHO cells transfected with pSDH-CSP, pSDH-CSP-STAR6, or pSDH-CSP-STAR49 was determined. The STAR-containing constructs confer greater predictability and elevated yield relative to the pSDH-CSP construct alone.
[0052]FIG. 6 is a graph showing the minimal essential sequences of STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10) and STAR27 (SEQ ID NO:27). Portions of the STAR elements were amplified by PCR: STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10) was amplified with primers E23 (SEQ ID NO:166) and E12 (SEQ ID NO:155) to yield fragment 10A (corresponding approximately to the first 400 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:10), E13 (SEQ ID NO:156) and E14 (SEQ ID NO:157) to yield fragment 10B (corresponding approximately to the second 400 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:10), and E15 (SEQ ID NO:158) and E16 (SEQ ID NO:159) to yield fragment 10C (corresponding approximately to the third 400 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:10). STAR27 (SEQ ID NO:27) was amplified with primers E17 (SEQ ID NO:160) and E18 (SEQ ID NO:161) to yield fragment 27A (corresponding approximately to the first 500 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:27), E19 (SEQ ID NO:162) and E20 (SEQ ID NO:163) to yield fragment 27B (corresponding to the second 500 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:27), and E21 (SEQ ID NO:164) and E22 (SEQ ID NO:165) to yield fragment 27C (corresponding approximately to the third 500 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:27). These sub-fragments were cloned into the pSelect vector. After transfection into U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cells, the growth of the cultures in the presence of zeocin was monitored. Growth rates varied from vigorous (+++) to poor (+/-), while some cultures failed to survive zeocin treatment (-) due to absence of STAR activity in the DNA fragment tested.
[0053]FIG. 7 is a graph illustrating the STAR element function in the context of the SV40 promoter. pSDH-SV40 and pSDH-SV40-STAR6 were transfected into the human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cell line, and expression of luciferase was assayed with or without protection from gene silencing by STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) in puromycin-resistant clones.
[0054]FIG. 8 is a graph showing the STAR element function in the context of the Tet-Off promoter. pSDH-Tet and pSDH-Tet-STAR6 were transfected into the human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cell line, and expression of luciferase was assayed with or without protection from gene silencing by STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) in puromycin-resistant clones.
[0055]FIG. 9 is a schematic diagram of the orientation of STAR elements as they are cloned in the pSelect vector (panel A), as they are cloned into pSDH vectors to preserve their native orientation (panel B), and as they are cloned into pSDH vector in the opposite orientation (panel C).
[0056]FIG. 10 is a graph showing directionality of STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) function. The STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) element was cloned into pSDH-Tet in either the native (STAR66 native) or the opposite orientation (STAR66 opposite) and transfected into U-2 OS cells. Luciferase activity was assayed in puromycin resistant clones.
[0057]FIG. 11 is a southern blot showing copy number-dependence of STAR function. Southern blot of luciferase expression units in pSDH-Tet-STAR10, integrated into U-2 OS genomic DNA. Radioactive luciferase DNA probe was used to detect the amount of transgene DNA in the genome of each clone, which was then quantified with a phosphorimager.
[0058]FIG. 12 is a graph illustrating copy number-dependence of STAR function. The copy number of pSDH-Tet-STAR10 expression units in each clone was determined by phosphorimagery and compared with the activity of the luciferase reporter enzyme expressed by each clone.
[0059]FIG. 13 is a schematic diagram and graphs depicting enhancer-blocking and enhancer assays. The luciferase expression vectors used for testing STARs for enhancer-blocking and enhancer activity are shown schematically. The E-box binding site for the E47 enhancer protein is upstream of a cloning site for STAR elements. Downstream of the STAR cloning site is the luciferase gene under control of a human alkaline phosphatase minimal promoter (mp). The histograms indicate the expected outcomes for the three possible experimental situations (see text). Panel A: Enhancer-blocking assay. Panel B: Enhancer assay.
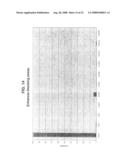
[0060]FIG. 14 is a graph showing enhancer-blocking assay. Luciferase expression from a minimal promoter is activated by the E47/E-box enhancer in the empty vector (vector). Insertion of enhancer-blockers (scs, HS4) or STAR elements (STAR elements 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18, and 27; SEQ ID NOS:1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18 and 27, respectively) block luciferase activation by the E47/E-box enhancer.
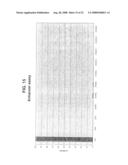
[0061]FIG. 15 is a graph illustrating enhancer assay. Luciferase expression from a minimal promoter is activated by the E47/E-box enhancer in the empty vector (E47). Insertion of the scs and HS4 elements or various STAR elements (STARs 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18, and 27; SEQ ID NOS:1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18 and 27, respectively) do not activate transcription of the reporter gene.
[0062]FIG. 16 illustrates STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) sequence conservation between mouse and human. The region of the human genome containing 497 base pair STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) is shown (black boxes); the element occurs between the HOXD8 and HOXD4 homeobox genes on human chromosome 2. It is aligned with a region in mouse chromosome 2 that shares 72% sequence identity. The region of human chromosome 2 immediately to the left of STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) is also highly conserved with mouse chromosome 2 (73% identity; gray boxes); beyond these region, the identity drops below 60%. The ability of these regions from human and mouse, either separately or in combination, to confer growth on zeocin is indicated: -, no growth; +, moderate growth; ++, vigorous growth; +++, rapid growth.
[0063]FIG. 17 is a schematic diagram of bio-informatic analysis workflow. For details, see text.
[0064]FIG. 18 is a schematic diagram showing the results of discriminant analysis on classification of the training set of 65 STAR elements. STAR elements that are correctly classified as STARs by Stepwise Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA) are shown in a Venn diagram. The variables for LDA were selected from frequency analysis results for hexameric oligonucleotides ("oligos") and for dyads. The diagram indicates the concordance of the two sets of variables in correctly classifying STARs.
[0065]FIG. 19 is a graph illustrating that U-2 OS/Tet-Off/lexA-HP1 cells were transfected with candidate Arabidopsis STAR elements and cultivated at low doxycycline concentrations. Total RNA was isolated and subjected to RT-PCR; the bands corresponding to the zeocin and hygromycin resistance mRNAs were detected by Southern blotting and quantified with a phosphorimager. The ratio of the zeocin to hygromycin signals is shown for transfectants containing zeocin expression units flanked by 12 different Arabidopsis STAR elements, the Drosophila scs element, or no flanking element.
[0066]FIG. 20 is a schematic diagram and graph illustrating that STAR elements improve GFP expression in CHO cells. The ppGIZ and ppGIZ-STAR7 plasmids used for testing STAR activity are shown. The expression unit comprises (from 5' to 3') a transgene (encoding for the GFP protein), an IRES, and a selectable marker (zeo, conferring zeocin resistance) under control of the CMV promoter. The expression unit has the SV40 transcriptional terminator at its 3' end (t). The entire cassette with the expression unit is either flanked by STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) elements (STAR7-shielded) or not (Control). The constructs are transfected to CHO-K1 cells. Stable colonies are expanded and the GFP signal is determined on a XL-MCL Beckman Coulter flow cytometer. For each independent colony the mean of the GFP signal is plotted. This is taken as measure for the level of GFP expression. The results in FIG. 20 show that in CHO cells the STAR7-shielded construct confers greater predictability and elevated GFP expression relative to the ppGIZ control construct alone.
[0067]FIG. 21 is a schematic diagram and graph showing that STAR elements improve GFP expression in NSO cells. The ppGIZ and ppGIZ-STAR7 plasmids used for testing STAR activity are shown as in FIG. 20. The constructs are transfected to NSO cells. Stable colonies are expanded and the GFP signal is determined on a XL-MCL Beckman Coulter flow cytometer. For each independent colony the mean of the GFP signal is plotted. This is taken as measure for the level of GFP expression. The results in FIG. 21 show that in NSO cells the STAR7-shielded (SEQ ID NO:7) construct confers greater predictability and elevated GFP expression relative to the ppGIZ control construct alone.
[0068]FIG. 22 is a schematic diagram and graph depicting that STAR elements improve GFP expression in 293 cells. The ppGIZ and ppGIZ-STAR7 plasmids used for testing STAR activity are shown as in FIG. 20. The constructs are transfected to 293 cells. Stable colonies are expanded and the GFP signal is determined on a XL-MCL Beckman Coulter flow cytometer. For each independent colony, the mean of the GFP signal is plotted. This is taken as measure for the level of GFP expression. The results in FIG. 22 show that in 293 cells the STAR7-shielded (SEQ ID NO:7) construct confers greater predictability and elevated GFP expression relative to the ppGIZ control construct alone.
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF THE INVENTION
Definitions
Quality
[0069]The term "quality" in relation to a sequence refers to an activity of the sequence.
STAR and STAR Sequence
[0070]The terms "STAR," "STAR sequence" or "STAR element," as used herein, refer to a DNA sequence comprising one or more of the mentioned gene transcription modulating qualities.
DNA Sequence
[0071]The term "DNA sequence" as used herein, unless otherwise specified, does not refer to a listing of specific ordering of bases, but rather to a physical piece of DNA. A transcription quality with reference to a DNA sequence refers to an effect that the DNA sequence has on transcription of a gene of interest. "Quality" as used herein refers to detectable properties or attributes of a nucleic acid or protein in a transcription system.
Proteinaceous Molecule
[0072]By a "proteinaceous molecule" is meant herein a molecule comprising amino acids. At least a part of the amino acids are bound to each other to form a peptide. Preferably, the proteinaceous molecule comprises a polypeptide. In this application, the term "proteinaceous molecule" also includes "polypeptide."
Essentially the Same Properties
[0073]By "essentially the same properties" is meant that the properties are essentially the same in kind, not necessarily in amount. For instance, if a proteinaceous molecule has essentially the same properties as a pharmaceutically active compound, the proteinaceous molecule also displays such pharmaceutical activity in kind, not necessarily in amount.
Naturally Occurring Proteinaceous Molecule of the Same Kind
[0074]By a "naturally occurring proteinaceous molecule of the same kind" is meant a proteinaceous molecule with the same primary structure, which is naturally produced in vivo, not influenced by human interference. Examples comprise an antibody produced in vivo by a lymphocyte and erythropoietin produced in vivo by a hepatocyte.
Host Cell, Host Cell Line
[0075]As used herein, the terms "host cell" and "host cell line" refer to a cell and to homogeneous populations thereof that are capable of expressing a nucleic acid encoding a proteinaceous molecule.
Recombinant Host Cell, Recombinant Host Cell Line
[0076]The terms "recombinant host cell" and "recombinant host cell line" refer to a host cell and to homogeneous populations thereof into which a nucleic acid has been introduced.
Expression
[0077]As used herein, the term "expression" refers to production of a proteinaceous molecule, encoded by a nucleic acid. The production, for instance, involves transcription of a DNA sequence, translation of the corresponding mRNA sequence, and/or posttranslational modification. In case of secreted proteins, it can also refer to the processes of transcription, translation, and/or post-translational modification (e.g., glycosylation, disulfide bond formation, etc.), followed by exocytosis. In the case of multimeric proteins, it can include assembly of the multimeric structure from the polypeptide monomers.
Silencing
[0078]The term "silencing" refers to diminution of a level of expression of a gene or genes, including transgenes, typically over time. The expression level can be diminished but still detectable, or diminished below the threshold of detection.
Enhanced Expression
[0079]As used herein, "enhanced expression" of a gene encoding a proteinaceous molecule, or enhanced production of a proteinaceous molecule, can either involve a higher yield of the proteinaceous molecule, a higher proportion of host cells with acceptable expression levels, and/or a higher stability of a gene expression level.
Affiliated Proteinaceous Molecule of a Cell
[0080]By an "affiliated proteinaceous molecule of a cell" is meant a proteinaceous molecule which is naturally produced by the kind of cell in the organism from which the cell is derived.
[0081]For instance, erythropoietin is an affiliated proteinaceous molecule of a hepatocyte, or of a hepatocyte-derived cell line. Likewise, an antibody is an affiliated proteinaceous molecule of a lymphocyte, or of a lymphocyte-derived cell line, typically of a B-cell or a B-cell derived cell line.
Specific Host Cell Line
[0082]A "specific host cell line" is a host cell line derived from a cell which normally expresses a particular proteinaceous molecule (or class of proteinaceous molecules) in the organism from which the cell is derived.
Heterologous STAR Sequence
[0083]The term "heterologous STAR sequence" is herein used to define a STAR sequence that is, for example, obtained from a different cell type (from the same species or organism) or is obtained from a different species or organism (either from the same cell type or a different cell type) compared to the cell in which it is used.
Stable
[0084]Stable" means that the observed transcription level is not significantly changed over at least 30 cell divisions. A stable quality is useful in situations wherein expression characteristics should be predictable over many cell divisions. Typical examples are cell lines transfected with foreign genes. Other examples are transgenic animals and plants and gene therapies. Very often, introduced expression cassettes function differently after increasing numbers of cell divisions or plant or animal generations. A stable quality preferably comprises a capacity to maintain gene transcription in subsequent generations of a transgenic plant or animal. Of course, in the case where expression is inducible, the quality comprises the quality to maintain inducibility of expression in subsequent generations of a transgenic plant or animal.
Acceptable Expression Level
[0085]An "acceptable expression level" means an acceptable expression level for commercial exploitation. Whether or not a certain expression level is acceptable for commercial exploitation often depends on the kind of proteinaceous molecule that is produced. Acceptable expression levels of different kinds of proteinaceous molecules often involve different amounts of produced proteinaceous molecule.
[0086]A STAR sequence, a collection of STAR sequences, and/or a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence obtainable by a method of the invention, is of course suitable for use in a method of the invention for producing a proteinaceous molecule in a cell. In one aspect, the invention, therefore, provides a method for producing a proteinaceous molecule in a cell comprising selecting a cell for its suitability for producing the proteinaceous molecule, providing a nucleic acid encoding the proteinaceous molecule with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence, expressing the resulting nucleic acid in the cell and collecting the proteinaceous molecule, wherein the nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence is obtainable by a method of the invention for identifying and obtaining a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence. The nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence can be identified and obtained using at least one pattern that is representative for sequences comprising STAR activity. Preferably, the nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence is identified and obtained using at least one pattern as depicted in Table 6 (SEQ ID NOS:177-342) or Table 7 (SEQ ID NOS:343-1072).
[0087]A cell can be selected for its suitability for producing a proteinaceous molecule in many different ways. For instance, it can be determined whether the cell is competent of nucleic acid uptake. A nucleic acid encoding a proteinaceous molecule is preferably easily introduced into the cell. Furthermore it can be determined whether the cell secretes produced proteinaceous molecule. Secreted proteinaceous molecule can usually be easily collected. Collecting proteinaceous molecules that are not secreted usually involves sacrificing at least part of a culture. This implicates separating a proteinaceous molecule of interest from other cell components, optionally starting up a new culture, etc. This is more cumbersome. Hence, in a preferred embodiment, a method of the invention is provided wherein the proteinaceous molecule is secreted by the cell.
[0088]In another preferred embodiment, a method of the invention is provided wherein the cell is selected for its capability of post-translationally modifying the proteinaceous molecule, such that the proteinaceous molecule has essentially the same properties as a naturally occurring proteinaceous molecule of the same kind. As has been explained above, different kinds of cells display different post-translational modifications. As a result, the same proteinaceous molecule can be modified differently when produced in different host cells. These differences can affect the properties of such proteinaceous molecules, such as for instance pharmaceutical properties. It is, therefore, highly preferred to select a cell which produces a proteinaceous molecule with essentially the same properties as its naturally occurring counterpart. This does not necessarily mean that the host cell has to display exactly the same kind of post-translational modifications, as long as the produced proteinaceous molecule has essentially the same properties. A proteinaceous molecule can be produced that is physically different from its natural counterpart, but which is functionally essentially the same.
[0089]In one embodiment, of the invention, however, a cell is selected for its capability of post-translationally modifying the proteinaceous molecule in essentially the same way as the proteinaceous molecule is post-translationally modified in nature.
[0090]In one aspect, the invention provides a method of the invention wherein the proteinaceous molecule comprises an affiliated proteinaceous molecule of the cell.
[0091]It is especially preferred to choose a host cell, or a cell line derived from a cell, which normally produces a proteinaceous molecule of interest in the organism from which the cell is derived. These cells are capable of carrying out post-translational modifications of their affiliated proteinaceous molecules such that the resulting proteinaceous molecule has the same kind of properties in kind, not necessarily in amount, as a proteinaceous molecule of the same kind which is normally present in the organism. Such specific cells are naturally adapted for production of the affiliated proteinaceous molecule. Apart from other activities of STAR sequences it is also possible to at least partly solve a problem of low production of proteinaceous molecules, which often occurs with such specific cells. Providing at least one STAR sequence to a nucleic acid encoding such proteinaceous molecule will enhance production (yield) of the proteinaceous molecule by the specific cell, increase the proportion of host cells with acceptable expression levels, and/or increase stability of a gene expression level.
[0092]In another preferred embodiment, a method of the invention is disclosed wherein the cell is selected for suitable growth in a suspension culture. This facilitates culturing of the cell, and collection of produced proteinaceous molecule, especially when the proteinaceous molecule is secreted into the suspension. More preferably, the cell is selected for suitable growth in a serum-free culture, since serum can contain contaminants and pathogens. Such contaminants/pathogens often have to be separated from produced proteinaceous molecule. This requires an extra step, which consumes time and chemicals, with a potential loss of produced proteinaceous molecule. Moreover, a possibility of a presence of pathogens involves a potential risk for employees. If a pathogen has been present in a culture, a produced proteinaceous molecule is not allowed to be used anymore for commercial and/or medical applications.
[0093]In yet another preferred embodiment, the cell is selected for the presence of an adenovirus Early Region 1 (E1) sequence. The presence of an adenoviral E1 sequence enhances protein production in a cell. Hence, an adenoviral E1 sequence is suitable for host cells engineered for protein production.
[0094]The invention also provides a method for producing a proteinaceous molecule comprising: [0095]providing a host cell with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence; [0096]selecting a cell with enhanced expression of a proteinaceous molecule; and [0097]collecting the proteinaceous molecule.
[0098]In one embodiment, the method is performed with a host cell whose genome has not been modified by human interference. The method then results in enhanced expression of a proteinaceous molecule which is encoded by the genome of the host cell. The proteinaceous molecule may be normally expressed by the host cell in the organism from which the cell is derived, but it may also normally be subject to silencing, resulting in little or no expression in the host cell under normal conditions. Introduction of at least one STAR sequence can at least in part inhibit silencing of a gene of interest induced by gene-transcription repressing chromatin. Expression of a proteinaceous molecule is enhanced by introduction of a STAR sequence.
[0099]In another embodiment, the host cell is transfected with a nucleic acid of interest. Such nucleic acid for instance, encodes a heterologous proteinaceous molecule which is not naturally encoded by the genome of the host cell. Introduction of a STAR sequence also enhances expression of such heterologous proteinaceous molecule.
[0100]The STAR sequence can be introduced randomly into the genome of the host cell, using methods known in the art (for instance calcium precipitation, transfection with a vector comprising a nucleic acid of interest, use of a gene delivery vehicle, etc). If a STAR sequence is introduced near a nucleic acid sequence encoding a proteinaceous molecule, it is capable of enhancing expression of the proteinaceous molecule. Cells expressing a desired proteinaceous molecule can be isolated from cultures with randomly inserted STAR sequences.
[0101]Preferably, the STAR sequence is introduced into the host cell by homologous recombination. A nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence can be provided with an additional sequence. The additional sequence can be chosen such that it is at least in part homologous to a nucleic acid sequence in the host cell which is known to be present in vicinity of a gene encoding a proteinaceous molecule of interest. If a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence and such additional sequence is provided to the host cell, it can be incorporated into the host cell's genome by homologous recombination at the site with the (partly) homologous nucleic acid sequence. As a result, the STAR sequence is introduced in vicinity of the gene encoding the proteinaceous molecule of interest. Expression of the proteinaceous molecule is then enhanced by the introduced STAR sequence.
[0102]A preferred embodiment of the invention provides a method of the invention wherein the STAR sequence comprises a species-specific STAR sequence. More preferably, the STAR sequence comprises a cell type-specific STAR sequence.
[0103]Two types of STAR elements have been identified. Promiscuous STAR elements are able to function in more than one host cell line. For example, STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) increases the predictability, yield, and stability of a transgene in both the U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cell line and in CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cells. Other STAR elements are species-specific and/or cell type-specific; for example, STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) increases the predictability, yield, and stability of transgenes in U-2 OS cells, but not in CHO cells (see Examples 2 and 3 and FIGS. 3 and 4).
[0104]If a certain type of host cell (line) is chosen for expression of a proteinaceous molecule (for instance, because it is known to possess a preferred post-translational modification system) a STAR sequence which is naturally present in the cell can be used in a method of the invention. Such STAR sequence is referred to as a cell type-specific STAR sequence. A STAR sequence which is naturally present in a species from which the cell is derived can also be used. Such STAR sequence is referred to as a species-specific STAR sequence. A species-specific STAR sequence may be naturally present in the cell type, although this is not necessary.
[0105]A known species-specific STAR sequence or cell-type specific STAR sequence can be used in a method of the invention. Alternatively, a (previously unknown) species-specific STAR sequence or cell-type specific STAR sequence can be detected and isolated by a method as described by the present inventors (EP 01202581.3). The use of a species-specific STAR sequence or cell type-specific STAR sequence is preferred because such sequence is especially active in the host cell and is adapted to the specific circumstances within the cell. For instance, such cell type-specific STAR sequence may interact with a protein which is not present in some other cell-types. In that case, the cell type-specific STAR sequence will be less capable--if at all--of enhancing expression in cells lacking the protein. A species-specific or cell type-specific STAR element often has functional characteristics that are superior to promiscuous STAR elements. Furthermore, a cell line-specific STAR element can satisfy product safety or ethical considerations for use of the host cell line.
[0106]A promiscuous STAR sequence is particularly useful if no tissue specific or cell-type specific STAR sequence is known. In that case a known promiscuous STAR sequence can be used. This saves efforts to detect and isolate a cell-type specific STAR sequence.
[0107]Several STAR sequences are listed in SEQ ID NOS:1-119. Hence, in one aspect, a method of the invention is provided wherein the STAR sequence comprises a sequence as depicted in SEQ ID NOS:1-119.
[0108]In a preferred embodiment, the invention provides a cell line that comprises at least one heterologous STAR sequence or a functional equivalent and/or a functional fragment thereof. In an even more preferred embodiment, the cell line is a human cell line. The invention provides multiple examples of STAR sequences and also methods of testing STAR sequences and hence, a person skilled in the art is very well capable of obtaining a functional equivalent and/or a functional fragment of a STAR sequence, for example by deletion or mutation. In yet another preferred embodiment, the invention provides a non-human cell line that comprises at least one recombinant STAR sequence derived or obtained from a human cell, i.e., a human STAR sequence. The amount of STAR sequences may vary, e.g., a cell line according to the invention may comprise two, three, or four, or even more STAR sequences which may either be identical or different from each other.
[0109]In one aspect, the invention provides a cell line provided with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence, wherein the cell line is selected for its suitability for producing a proteinaceous molecule. Preferably, a cell line of the invention comprises a vertebrate or plant cell line. A vertebrate cell line is very suitable for producing a human proteinaceous molecule of interest, because vertebrates are phylogenetically close related.
[0110]Plant cells are for instance very suitable for vaccine production. Vaccine production in plants can be inexpensive, while the vaccine can be easily delivered to an individual by eating the edible portion of the plant (Mercenier et al., 2001).
[0111]A cell line of the invention is particularly suitable for production of a proteinaceous molecule of interest, because the STAR sequence can enhance expression of a gene of interest (higher yield of a proteinaceous molecule, higher proportion of host cells with acceptable expression levels, and/or higher stability of a gene expression level). Methods for generating a cell line are known in the art and many techniques are known to provide a cell with a nucleic acid of interest. Furthermore, many general purpose cell lines are available. Such cell lines can be dedicated to production of a certain proteinaceous molecule using recombinant techniques. Examples of available cell lines include CHO cells from Chinese hamster ovary and BHK cells from baby hamster kidney (as described above).
[0112]Another embodiment of the invention provides a cell line provided with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence, wherein the cell line comprises an adenovirus Early Region 1 sequence. As has been described above, an adenoviral E1 sequence enhances cellular protein production. More preferably a cell line of the invention is provided wherein the cell line comprises a U-2 OS osteosarcoma, CHO, 293, HuNS-1 myeloma, WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma, BHK, Vero, non-secreting mouse myeloma Sp2/0-Ag 14, non-secreting mouse myeloma NSO, or NCI-H295R adrenal gland carcinoma (ATCC CRL-2128) cell line.
[0113]A cell line of the invention is particularly suitable for production of a proteinaceous molecule, because production can be enhanced by one or more STAR sequences (higher yield of a proteinaceous molecule, higher proportion of host cells with acceptable expression levels, and/or higher stability of a gene expression level). A cell line of the invention can comprise promiscuous, species-specific and/or cell type-specific STAR sequences. Furthermore, a cell line of the invention can be used to produce a heterologous proteinaceous molecule, and/or an affiliated proteinaceous molecule.
[0114]Hence, a use of a cell line of the invention for the production of a proteinaceous molecule is also herewith provided. Preferably, the proteinaceous molecule comprises an affiliated protein of the cell line.
[0115]Of course, a proteinaceous molecule obtainable by a method of the invention is also provided by the invention.
[0116]In one aspect, the invention provides a method for selecting a cell suitable for producing a proteinaceous molecule comprising: [0117]providing a nucleic acid encoding the proteinaceous molecule with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence; [0118]expressing the resulting nucleic acid in the cell; and [0119]determining whether produced proteinaceous molecule has a desired property.
[0120]The desired property, for instance, comprises a pharmaceutical property. The property can be influenced by post translational modification(s), a configuration of a produced proteinaceous molecule, etc.
[0121]In yet another aspect, the invention provides a method for selecting a cell suitable for producing a proteinaceous molecule comprising: [0122]providing a host cell with a nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence; [0123]selecting a cell with enhanced expression of a proteinaceous molecule; and [0124]determining whether the proteinaceous molecule has a desired property.
[0125]As has been discussed above, the nucleic acid comprising a STAR sequence can be randomly introduced into the genome of the host cell. Preferably, however, the nucleic acid sequence is introduced into the genome of the host cell by homologous recombination.
[0126]The invention is further explained in the following examples. The examples do not limit the invention in any way. They merely serve to clarify the invention.
EXAMPLES
Example 1
Method for Isolation of STAR Elements from the Human Genome
[0127]STAR elements are identified and cloned from human genomic DNA based on their ability to block the spread of transcriptional repression from DNA binding sites for repressor proteins in a test vector, as described in this example. The method described in this example is applicable in principle to any mammalian cell line, for isolation of both promiscuous and cell line-specific STAR elements.
A Method to Isolate Human STAR Elements Functional in U-2 OS Cell
Materials and Methods
[0128]Plasmids and strains. The selection vector for STAR elements, pSelect-SV40-zeo ("pSelect," FIG. 1) was constructed as follows: the pREP4 vector (Invitrogen V004-50) was used as the plasmid backbone. It provides the Epstein Barr oriP origin of replication and EBNA-1 nuclear antigen for high-copy episomal replication in primate cell lines; the hygromycin resistance gene with the thymidine kinase promoter and polyadenylation site, for selection in mammalian cells; and the ampicillin resistance gene and co1E1 origin of replication for maintenance in Escherichia coli. The vector contains four consecutive LexA operator sites between XbaI and NheI restriction sites (Bunker and Kingston, 1994). Embedded between the LexA operators and the NheI site is a polylinker consisting of the following restriction sites: HindIII-AscI-BamHI-AscI-HindIII. Between the NheI site and a SalI site is the zeocin resistance gene with the SV40 promoter and polyadenylation site, derived from pSV40/Zeo (Invitrogen V502-20); this is the selectable marker for the STAR screen.
[0129]Gene libraries were constructed by Sau3AI digestion of human genomic DNA, either purified from placenta (Clontech 6550-1) or carried in bacterial/P1 (BAC/PAC) artificial chromosomes. The BAC/PAC clones contain genomic DNA from the 1q12 cytogenetic region (clones RP1154H19 and RP3328E19), from the HOX cluster of homeotic genes (clones RP1167F23, RP1170019, and RP11387A1), or from human chromosome 22 (Research Genetics 96010-22). The DNAs were size-fractionated, and the 0.5-2 kb size fraction ligated into BamHI-digested pSelect vector, by standard techniques (Sambrook et al., 1989).
[0130]The construction of the host strains has been described (van der Vlag et al., 2000). Briefly, they are based on the U-2 OS human osteosarcoma cell line (American Type Culture Collection HTB-96). U-2 OS was stably transfected with the pTet-Off plasmid (Clontech K1620-A), encoding a protein chimera consisting of the Tet-repressor DNA binding domain and the VP16 transactivation domain. The cell line was subsequently stably transfected with fusion protein genes containing the LexA DNA binding domain, and the coding regions of HP1, MeCP2, or HPC2 (three Drosophila proteins that repress gene expression when tethered to DNA). The LexA-repressor genes are under control of the Tet-Off transcriptional regulatory system (Gossen and Bujard, 1992).
[0131]Library screening and STAR element characterization. The gene libraries in pSelect were transfected into U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-repressor cell lines by calcium phosphate precipitation (Graham and van der Eb, 1973, Wigler et al., 1978) as recommended by the supplier of the transfection reagent (Life Technologies). Transfected cells were cultured under hygromycin selection (25 μg/ml) and tetracycline repression (doxycycline, 10 ng/ml) for one week (50% confluence). Then the doxycycline concentration was reduced to 0.1 ng/ml to induce the LexA-repressor genes, and after two days zeocin was added to 250 μg/ml. The cells are cultured for a further four to five weeks, until the control cultures (transfected with empty pSelect) were killed by the zeocin.
[0132]Zeocin-resistant colonies from the library transfection were propagated, and plasmid DNA isolated and rescued into E. coli by standard techniques (Sambrook et al., 1989). The candidate STAR elements in the rescued DNA were analyzed by restriction endonuclease mapping (Sambrook et al., 1989), and tested for STAR activity (zeocin resistance) after re-transfection to U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-repressor cells and lowering the doxycycline concentration.
[0133]The human genomic DNA inserts in these plasmids were sequenced by the dideoxy method (Sanger et al., 1977) using a Beckman CEQ®2000 automated DNA sequencer, using the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, DNA was purified from E. coli using QIAprep® Spin Miniprep and Plasmid Midi Kits (QIAGEN® 27106 and 12145, respectively). Cycle sequencing was carried out using custom oligonucleotides corresponding to the pSelect vector (primers D89 (SEQ ID NO:149) and D95 (SEQ ID NO:154); all oligonucleotides are described in Table 2), in the presence of dye terminators (CEQ® Dye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit, Beckman 608000). Assembled STAR DNA sequences were located in the human genome using BLAST (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool (Altschul et al., 1990); WorldWideWeb.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/BLAST/).
Results
[0134]The screens of human genomic DNA have yielded 66 STAR elements; the lengths and chromosomal locations of these elements are tabulated in SEQ ID NO:1-SEQ ID NO:66. They confer zeocin resistance on U-2 OS host cells when placed between LexA-repressor binding sites and the zeocin resistance gene. Their anti-repression activity was demonstrated both in the initial screen and upon re-transfection (demonstrating that the anti-repression activity is due to the STAR element and not to somatic acquisition of zeocin resistance). The STAR elements correspond to known and unique sequences in the human genome, as demonstrated by BLAST searches (Table 3). In some cases, the cloned element is a chimera of two unlinked genomic loci (e.g., STAR3 (SEQ ID NO:3), Table 3). They range in length from 500 to 2361 base pairs in length.
Example 2
Predictability and Yield is Improved by Promiscuous STAR Elements in More than One Host Cell Line
[0135]STAR elements function to block the effect of transcriptional repression influences on transgene expression units. These repression influences can be due to heterochromatin ("position effects") or to adjacent copies of the transgene ("repeat-induced gene silencing"). Two of the benefits of STAR elements for heterologous protein production are increased predictability of finding high-expressing primary recombinant host cells and increased yield during production cycles. These benefits are illustrated in this example.
Materials and Methods
[0136]Construction of the pSDH vectors and STAR-containing derivatives: The pSDH-Tet vector was constructed by polymerase chain reaction amplification (PCR) of the luciferase open reading frame from plasmid pREP4-HSF-Luc (van der Vlag et al., 2000) using primers C67 (SEQ ID NO:136) and C68 (SEQ ID NO:137), and insertion of the SacII/BamHI fragment into SacII/BamHI-digested pUHD10-3 (Gossen and Bujard, 1992). The luciferase expression unit was re-amplified with primers C65 (SEQ ID NO:134) and C66 (SEQ ID NO:135), and re-inserted into pUHD10-3 in order to flank it with multiple cloning sites (MCSI and MCSII). An AscI site was then introduced into MCSI by digestion with EcoRI and insertion of a linker (comprised of annealed oligonucleotides D93 (SEQ ID NO:152) and D94 (SEQ ID NO:153)). The CMV promoter was amplified from plasmid pCMV-Bsd (Invitrogen K510-01) with primers D90 (SEQ ID NO:150) and D91 (SEQ ID NO:151), and used to replace the Tet-Off promoter in pSDH-Tet by SalI/SacII digestion and ligation to create vector pSDH-CMV. The luciferase open reading frame in this vector was replaced by SEAP (Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase) as follows: vector pSDH-CMV was digested with SacII and BamHI and made blunt; the SEAP open reading frame was isolated from pSEAP-basic (Clontech 6037-1) by EcoRI/SalI digestion, made blunt and ligated into pSDH-CMV to create vector pSDH-CS. The puromycin resistance gene under control of the SV40 promoter was isolated from plasmid pBabe-Puro (Morgenstern and Land, 1990) by PCR, using primers C81 (SEQ ID NO:138) and C82 (SEQ ID NO:139). This was ligated into vector pGL3-control (BamHI site removed) (Promega E1741) digested with NcoI/XbaI to create pGL3-puro. pGL3-puro was digested with BglII/SalI to isolate the SV40-puro resistance unit, which was made blunt and ligated into NheI digested, blunt-ended pSDH-CS. The resulting vector, pSDH-CSP, is shown in FIG. 2. All cloning steps were carried out following the instructions provided by the manufacturers of the reagents used, according to methods known in the art (Sambrook et al., 1989).
[0137]STAR elements were inserted into MCSI and MCSII in two steps, by digestion of the STAR element and the pSDH-CSP vector with an appropriate restriction enzyme, followed by ligation. The orientation of STAR elements in recombinant pSDH vectors was determined by restriction mapping, and in all cases verified by DNA sequence analysis using primers C85 (SEQ ID NO:140), E42 (SEQ ID NO:168), and E25 (SEQ ID NO:167) (Table 2; see Example 1).
[0138]Transfection and culture of U-2 OS cells with pSDH-CMV plasmids: The human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cell line (ATCC #HTB-96) was cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium+10% Fetal Calf Serum containing glutamine, penicillin, and streptomycin (supra) at 37° C./5% CO2. Cells were co-transfected with the pSDH-CMV vector and its derivatives containing STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) or STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) in MCSI and MCSII (along with plasmid pBabe-Puro) using SuperFect® (supra). Puromycin selection was complete in two weeks, after which time individual puromycin resistant U-2 OS/pSDH-CMV clones were isolated at random and cultured further.
[0139]Luciferase assay: Luciferase activity (Himes and Shannon, 2000) was assayed in resuspended cells according to the instructions of the assay kit manufacturer (Roche 1669893), using a luminometer (Turner 20/20TD). Total cellular protein concentration was determined by the bicinchoninic acid method according to the manufacturer's instructions (Sigma B-9643), and used to normalize the luciferase data.
[0140]Transfection and culture of CHO cells with pSDH-CSP plasmids: The Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line CHO-K1 (ATCC CCL-61) was cultured in HAMS-F12 medium+10% Fetal Calf Serum containing 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 micrograms/ml streptomcyin at 37° C./5% CO2. Cells were transfected with recombinant pSDH-CSP vectors using SuperFect® (QIAGEN®) as described by the manufacturer. Briefly, cells were seeded to culture vessels and grown overnight to 70-90% confluence. SuperFect® reagent was combined with plasmid DNA (linearized in this example by digestion with PvuI) at a ratio of 6 microliters per microgram (e.g., for a 10 cm Petri dish, 20 micrograms DNA and 120 microliters SuperFect®) and added to the cells. After overnight incubation, the transfection mixture was replaced with fresh medium, and the transfected cells were incubated further. After overnight cultivation, 5 micrograms/ml puromycin was added. Puromycin selection was complete in two weeks, after which time individual puromycin resistant CHO/pSDH-CSP clones were isolated at random and cultured further.
[0141]Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase (SEAP) assay: SEAP activity (Berger et al., 1988, Henthorn et al., 1988, Kain, 1997, Yang et al., 1997) in the culture medium of CHO/pSDH-CSP clones was determined as described by the manufacturer (Clontech Great EscAPe kit #K2041). Briefly, an aliquot of medium was heat inactivated at 65° C., then combined with assay buffer and CSPD chemiluminescent substrate and incubated at room temperature for ten minutes. The rate of substrate conversion was then determined in a luminometer (Turner 20/20TD). Cell density was determined by counting trypsinized cells in a Coulter ACT10 cell counter. Luminescence units were converted into picograms SEAP based on a SEAP positive control calibration curve, and normalized to cell number.
Results
[0142]Recombinant U-2 OS cell clones containing the pSDH-CMV vector, or a pSDH-CMV plasmid containing STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) (Table 3), were cultured for three weeks. The luciferase activity in the host cells was then determined, and is expressed as relative luciferase units (FIG. 3), normalized to total cell protein. The recombinant U-2 OS clones with STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) flanking the expression units had higher yields than the STAR-less clones: the STAR6 clones had maximal luciferase expression levels five-fold higher than the STAR-less clones. The STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) element conferred greater predictability as well: 15-20% of the clones expressed luciferase at levels comparable to or greater than the STAR-less clone with the highest expression level.
[0143]Recombinant CHO cell clones containing the pSDH-CSP vector, or a pSDH-CSP plasmid containing STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6), were cultured for three weeks. The SEAP activity in the culture supernatants was then determined, and is expressed on the basis of cell number (FIG. 4). As can be seen, clones with the STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) element in the expression units were isolated that express two- to three-fold higher SEAP activity than clones whose expression units do not include this STAR element. Furthermore, the number of STAR6-containing (SEQ ID NO:6-containing) clones that express SEAP activity at or above the maximal activity of the STAR-less clones is quite high: 40% of the STAR6 clone populations exceed the highest SEAP expression of the pSDH-CSP clones.
[0144]These results demonstrate that, when used with the strong CMV promoter, the STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) element increases the yield of this heterologous protein in both of the host cell lines tested. STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) also confers increased predictability, as manifested by the large proportion of the clones with yields equal to or greater than the highest yield displayed by the STAR-less clones. Thus, STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) is an example of a promiscuous STAR element, able to suppress transgene repression in more than one host cell line. The cell lines used are derived from different species (human and hamster) and different tissue types (bone and ovary), reflecting the broad range of host cells in which this STAR element can be utilized in improving heterologous protein expression.
Example 3
STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) is a Cell Line-Specific STAR Element
[0145]The patterns of gene expression and epigenetic gene regulation in a host cell line reflect the developmental state of the somatic cells from which they are derived. Furthermore, the biotechnology industry takes advantage of general purpose cell lines from different species according to specific requirements of a heterologous protein production process. Therefore, it is expected that some STAR elements will not function in cell lines other than those in which they are isolated. This expectation has been fulfilled by some of the STAR elements shown in Table 3. One example will be given here.
Materials and Methods
[0146]pSDH vector construction, transfection and cultivation of CHO and U-2 OS cell lines, and assay methods for the SEAP and luciferase reporter genes has been described in Example 2.
Results
[0147]Recombinant U-2 OS cell clones containing the pSDH-CMV vector, or a pSDH-CMV plasmid containing STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) (Table 3), were cultured for three weeks. The luciferase activity in the host cells was then determined, and is expressed as relative luciferase units (FIG. 3), normalized to total cell protein. The recombinant U-2 OS clones with the STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) element flanking the expression units had higher yields than the STAR-less clones: the highest expression observed from STAR8 clones was two- to three-fold higher than the expression from STAR-less clones. The STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) element conferred greater predictability as well: for this STAR element, ˜15% of the clones displayed luciferase expression at levels comparable to or greater than the STAR-less clone with the highest expression level.
[0148]Recombinant CHO cell clones transfected with the pSDH-CSP vector, or a pSDH-CSP plasmid containing STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8), were cultured for three weeks. The SEAP activity in the culture supernatants was then determined, and is expressed on the basis of cell number (FIG. 4). As can be seen, one clone with the STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) element in the expression unit had a yield approximately two-fold higher than the highest-expressing STAR-less clone. However, the rest of the STAR8 clones expressed very poorly relative to the STAR-less clone population. Since only one individual in the STAR8 population had a good yield, it is probable that the expression unit in this clone was integrated in open, transcriptionally active chromatin, and the high yield does not reflect anti-repression activity of STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) in CHO cells. Certainly in the CHO clones transfected with STAR8-containing (SEQ ID NO:8-containing) expression units the predictability is quite poor; of the 17 puromycin-resistant clones, only one clone had a yield of SEAP activity above the background level of expression.
[0149]This example demonstrates that good performance of a STAR element in one cell line (in this case, the U-2 OS cell line in which STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) was originally isolated) is not an accurate predictor of its performance in other cell lines. STAR8 (SEQ ID NO:8) is thus an example of a cell line-specific STAR element.
Example 4
STAR Elements Functionality in Diverse Cell Line
Materials and Methods
[0150]Cell lines including the U-2 OS osteosarcoma and CHO (Chinese hamster ovary) cell lines (supra), the 293 cell line (ATCC CRL-1573) derived from human embryonal kidney (immortalized by adenovirus 5 transfection), the HuNS-1 myeloma (ATCC CRL-8644) and the WERI-Rb-1 retinoblastoma cell line (ATCC HTB-169), the NCI-H295R adrenal gland carcinoma (ATCC CRL-2128), and the non-secreting mouse myelomas Sp2/0-Ag 14 and NSO are examined according to the previous examples.
Example 5
STAR Elements Improve the Stability of Transgene Expression
[0151]During cultivation of recombinant host cells, it is common practice to maintain antibiotic selection. This is intended to prevent transcriptional silencing of the transgene, or loss of the transgene from the genome by processes such as recombination. However it is undesirable for production of heterologous proteins, for a number of reasons. First, the antibiotics that are used are quite expensive, and contribute significantly to the unit cost of the product. Second, for biopharmaceutical use, the protein must be demonstrably pure, with no traces of the antibiotic in the product. One advantage of STAR elements for heterologous protein production is that they confer stable expression on transgenes during prolonged cultivation, even in the absence of antibiotic selection; this property is demonstrated in this example.
Materials and Methods
[0152]The U-2 OS cell line was transfected with the plasmid pSDH-Tet-STAR6 and cultivated as described in Example 2. Individual puromycin-resistant clones were isolated and cultivated further in the absence of doxycycline. At weekly intervals the cells were transferred to fresh culture vessels at a dilution of 1:20. Luciferase activity was measured at periodic intervals as described in Example 2. After 15 weeks, the cultures were divided into two replicates; one replicate continued to receive puromycin, while the other replicate received no antibiotic for the remainder of the experiment (25 weeks total).
Results
[0153]Table 4 presents the data on luciferase expression by an expression unit flanked with STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) during prolonged growth with or without antibiotic. As can be seen, the expression of the reporter transgene, luciferase, remains stable in the U-2 OS host cells for the duration of the experiment. After the cultures were divided into two treatments (plus antibiotic and without antibiotic) the expression of luciferase was essentially stable in the absence of antibiotic selection. This demonstrates the ability of STAR elements to protect transgenes from silencing or loss during prolonged cultivation. It also demonstrates that this property is independent of antibiotic selection. Therefore, production of heterologous proteins is possible without incurring the costs of the antibiotic or of difficult downstream processing.
Example 6
Minimal Essential Sequences of STAR Elements
[0154]STAR elements are isolated from the genetic screen described in Example 1. The screen uses libraries constructed with human genomic DNA that was size-fractionated to approximately 0.5-2 kilobases (supra). The STAR elements range from 500 to 2361 base pairs (Table 3). It is likely that, for many of the STAR elements that have been isolated, STAR activity is conferred by a smaller DNA fragment than the initially isolated clone. It is useful to determine these minimum fragment sizes that are essential for STAR activity, for two reasons. First, smaller functional STAR elements would be advantageous in the design of compact expression vectors, since smaller vectors transfect host cells with higher efficiency. Second, determining minimum essential STAR sequences permits the modification of those sequences for enhanced functionality. Two STAR elements have been fine-mapped to determine their minimal essential sequences.
Materials and Methods
[0155]STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10) (1167 base pairs) and STAR27 (SEQ ID NO:27) (1520 base pairs) have been fine-mapped. They have been amplified by PCR to yield sub-fragments of approximately equal length (FIG. 6 legend). For initial testing, these have been cloned into the pSelect vector at the BamHI site, and transfected into U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cells as described in Example 1. After selection for hygromycin resistance, LexA-HP1 was induced by lowering the doxycycline concentration. Transfected cells were then incubated with zeocin to test the ability of the STAR fragments to protect the SV40-Zeo expression unit from repression due to LexA-HP1 binding.
Results
[0156]In this experiment STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10) and STAR 27 (SEQ ID NO:27) confer good protection against gene silencing, as expected (FIG. 6). This is manifested by robust growth in the presence of zeocin.
[0157]Of the three STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10) sub-fragments, 10A (˜400 base pairs, corresponding to approximately the first 400 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:10) confers on transfected cells vigorous growth in the presence of zeocin, exceeding that of the full-length STAR element. Cells transfected with pSelect constructs containing the other two sub-fragments do not grow in the presence of zeocin. These results identify the ˜400 base pair 10A fragment as encompassing the DNA sequence responsible for the anti-repression activity of STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10).
[0158]STAR27 (SEQ ID NO:27) confers moderate growth in zeocin to transfected cells in this experiment (FIG. 6). One of the sub-fragments of this STAR, 27B (˜500 base pairs, corresponding to approximately the second 500 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:27), permits weak growth of the host cells in zeocin-containing medium. This suggests that the anti-repression activity of this STAR is partially localized on sub-fragment 27B, but full activity requires sequences from 27A (corresponding to approximately the first 500 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:27) and/or 27C (corresponding to approximately the third 500 nucleotides of SEQ ID NO:27) (each 500 base pairs) as well.
Example 7
STAR Elements Function in the Context of Various Transcriptional Promoters
[0159]Transgene transcription is achieved by placing the transgene open reading frame under control of an exogenous promoter. The choice of promoter is influenced by the nature of the heterologous protein and the production system. In most cases, strong constitutive promoters are preferred because of the high yields they can provide. Some viral promoters have these properties; the promoter/enhancer of the cytomegalovirus immediate early gene ("CMV promoter") is generally regarded as the strongest promoter in common biotechnological use (Boshart et al., 1985, Doll et al., 1996, Foecking and Hofstetter, 1986). The simian virus SV40 promoter is also moderately strong (Boshart et al., 1985, Foecking and Hofstetter, 1986) and is frequently used for ectopic expression in mammalian cell vectors. The Tet-Off promoter is inducible: the promoter is repressed in the presence of tetracycline or related antibiotics (doxycycline is commonly used) in cell-lines which express the tTA plasmid (Clontech K1620-A), and removal of the antibiotic results in transcriptional induction (Deuschle et al., 1995, Gossen and Bujard, 1992, Izumi and Gilbert, 1999, Umana et al., 1999).
Materials and Methods
[0160]The construction of the pSDH-Tet and pSDH-CMV vectors is described in Example 2. pSDH-SV40 was constructed by PCR amplification of the SV40 promoter (primers D41 (SEQ ID NO:142) and D42 (SEQ ID NO:143)) from plasmid pSelect-SV40-Zeo (Example 1), followed by digestion of the PCR product with SacII and SalI. The pSDH-CMV vector was digested with SacII and SalI to remove the CMV promoter, and the vector and SV40 fragment were ligated together to create pSDH-SV40. STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) was cloned into MCSI and MCSII as described in Example 2. The plasmids pSDH-Tet, pSDH-Tet-STAR6, pSDH-Tet-STAR7, pSDH-SV40 and pSDH-SV40-STAR6 were co-transfected with pBabe-Puro into U-2 OS using SuperFect® as described by the manufacturer. Cell cultivation, puromycin selection, and luciferase assays were carried out as described in Example 2.
Results
[0161]FIGS. 3, 7, and 8 compare the expression of the luciferase reporter gene from three different promoters: two strong and constitutive viral promoters (CMV and SV40), and the inducible Tet-Off promoter. All three promoters were tested in the context of the STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) element in U-2 OS cells. The results demonstrate that the yield and predictability from all three promoters are increased by STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6). As described in Examples 2 and 5, STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) is beneficial in the context of the CMV promoter (FIG. 3). Similar improvements are seen in the context of the SV40 promoter (FIG. 7): the yield from the highest-expressing STAR6 clone is two- to three-fold greater than the best pSDH-SV40 clones, and six STAR clones (20% of the population) have yields higher than the best STAR-less clones. In the context of the Tet-Off promoter under inducing (low doxycycline) concentrations, STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) also improves the yield and predictability of transgene expression (FIG. 8): the highest-expressing STAR6 clone has a 20-fold higher yield than the best pSDH-Tet clone, and nine STAR6 clones (35% of the population) have yields higher than the best STAR-less clone. It is concluded that this STAR element is versatile in its transgene-protecting properties, since it functions in the context of various biotechnologically useful promoters of transcription.
Example 8
STAR Element Function can be Directional
[0162]While short nucleic acid sequences can be symmetrical (e.g., palindromic), longer, naturally-occurring sequences are typically asymmetrical. As a result, the information content of nucleic acid sequences is directional and the sequences themselves can be described with respect to their 5' and 3' ends. The directionality of nucleic acid sequence information affects the arrangement in which recombinant DNA molecules are assembled using standard cloning techniques known in the art (Sambrook et al., 1989). STAR elements are long, asymmetrical DNA sequences, and have a directionality based on the orientation in which they were originally cloned in the pSelect vector. In the examples given above, using two STAR elements in pSDH vectors, this directionality was preserved. This orientation is described as the native or 5'-3' orientation, relative to the zeocin resistance gene (see FIG. 9). In this example the importance of directionality for STAR function is tested in the pSDH-Tet vector. Since the reporter genes in the pSDH vectors are flanked on both sides by copies of the STAR element of interest, the orientation of each STAR copy must be considered. This example compares the native orientation with the opposite orientation (FIG. 9).
Materials and Methods
[0163]The STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) element was cloned into pSDH-Tet as described in Example 2. U-2 OS cells were co-transfected with plasmids pSDH-Tet-STAR66-native and pSDH-Tet-STAR66-opposite, and cultivated as described in Example 2. Individual clones were isolated and cultivated; the level of luciferase expression was determined as described (supra).
Results
[0164]The results of the comparison of STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) activity in the native orientation and the opposite orientation are shown in FIG. 10. When STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) is in the opposite orientation, the yield of only one clone is reasonably high (60 luciferase units). In contrast, the yield of the highest-expressing clone when STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) is in the native orientation is considerably higher (100 luciferase units) and the predictability is much higher, as well: seven clones of the native-orientation population (30%) express luciferase above the level of the highest-expressing clone from the opposite-orientation population, and 15 of the clones in the native-orientation population (60%) express luciferase above ten relative luciferase units. Therefore, it is demonstrated that STAR66 (SEQ ID NO:66) function is directional.
Example 9
Transgene Expression in the Context of STAR Elements is Copy Number-Dependent
[0165]Transgene expression units for heterologous protein expression are generally integrated into the genome of the host cell to ensure stable retention during cell division. Integration can result in one or multiple copies of the expression unit being inserted into the genome; multiple copies may or may not be present as tandem arrays. The increased yield demonstrated for transgenes protected by STAR elements (supra) suggests that STAR elements are able to permit the transgene expression units to function independently of influences on transcription associated with the site of integration in the genome (independence from position effects (Boivin and Dura, 1998)). It suggests further that the STAR elements permit each expression unit to function independently of neighboring copies of the expression unit when they are integrated as a tandem array (independence from repeat-induced gene silencing (Garrick et al., 1998)). Copy number-dependence is determined from the relationship between transgene expression levels and copy number, as described in the example below.
Materials and Methods
[0166]U-2 OS cells were co-transfected with pSDH-Tet-STAR10 and cultivated under puromycin selection as described (supra). Eight individual clones were isolated and cultivated further. Then cells were harvested, and one portion was assayed for luciferase activity as described (supra). The remaining cells were lysed and the genomic DNA purified using the DNeasy® Tissue Kit (QIAGEN® 69504) as described by the manufacturer. DNA samples were quantitated by UV spectrophotometry. Three micrograms of each genomic DNA sample were digested with PvuII and XhoI overnight as described by the manufacturer (New England Biolabs), and resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis. DNA fragments were transferred to a nylon membrane as described (Sambrook et al., 1989), and hybridized with a radioactively labeled probe to the luciferase gene (isolated from BamHI/SacII-digested pSDH-Tet). The blot was washed as described (Sambrook et al., 1989) and exposed to a phosphorimager screen (Personal F/X, BioRad). The resulting autoradiogram (FIG. 11) was analyzed by densitometry to determine the relative strength of the luciferase DNA bands, which represents the transgene copy number.
Results
[0167]The enzyme activities and copy numbers (DNA band intensities) of luciferase in the clones from the pSDH-Tet-STAR10 clone population is shown in FIG. 12. The transgene copy number is highly correlated with the level of luciferase expression in these pSDH-Tet-STAR10 clones (r=0.86). This suggests that STAR10 (SEQ ID NO:10) confers copy number-dependence on the transgene expression units, making transgene expression independent of other transgene copies in tandem arrays and independent of gene-silencing influences at the site of integration.
Example 10
STAR Elements Function as Enhancer Blockers but not Enhancers
[0168]Gene promoters are subject to both positive and negative influences on their ability to initiate transcription. An important class of elements that exert positive influences are enhancers. Enhancers are characteristically able to affect promoters even when they are located far away (many kilobase pairs) from the promoter. Negative influences that act by heterochromatin formation (e.g., Polycomb group proteins) have been described above, and these are the target of STAR activity. The biochemical basis for enhancer function and for heterochromatin formation is fundamentally similar, since they both involve binding of proteins to DNA. Therefore, it is important to determine whether STAR elements are able to block positive influences as well as negative influences, in other words, to shield transgenes from genomic enhancers in the vicinity of the site of integration. The ability to shield transgenes from enhancer activity ensures stable and predictable performance of transgenes in biotechnological applications. This example examines the performance of STAR elements in an enhancer-blocking assay.
[0169]Another feature of STAR activity that is important to their function is the increased yield they confer on transgenes (Example 2). STARs are isolated on the basis of their ability to maintain high levels of zeocin expression when heterochromatin-forming proteins are bound adjacent to the candidate STAR elements. High expression is predicted to occur because STARs are anticipated to block the spread of heterochromatin into the zeocin expression unit. However, a second scenario is that the DNA fragments in zeocin-resistant clones contain enhancers. Enhancers have been demonstrated to have the ability to overcome the repressive effects of Polycomb-group proteins such as those used in the method of the STAR screen (Zink and Paro, 1995). Enhancers isolated by this phenomenon would be considered false positives, since enhancers do not have the properties claimed here for STARs. In order to demonstrate that STAR elements are not enhancers, they have been tested in an enhancer assay.
[0170]The enhancer-blocking assay and the enhancer assay are methodologically and conceptually similar. The assays are shown schematically in FIG. 13. The ability of STAR elements to block enhancers is performed using the E47/E-box enhancer system. The E47 protein is able to activate transcription by promoters when it is bound to an E-box DNA sequence located in the vicinity of those promoters (Quong et al., 2002). E47 is normally involved in regulation of B and T lymphocyte differentiation (Quong et al., 2002), but it is able to function in diverse cell types when expressed ectopically (Petersson et al., 2002). The E-box is a palindromic DNA sequence, CANNTG (Knofler et al., 2002). In the enhancer-blocking assay, an E-box is placed upstream of a luciferase reporter gene (including a minimal promoter) in an expression vector. A cloning site for STAR elements is placed between the E-box and the promoter. The E47 protein is encoded on a second plasmid. The assay is performed by transfecting both the E47 plasmid and the luciferase expression vector into cells; the E47 protein is expressed and binds to the E-box, and the E47/E-box complex is able to act as an enhancer. When the luciferase expression vector does not contain a STAR element, the E47/E-box complex enhances luciferase expression (FIG. 13A, situation 1). When STAR elements are inserted between the E-box and the promoter, their ability to block the enhancer is demonstrated by reduced expression of luciferase activity (FIG. 13A, situation 2); if STARs cannot block enhancers, luciferase expression is activated (FIG. 13A, situation 3).
[0171]The ability of STAR elements to act as enhancers utilizes the same luciferase expression vector. In the absence of E47, the E-box itself does not affect transcription. Instead, enhancer behavior by STAR elements will result in activation of luciferase transcription. The assay is performed by transfecting the luciferase expression vector without the E47 plasmid. When the expression vector does not contain STAR elements, luciferase expression is low (FIG. 13B, situation 1). If STAR elements do not have enhancer properties, luciferase expression is low when a STAR element is present in the vector (FIG. 13B, situation 2). If STAR elements do have enhancer properties, luciferase expression will be activated in the STAR-containing vectors (FIG. 13B, situation 3).
Materials and Methods
[0172]The luciferase expression vector was constructed by inserting the E-box and a human alkaline phosphatase minimal promoter from plasmid mu-E5+E2x6-cat(x) (Ruezinsky et al., 1991) upstream of the luciferase gene in plasmid pGL3-basic (Promega E1751), to create pGL3-E-box-luciferase (gift of W. Romanow). The E47 expression plasmid contains the E47 open reading frame under control of a beta-actin promoter in the pHBAPr-1-neo plasmid; E47 in constitutively expressed from this plasmid (gift of W. Romanow).
[0173]STAR elements 1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18, and 27 (SEQ ID NOS:1, 2, 3, 6, 10, 11, 18, and 27, respectively) have been cloned into the luciferase expression vector. Clones containing the Drosophila scs element and the chicken beta-globin HS4-6x core ("HS4") element have been included as positive controls (they are known to block enhancers, and to have no intrinsic enhancer properties (Chung et al., 1993, Kellum and Schedl, 1992)), and the empty luciferase expression vector has been included as a negative control. All assays were performed using the U-2 OS cell line. In the enhancer-blocking assay, the E47 plasmid was co-transfected with the luciferase expression vectors (empty vector, or containing STAR or positive-control elements). In the enhancer assay, the E47 plasmid was co-transfected with STARless luciferase expression vector as a positive control for enhancer activity; all other samples received a mock plasmid during co-transfection. The transiently transfected cells were assayed for luciferase activity 48 hours after plasmid transfection (supra). The luciferase activity expressed from a plasmid containing no E-box or STAR/control elements was subtracted, and the luciferase activities were normalized to protein content as described (supra).
Results
[0174]FIG. 14 shows the results of the enhancer-blocking assay. In the absence of STAR elements (or the known enhancer-blocking elements scs and HS4), the E47/E-box enhancer complex activates expression of luciferase ("vector"); this enhanced level of expression has been normalized to 100. Enhancer activity is blocked by all STAR elements tested. Enhancer activity is also blocked by the HS4 and scs elements, as expected (Bell et al., 2001, Gerasimova and Corces, 2001). These results demonstrate that in addition to their ability to block the spreading of transcriptional silencing (negative influences), STAR elements are able to block the action of enhancers (positive influences).
[0175]FIG. 15 shows the results of the enhancer assay. The level of luciferase expression due to enhancement by the E47/E-box complex is set at 100 ("E47"). By comparison, none of the STAR elements bring about significant activation of luciferase expression. As expected, the scs and HS4 elements also do not bring about activation of the reporter gene. Therefore, it is concluded that at least the tested STAR elements do not possess enhancer properties.
Example 11
STAR Elements are Conserved Between Mouse and Human
[0176]BLAT analysis of the STAR DNA sequence against the human genome database (http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway) reveals that some of these sequences have high sequence conservation with other regions of the human genome. These duplicated regions are candidate STAR elements; if they do show STAR activity, they would be considered paralogs of the cloned STARs (two genes or genetic elements are said to be paralogous if they are derived from a duplication event (Li, 1997)).
[0177]BLAST analysis of the human STARs against the mouse genome (WorldWideWeb.ensembl.org/Mus_musculus/blastview) also reveals regions of high sequence conservation between mouse and human. This sequence conservation has been shown for fragments of 15 out of the 65 human STAR elements. The conservation ranges from 64% to 89%, over lengths of 141 base pairs to 909 base pairs (Table 5). These degrees of sequence conservation are remarkable and suggest that these DNA sequences may confer STAR activity within the mouse genome as well. Some of the sequences from the mouse and human genomes in Table 5 could be strictly defined as orthologs (two genes or genetic elements are said to be orthologous if they are derived from a speciation event (Li, 1997)). For example, STAR6 (SEQ ID NO:6) is between the SLC8A1 and HAAO genes in both the human and mouse genomes. In other cases, a cloned human STAR has a paralog within the human genome, and its ortholog has been identified in the mouse genome. For example, STAR3a is a fragment of the 15q11.2 region of human chromosome 15. This region is 96.9% identical (paralogous) with a DNA fragment at 5q33.3 on human chromosome 5, which is near the IL12B interleukin gene. These human DNAs share approximately 80% identity with a fragment of the 11B2 region on mouse chromosome 11. The 11B2 fragment is also near the (mouse) IL12B interleukin gene. Therefore, STAR3a and the mouse 11B2 fragment can be strictly defined as paralogs.
[0178]In order to test the hypothesis that STAR activity is shared between regions of high sequence conservation in the mouse and human genome, one of the human STARs with a conserved sequence in mouse, STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18), has been analyzed in greater detail. The sequence conservation in the mouse genome detected with the original STAR18 clone extends leftward on human chromosome 2 for about 500 base pairs (FIG. 16; left and right relate to the standard description of the arms of chromosome 2). In this example, we examine whether the region of sequence conservation defines a "naturally occurring" STAR element in human that is more extensive in length than the original clone. We also examine whether the STAR function of this STAR element is conserved between mouse and human.
Materials and Methods
[0179]The region of mouse/human sequence conservation around STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) was recovered from human BAC clone RP11-387A1 by PCR amplification, in three fragments: the entire region (primers E93 (SEQ ID NO:171) and E94 (SEQ ID NO:172)), the leftward half (primers E93 (SEQ ID NO:171) and E92 (SEQ ID NO:170)), and the rightward half (primers E57 (SEQ ID NO:169) and E94 (SEQ ID NO:172)). The corresponding fragments from the homologous mouse region were recovered from BAC clone RP23-400H17 in the same fashion (primers E95 (SEQ ID NO:173) and E98 (SEQ ID NO:176), E95 (SEQ ID NO:173) and E96 (SEQ ID NO:174), and E97 (SEQ ID NO:175) and E98 (SEQ ID NO:176), respectively). All fragments were cloned into the pSelect vector and transfected into a U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cell line (supra). Following transfection, hygromycin selection was carried out to select for transfected cells. The LexA-HP1 protein was induced by lowering the doxycycline concentration, and the ability of the transfected cells to withstand the antibiotic zeocin (a measure of STAR activity) was assessed by monitoring cell growth.
Results
[0180]The original STAR18 clone was isolated from Sau3AI digested human DNA ligated into the pSelect vector on the basis of its ability to prevent silencing of a zeocin resistance gene. Alignment of the human STAR18 clone (497 base pairs) with the mouse genome revealed high sequence similarity (72%) between the orthologous human and mouse STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) regions. It also uncovered high similarity (73%) in the region extending for 488 base pairs immediately to the left of the Sau3AI site that defines the left end of the cloned region (FIG. 16). Outside these regions the sequence similarity between human and mouse DNA drops below 60%.
[0181]As indicated in FIG. 16, both the human and the mouse STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) elements confer survival on zeocin to host cells expressing the lexA-HP1 repressor protein. The original 497 base pair STAR18 clone and its mouse ortholog both confer the ability to grow (FIG. 16, a and d). The adjacent 488 base pair regions of high similarity from both genomes also confer the ability to grow, and in fact their growth phenotype is more vigorous than that of the original STAR18 clone (FIG. 16, b and e). When the entire region of sequence similarity was tested, these DNAs from both mouse and human confer growth, and the growth phenotype is more vigorous than the two sub-fragments (FIG. 16, c and f). These results demonstrate that the STAR activity of human STAR18 (SEQ ID NO:18) is conserved in its ortholog from mouse. The high sequence conservation between these orthologous regions is particularly noteworthy because they are not protein-coding sequences, leading to the conclusion that they have some regulatory function that has prevented their evolutionary divergence through mutation.
[0182]This analysis demonstrates that cloned STAR elements identified by the original screening program may in some cases represent partial STAR elements, and that analysis of the genomic DNA in which they are embedded can identify sequences with stronger STAR activity.
Example 12
STAR Elements Contain Characteristic DNA Sequence Motifs
[0183]STAR elements are isolated on the basis of their anti-repression phenotype with respect to transgene expression. This anti-repression phenotype reflects underlying biochemical processes that regulate chromatin formation which are associated with the STAR elements. These processes are typically sequence-specific and result from protein binding or DNA structure. This suggests that STAR elements will share DNA sequence similarity. Identification of sequence similarity among STAR elements will provide sequence motifs that are characteristic of the elements that have already been identified by functional screens and tests. The sequence motifs will also be useful to recognize and claim new STAR elements whose functions conform to the claims of this patent. The functions include improved yield and stability of transgenes expressed in eukaryotic host cells.
[0184]Other benefits of identifying sequence motifs that characterize STAR elements include: (1) provision of search motifs for prediction and identification of new STAR elements in genome databases, (2) provision of a rationale for modification of the elements, and (3) provision of information for functional analysis of STAR activity. Using bio-informatics, sequence similarities among STAR elements have been identified; the results are presented in this example.
Bio-Informatic and Statistical Background
[0185]Regulatory DNA elements typically function via interaction with sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. Bio-informatic analysis of DNA elements, such as STAR elements whose regulatory properties have been identified, but whose interacting proteins are unknown, requires a statistical approach for identification of sequence motifs. This can be achieved by a method that detects short DNA sequence patterns that are over-represented in a set of regulatory DNA elements (e.g., the STAR elements) compared to a reference sequence (e.g., the complete human genome). The method determines the number of observed and expected occurrences of the patterns in each regulatory element. The number of expected occurrences is calculated from the number of observed occurrences of each pattern in the reference sequence.
[0186]The DNA sequence patterns can be oligonucleotides of a given length, e.g., six base pairs. In the simplest analysis, for a six-base-pair oligonucleotide (hexamer) composed of the four nucleotides (A, C, G, and T) there are 46=4096 distinct oligonucleotides (all combinations from AAAAAA (SEQ ID NO:121) to TTTTTT (SEQ ID NO:122)). If the regulatory and reference sequences were completely random and had equal proportions of the A, C, G, and T nucleotides, then the expected frequency of each hexamer would be 1/4096 (˜0.00024). However, the actual frequency of each hexamer in the reference sequence is typically different than this due to biases in the content of G:C base pairs, etc. Therefore, the frequency of each oligonucleotide in the reference sequence is determined empirically by counting, to create a "frequency table" for the patterns.
[0187]The pattern frequency table of the reference sequence is then used to calculate the expected frequency of occurrence of each pattern in the regulatory element set. The expected frequencies are compared with the observed frequencies of occurrence of the patterns. Patterns that are "over-represented" in the set are identified; for example, if the hexamer ACGTGA (SEQ ID NO:123) is expected to occur five times in 20 kilobase pairs of sequence, but is observed to occur 15 times, then it is three-fold over-represented. Ten of the 15 occurrences of that hexameric sequence pattern would not be expected in the regulatory elements if the elements had the same hexamer composition as the entire genome. Once the over-represented patterns are identified, a statistical test is applied to determine whether their over-representation is significant, or may be due to chance. For this test, a significance index, "sig," is calculated for each pattern. The significance index is derived from the probability of occurrence of each pattern, which is estimated by a binomial distribution. The probability takes into account the number of possible patterns (4096 for hexamers). The highest sig values correspond to the most overrepresented oligonucleotides (van Helden et al., 1998). In practical terms, oligonucleotides with sig≧0 are considered as over-represented. A pattern with sig≧0 is likely to be over-represented due to chance once (=100) in the set of regulatory element sequences. However, at sig≧1 a pattern is expected to be over-represented once in ten (=101) sequence sets, sig≧2 once in 100 (=102) sequence sets, etc.
[0188]The patterns that are significantly over-represented in the regulatory element set are used to develop a model for classification and prediction of regulatory element sequences. This employs Discriminant Analysis, a so-called "supervised" method of statistical classification known to one of ordinary skill in the art (Huberty, 1994). In Discriminant Analysis, sets of known or classified items (e.g., STAR elements) are used to "train" a model to recognize those items on the basis of specific variables (e.g., sequence patterns such as hexamers). The trained model is then used to predict whether other items should be classified as belonging to the set of known items (e.g., is a DNA sequence a STAR element). In this example, the known items in the training set are STAR elements (positive training set). They are contrasted with sequences that are randomly selected from the genome (negative training set) which have the same length as the STAR elements. Discriminant Analysis establishes criteria for discriminating positives from negatives based on a set of variables that distinguish the positives; in this example, the variables are the significantly over-represented patterns (e.g., hexamers).
[0189]When the number of over-represented patterns is high compared to the size of the training set, the model could become biased due to over-training. Over-training is circumvented by applying a forward stepwise selection of variables (Huberty, 1994). The goal of Stepwise Discriminant Analysis is to select the minimum number of variables that provides maximum discrimination between the positives and negatives. The model is trained by evaluating variables one-by-one for their ability to properly classify the items in the positive and negative training sets. This is done until addition of new variables to the model does not significantly increase the model's predictive power (i.e., until the classification error rate is minimized). This optimized model is then used for testing, in order to predict whether "new" items are positives or negatives (Huberty, 1994).
[0190]It is inherent in classification statistics that for complex items such as DNA sequences, some elements of the positive training set will be classified as negatives (false negatives), and some members of the negative training set will be classified as positives (false positives). When a trained model is applied to testing new items, the same types of misclassifications are expected to occur.
[0191]In the bio-informatic method described here, the first step, Pattern Frequency Analysis, reduces a large set of sequence patterns (e.g., all 4096 hexamers) to a smaller set of significantly over-represented patterns (e.g., 100 hexamers); in the second step, Stepwise Discriminant Analysis reduces the set of over-represented patterns to the subset of those patterns that have maximal discriminative power (e.g., five to ten hexamers). Therefore, this approach provides simple and robust criteria for identifying regulatory DNA elements such as STAR elements.
[0192]DNA-binding proteins can be distinguished on the basis of the type of binding site they occupy. Some recognize contiguous sequences; for this type of protein, patterns that are oligonucleotides of length six base pairs (hexamers) are fruitful for bio-informatic analysis (van Helden et al., 1998). Other proteins bind to sequence dyads: contact is made between pairs of highly conserved trinucleotides separated by a non-conserved region of fixed width (van Helden et al., 2000). In order to identify sequences in STAR elements that may be bound by dyad-binding proteins, frequency analysis was also conducted for this type of pattern, where the spacing between the two trinucleotides was varied from 0 to 20 (i.e., XXXN{0-20}XXX where X's are specific nucleotides composing the trinucleotides, and N's are random nucleotides from 0 to 20 base pairs in length). The results of dyad frequency analysis are also used for Linear Discriminant Analysis as described above.
Materials and Methods
[0193]Using the genetic screen described in the original patent application, sixty-six (66) STAR elements were initially isolated from human genomic DNA and characterized in detail (Table 3). The screen was performed on gene libraries constructed by Sau3AI digestion of human genomic DNA, either purified from placenta (Clontech 6550-1) or carried in bacterial/P1 (BAC/PAC) artificial chromosomes. The BAC/PAC clones contain genomic DNA from regions of chromosome 1 (clones RP1154H19 and RP3328E19), from the HOX cluster of homeotic genes (clones RP1167F23, RP1170019, and RP11387A1), or from human chromosome 22 (Research Genetics 96010-22). The DNAs were size-fractionated, and the 0.5-2 kb size fraction was ligated into BamHI-digested pSelect vector, by standard techniques (Sambrook et al., 1989). pSelect plasmids containing human genomic DNA that conferred resistance to zeocin at low doxycycline concentrations were isolated and propagated in Escherichia coli. The screens that yielded the STAR elements of Table 3 have assayed approximately 1-2% of the human genome.
[0194]The human genomic DNA inserts in these 66 plasmids were sequenced by the dideoxy method (Sanger et al., 1977) using a Beckman CEQ®2000 automated DNA sequencer, using the manufacturer's instructions. Briefly, DNA was purified from E. coli using QIAprep® Spin Miniprep and Plasmid Midi Kits (QIAGEN® 27106 and 12145, respectively). Cycle sequencing was carried out using custom oligonucleotides corresponding to the pSelect vector (primers D89 (SEQ ID NO:149) and D95 (SEQ ID NO:154), Table 2), in the presence of dye terminators (CEQ® Dye Terminator Cycle Sequencing Kit, Beckman 608000). Assembled STAR DNA sequences were located in the human genome (database builds August and December 2001) using BLAT (Basic Local Alignment Tool (Kent, 2002); http://genome.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway; Table 3). In aggregate, the combined STAR sequences comprise 85.6 kilobase pairs, with an average length of 1.3 kilobase pairs.
[0195]Sequence motifs that distinguish STAR elements within human genomic DNA were identified by bio-informatic analysis using a two-step procedure, as follows (see FIG. 17 for a schematic diagram). The analysis has two input datasets: (1) the DNA sequences of the STAR elements (STAR1-STAR65 (SEQ ID NOS:1-65) were used; Table 3); and (2) the DNA sequence of the human genome (except for chromosome 1, which was not feasible to include due to its large size; for dyad analysis a random subset of human genomic DNA sequence (˜27 Mb) was used).
Pattern Frequency Analysis
[0196]The first step in the analysis uses RSA-Tools software (Regulatory Sequence Analysis Tools; WorldWideWeb.ucmb.ulb.ac.be/bioinformatics/rsa-tools/; references (van Helden et al., 1998, van Helden et al., 2000, van Helden et al., 2000)) to determine the following information: (1) the frequencies of all dyads and hexameric oligonucleotides in the human genome; (2) the frequencies of the oligonucleotides and dyads in the 65 STAR elements; and (3) the significance indices of those oligonucleotides and dyads that are over-represented in the STAR elements compared to the genome. A control analysis was done with 65 sequences that were selected at random from the human genome (i.e., from 2689×103 kilobase pairs) that match the length of the STAR elements of Table 3.
Discriminant Analysis
[0197]The over-represented oligonucleotides and dyads were used to train models for prediction of STAR elements by Linear Discriminant Analysis (Huberty, 1994). A pre-selection of variables was performed by selecting the 50 patterns with the highest individual discriminatory power from the over-represented oligos or dyads of the frequency analyses. These pre-selected variables were then used for model training in a Stepwise Linear Discriminant Analysis to select the most discriminant combination of variables (Huberty, 1994). Variable selection was based on minimizing the classification error rate (percentage of false negative classifications). In addition, the expected error rate was estimated by applying the same discriminant approach to the control set of random sequences (minimizing the percentage of false positive classifications).
[0198]The predictive models from the training phase of Discriminant Analysis were tested in two ways. First, the STAR elements and random sequences that were used to generate the model (the training sets) were classified. Second, sequences in a collection of 19 candidate STAR elements (recently cloned by zeocin selection as described above) were classified. These candidate STAR elements are listed in Table 8 (SEQ ID NOS:66-84).
Results
[0199]Pattern frequency analysis was performed with RSA-Tools on 65 STAR elements, using the human genome as the reference sequence. One hundred sixty-six (166) hexameric oligonucleotides were found to be over-represented in the set of STAR elements (sig≧0) compared to the entire genome (Table 6). The most significantly over-represented oligonucleotide, CCCCAC (SEQ ID NO:177), occurs 107 times among the 65 STAR elements, but is expected to occur only 49 times. It has a significance coefficient of 8.76; in other words, the probability that its over-representation is due to random chance is 1/108.76, i.e., less than one in 500 million.
[0200]Ninety-five of the oligonucleotides have a significance coefficient greater than one, and are, therefore, highly over-represented in the STAR elements. Among the over-represented oligonucleotides, their observed and expected occurrences, respectively, range from 6 and 1 (for oligo 163, CGCGAA (SEQ ID NO:339), sig=0.02) to 133 and 95 (for oligo 120, CCCAGG (SEQ ID NO:296), sig=0.49). The differences in expected occurrences reflect factors such as the G:C content of the human genome. Therefore, the differences among the oligonucleotides in their number of occurrences is less important than their over-representation; for example, oligo 2 (CAGCGG (SEQ ID NO:178)) is 36/9=four-fold over-represented, which has a probability of being due to random chance of one in fifty million (sig=7.75).
[0201]Table 6 also presents the number of STAR elements in which each over-represented oligonucleotide is found. For example, the most significant oligonucleotide, oligo 1 (CCCCAC (SEQ ID NO:177)), occurs 107 times, but is found in only 51 STARs, i.e., on average it occurs as two copies per STAR. The least abundant oligonucleotide, number 166 (AATCGG (SEQ ID NO:342)), occurs on average as a single copy per STAR (thirteen occurrences on eleven STARs); single-copy oligonucleotides occur frequently, especially for the lower-abundance oligos. At the other extreme, oligo 4 (CAGCCC (SEQ ID NO:527)) occurs on average three times in those STARs in which it is found (37 STARs). The most widespread oligonucleotide is number 120 (CCCAGG (SEQ ID NO:296)), which occurs on 58 STARs (on average twice per STAR), and the least widespread oligonucleotide is number 114 (CGTCGC (SEQ ID NO:290)), which occurs on only six STARs (and on average only once per STAR).
[0202]Results of dyad frequency analysis are given in Table 7. Seven hundred thirty (730) dyads were found to be over-represented in the set of STAR elements (sig≧0) compared to the reference sequence. The most significantly over-represented dyad, CCCN{2}CGG (SEQ ID NO:343), occurs 36 times among the 65 STAR elements, but is expected to occur only seven times. It has a significance coefficient of 9.31; in other words, the probability that its over-representation is due to chance is 1/109.31, i.e., less than one in two billion.
[0203]Three hundred ninety-seven (397) of the dyads have a significance coefficient greater than 1, and are, therefore, highly over-represented in the STAR elements. Among the over-represented dyads, their observed and expected occurrences, respectively, range from 9 and 1 (for five dyads (numbers 380, 435, 493, 640, and 665)) to 118 and 63 (for number 30 (AGGN{2}GGG (SEQ ID NO:372)), sig=4.44).
[0204]The oligonucleotides and dyads found to be over-represented in STAR elements by pattern frequency analysis were tested for their discriminative power by Linear Discriminant Analysis. Discriminant models were trained by step-wise selection of the best combination among the 50 most discriminant oligonucleotide (Table 6) or dyad (Table 7) patterns. The models achieved optimal error rates after incorporation of four (dyad) or five variables. The discriminative variables from oligo analysis are numbers 11, 30, 94, 122, and 160 (Table 6); those from dyad analysis are numbers 73, 194, 419, and 497 (Table 7).
[0205]The discriminant models were then used to classify the 65 STAR elements in the training set and their associated random sequences. The model using oligonucleotide variables classifies 46 of the 65 STAR elements as STAR elements (true positives); the dyad model classifies 49 of the STAR elements as true positives. In combination, the models classify 59 of the 65 STAR elements as STAR elements (91%; FIG. 18). The false positive rates (random sequences classified as STARs) were seven for the dyad model, eight for the oligonucleotide model, and 13 for the combined predictions of the two models (20%). The STAR elements of Table 3 that were not classified as STARs by LDA are STAR7, STAR22, STAR35, STAR44, STAR46, and STAR65 (SEQ ID NOS:7, 22, 35, 44, 46 and 65, respectively). These elements display stabilizing anti-repressor activity in functional assays, so the fact that they are not classified as STARs by LDA suggests that they represent another class (or classes) of STAR elements.
[0206]The models were then used to classify the 19 candidate STAR elements in the testing set listed in Table 8. The dyad model classifies 12 of these candidate STARs as STAR elements, and the oligonucleotide model classifies 14 as STARs. The combined number of the candidates that are classified as STAR elements is 15 (79%). This is a lower rate of classification than obtained with the training set of 65 STARs; this is expected for two reasons. First, the discriminant models were trained with the 65 STARs of Table 3, and discriminative variables based on this training set may be less well represented in the testing set. Second, the candidate STAR sequences in the testing set have not yet been fully characterized in terms of in vivo function, and may include elements with only weak anti-repression properties.
[0207]This analysis demonstrates the power of a statistical approach to bio-informatic classification of STAR elements. The STAR sequences contain a number of dyad and hexameric oligonucleotide patterns that are significantly over-represented in comparison with the human genome as a whole. These patterns may represent binding sites for proteins that confer STAR activity; in any case they form a set of sequence motifs that can be used to recognize STAR element sequences.
[0208]Using these patterns to recognize STAR elements by Discriminant Analysis, a high proportion of the elements obtained by the genetic screen of the invention are in fact classified as STARs. This reflects underlying sequence and functional similarities among these elements. An important aspect of the method described here (pattern frequency analysis followed by Discriminant Analysis) is that it can be reiterated; for example, by including the 19 candidate STAR elements of Table 8 with the 66 STAR elements of Table 3 into one training set, an improved discriminant model can be trained. This improved model can then be used to classify other candidate regulatory elements as STARs. Large-scale in vivo screening of genomic sequences using the method of the invention, combined with reiteration of the bio-informatic analysis, will provide a means of discriminating STAR elements that asymptotically approaches 100% recognition and prediction of elements as the genome is screened in its entirety. These stringent and comprehensive predictions of STAR function will ensure that all human STAR elements are recognized, and are available for use in improving transgene expression.
Example 13
Cloning and Characterization of STAR Elements from Arabidopsis thaliana
[0209]Transgene silencing occurs in transgenic plants at both the transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels (Meyer, 2000, Vance and Vaucheret, 2001). In either case, the desired result of transgene expression can be compromised by silencing; the low expression and instability of the transgene results in poor expression of desirable traits (e.g., pest resistance) or low yields of recombinant proteins. It also results in poor predictability: the proportion of transgenic plants that express the transgene at biotechnologically useful levels is low, which necessitates laborious and expensive screening of transformed individuals for those with beneficial expression characteristics. This example describes the isolation of STAR elements from the genome of the dicot plant Arabidopsis thaliana for use in preventing transcriptional transgene silencing in transgenic plants. Arabidopsis was chosen for this example because it is a well-studied model organism: it has a compact genome, it is amenable to genetic and recombinant DNA manipulations, and its genome has been sequenced (Bevan et al., 2001, Initiative, 2000, Meinke et al., 1998).
Materials and Methods
[0210]Genomic DNA was isolated from Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia as described (Stam et al., 1998) and partially digested with MboI. The digested DNA was size-fractionated to 0.5-2 kilobase pairs by agarose gel electrophoresis and purification from the gel (QIAquick® Gel Extraction Kit, QIAGEN® 28706), followed by ligation into the pSelect vector (supra). Transfection into the U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cell line and selection for zeocin resistance at low doxycycline concentration was performed as described (supra). Plasmids were isolated from zeocin resistant colonies and re-transfected into the U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cell line.
[0211]Sequencing of Arabidopsis genomic DNA fragments that conferred zeocin resistance upon re-transfection was performed as described (supra). The DNA sequences were compared to the sequence of the Arabidopsis genome by BLAST analysis ((Altschul et al., 1990); URL WorldWideWeb.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/blast/Blast).
[0212]STAR activity was tested further by measuring mRNA levels for the hygromycin- and zeocin-resistance genes in recombinant host cells by reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR). Cells of the U-2 OS/Tet-Off/lexA-HP1 cell line were transfected with pSelect plasmids containing Arabidopsis STAR elements, the Drosophila scs element, or containing no insert (supra). These were cultivated on hygromycin for two weeks at high doxycycline concentration, then the doxycycline concentration was lowered to 0.1 ng/ml to induce the lexA-HP1 repressor protein. After ten days, total RNA was isolated by the RNeasy® mini kit (QIAGEN® 74104) as described by the manufacturer. First-strand cDNA synthesis was carried out using the RevertAid® First Strand cDNA Synthesis kit (MBI Fermentas 1622) using oligo(dT) 18 primer as described by the manufacturer. An aliquot of the cDNA was used as the template in a PCR reaction using primers D58 (SEQ ID NO:145) and D80 (SEQ ID NO:148) (for the zeocin marker), and D70 (SEQ ID NO:146) and D71 (SEQ ID NO:147) (for the hygromycin marker), and Taq DNA polymerase (Promega M2661). The reaction conditions were 15-20 cycles of 94° C. for one minute, 54° C. for one minute, and 72° C. for 90 seconds. These conditions result in a linear relationship between input RNA and PCR product DNA. The PCR products were resolved by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the zeocin and hygromycin bands were detected by Southern blotting as described (Sambrook et al., 1989), using PCR products produced as above with purified pSelect plasmid as template. The ratio of the zeocin and hygromycin signals corresponds to the normalized expression level of the zeocin gene.
Results
[0213]The library of Arabidopsis genomic DNA in the pSelect vector comprised 69,000 primary clones in E. coli, 80% of which carried inserts. The average insert size was approximately 1000 base pairs; the library, therefore, represents approximately 40% of the Arabidopsis genome.
[0214]A portion of this library (representing approximately 16% of the Arabidopsis genome) was transfected into the U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cell line. Hygromycin selection was imposed to isolate transfectants, which resulted in 27,000 surviving colonies. These were then subjected to zeocin selection at low doxycycline concentration. Putative STAR-containing plasmids from 56 zeocin-resistant colonies were rescued into E. coli and re-transfected into U-2 OS/Tet-Off/LexA-HP1 cells. Forty-four of these plasmids (79% of the plasmids tested) conferred zeocin resistance on the host cells at low doxycycline concentrations, demonstrating that the plasmids carried STAR elements. This indicates that the pSelect screen in human U-2 OS cells is highly efficient at detection of STAR elements from plant genomic DNA.
[0215]The DNA sequences of these 44 candidate STAR elements were determined. Thirty-five of them were identified as single loci in the database of Arabidopsis nuclear genomic sequence (Table 9; SEQ ID NO:85-SEQ ID NO:119). Four others were identified as coming from the chloroplast genome, four were chimeras of DNA fragments from two loci, and one was not found in the Arabidopsis genome database.
[0216]The strength of the cloned Arabidopsis STAR elements was tested by assessing their ability to prevent transcriptional repression of the zeocin-resistance gene, using an RT-PCR assay. As a control for RNA input among the samples, the transcript levels of the hygromycin-resistance gene for each STAR transfection were assessed too. This analysis has been performed for 12 of the Arabidopsis STAR elements. The results (FIG. 19) demonstrate that the Arabidopsis STAR elements are superior to the Drosophila scs element (positive control) and the empty vector ("SV40"; negative control) in their ability to protect the zeocin-resistance gene from transcriptional repression. In particular, STAR-A28 (SEQ ID NO:112) and STAR-A30 (SEQ ID NO:114) enable two-fold higher levels of zeocin-resistance gene expression than the scs element (normalized to the internal control of hygromycin-resistance gene mRNA) when the lexA-HP1 repressor is expressed.
[0217]These results demonstrate that the method of the invention can be successfully applied to recovery of STAR elements from genomes of other species than human. Its successful application to STAR elements from a plant genome is particularly significant because it demonstrates the wide taxonomic range over which the method of the invention is applicable and because plants are an important target of biotechnological development.
Example 14
STAR Elements Function in CHO Cells
[0218]STAR elements function to block the effect of transcriptional repression influences on transgene expression units. Two of the benefits of STAR elements for heterologous protein production are an increased predictability to find high-expressing primary recombinant host cells as well as increased protein production or yield in these cells. Importantly, the disclosed STAR elements are human DNA sequences, isolated in the human U-2 OS osteosarcoma cell line. It is, therefore, an important question whether the human STAR elements are functional in a) cell lines derived from species other than man, and/or in b) human cell lines other than the U-2 OS osteosarcoma cell line. In this example the functionality of STAR 7 (SEQ ID NO:7) in (CHO) Chinese hamster ovary are illustrated.
Material and Methods
[0219]The STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element is tested in the ppGIZ-STAR7 vector (FIG. 20). The construction of the pPlug&Play-GFP-ires-Zeo (ppGIZ) vector is described below. Plasmid pGFP (Clontech 6010-1) is modified by insertion of a linker at the BsiWI site to yield pGFP-link. The linker (made by annealing oligonucleotides 5' GTACGGATATCAGATCTTTAATTAAG 3' (SEQ ID NO:124) and 5' GTACCTTAATTAAAGATCTGATATCC 3' (SEQ ID NO:125)) introduces sites for the PacI, BglII, and EcoRV restriction endonucleases. This creates the multiple cloning site MCSII for insertion of STAR elements. Then primers 5' ATCAGATCTGGCGCGCCATTTAAATCGTC TCGCGCGTTTCGGTGATGACGG 3' (SEQ ID NO:126) and 5' AGGCGGATCCGAATG TATTTAGAAAAATAAACAAATAGGGG 3' (SEQ ID NO:127) are used to amplify a region of 0.37 kb from pGFP, which is inserted into the BglII site of pIRES (Clontech 6028-1) to yield pIRES-stuf. This introduces sites for the AscI and SwaI restriction endonucleases at MCSI, and acts as a "stuffer fragment" to avoid potential interference between STAR elements and adjacent promoters. pIRES-stuf is digested with BglII and FspI to liberate a DNA fragment composed of the stuffer fragment, the CMV promoter, the IRES element (flanked by multiple cloning sites MCS A and MCS B), and the SV40 polyadenylation signal. This fragment is ligated with the vector backbone of pGFP-link produced by digestion with BamHI and StuI, to yield pIRES-link.
[0220]The open reading frames of the zeocin-resistance gene is inserted into the BamHI/NotI sites of MCS B in pIRES-link as follows: the zeocin-resistance ORF is amplified by PCR with primers 5' GATCGGATCCTTCGAAATGGCCAAGTTGACCAGTGC 3' (SEQ ID NO:128) and 5' AGGCGCGGCCGCAATTCTCAGTCCTGCTCCTC 3' (SEQ ID NO:129) from plasmid pEM7/zeo, digested with BamHI and NotI, and ligated with BamHI/NotI-digested pIRES-link to yield pIRES-link-zeo. The GFP reporter ORF was introduced into pIRES-link-zeo by amplification of phr-GFP-1 with primers 5' GATCGAATTCTCGCGAATGGTGAGCAAGCAGATCCTGAAG 3' (SEQ ID NO:130) and 5' AGGCGAATTCACCGGTGTTTAAACTTACACCCACTCGTGCAGGCTGCCCAGG 3' (SEQ ID NO:131), and insertion of the EcoRI-digested GFP cassette into the EcoRI site in MCS A of the pIRES-link-zeo plasmid. This created the ppGIZ (for ppGFP-IRES-zeo). STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) is cloned into the SalI site (5') and into the PacI site (3').
Transfection and Culture of CHO Cells
[0221]The Chinese Hamster Ovary cell line CHO-K1 (ATCC CCL-61) is cultured in HAMS-F12 medium+10% Fetal Calf Serum containing 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 micrograms/ml streptomycin at 37° C./5% CO2. Cells are transfected with the plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) as described by the manufacturer. Briefly, cells are seeded to culture vessels and grown overnight to 70-90% confluence. Lipofectamine reagent is combined with plasmid DNA at a ratio of 7.5 microliters per 3 microgram (e.g., for a 10 cm Petri dish, 20 micrograms DNA and 120 microliters Lipofectamine) and added after a 30-minute incubation at 25° C. to the cells. After a six-hour incubation, the transfection mixture is replaced with fresh medium, and the transfected cells are incubated further. After overnight cultivation, cells are trypsinized and seeded into fresh petri dishes with fresh medium with zeocin added to a concentration of 100 μg/ml and the cells are cultured further. When individual colonies become visible (approximately ten days after transfection) medium is removed and replaced with fresh medium without zeocin. Individual clones are isolated and transferred to 24-well plates in medium with zeocin. Expression of the GFP reporter gene is assessed approximately three weeks after transfection.
[0222]The tested constructs consist of a bicistronic gene with the GFP gene, an IRES and the Zeocin resistance gene under control of the CMV promoter, but either with or without STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element to flank the entire construct (FIG. 20). The constructs are transfected to CHO-K1 cells. Stable colonies are expanded before the GFP signal is determined on a XL-MCL Beckman Coulter flow cytometer. The mean of the GFP signal is taken as measure for the level of GFP expression and this is plotted in FIG. 20.
Results
[0223]FIG. 20 shows that flanking a GFP reporter gene that is under the control of the CMV promoter results in a higher number of CHO colonies that express significantly higher levels of GFP protein, as compared to the control without STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element. The STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element, therefore, conveys a higher degree of predictability of transgene expression in CHO cells. The highest GFP expression level in STAR-shielded CHO colonies is also higher than in STAR-less control colonies. In addition, when the tested colonies were further grown for another 30 days without Zeocin in the culture medium, the GFP expression levels in the STAR-shielded colonies remained equally high, whereas the GFP expression levels in the STAR-less colonies dropped to at feast below 50% of the original values. It is, therefore, concluded that STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) is able to convey higher as well as more stable expression levels to a transgene in CHO cells, this being a cell line derived from another species than man.
Example 15
STAR Elements Function in NSO Cells
[0224]STAR elements function to block the effect of transcriptional repression influences on transgene expression units. Two of the benefits of STAR elements for heterologous protein production are an increased predictability to find high-expressing primary recombinant host cells, as well as increased protein production or yield in these cells. Importantly, the disclosed STAR elements are human DNA sequences, isolated in the human U-2 OS osteosarcoma cell line. It is, therefore, an important question whether the human STAR elements are functional in a) cell lines derived from species other than man, and/or in b) human cell lines other than the U-2 OS osteosarcoma cell line. In this example the functionality of STAR 7 (SEQ ID NO:7) in non-secreting mouse myeloma (NSO) cells are illustrated.
Materials and Methods
[0225]The tested constructs are the same as described in Example 14. NSO (Non-Secreting mouse myeloma) cells (ECACC 85110503) are suspension cells that are cultured in RPMI 1640 medium+10% Fetal Calf Serum containing 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 micrograms/ml streptomycin at 37° C./5% CO2. Cells are transfected with the plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) as described by the manufacturer. Briefly, cells are seeded to culture vessels and grown overnight to 4×105/ml. Lipofectamine reagent is combined with plasmid DNA at a ratio of 3 microliters per microgram DNA (e.g., for a 10 cm Petri dish, 20 micrograms DNA and 60 microliters Lipofectamine) and added after 30 minutes incubation at 25° C. temperature to the cells. After overnight incubation, the transfection mixture is replaced with fresh medium and the transfected cells are incubated further. After another overnight incubation, zeocin is added to a concentration of 100 μg/ml and the cells are cultured and further incubated for three days. Then the cells are seeded in 96-well plates in such dilutions that one well will contain ˜1 cell. After ten days growing colonies are transferred to 24-well plates.
Results
[0226]FIG. 21 shows that flanking a GFP reporter gene that is under the control of the CMV promoter results in a higher number of NSO colonies that express significantly higher levels of GFP protein, as compared to the control without STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element. The STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element, therefore, conveys a higher degree of predictability of transgene expression in NSO cells. The highest GFP expression level in STAR-shielded NSO colonies is also higher than in STAR-less control colonies. It is, therefore, concluded that STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) is able to convey higher expression levels to a transgene in NSO cells, this being a cell line derived from another species than man.
Example 16
STAR Elements Function in Human 293 Cells
[0227]STAR elements function to block the effect of transcriptional repression influences on transgene expression units. Two of the benefits of STAR elements for heterologous protein production are an increased predictability to find high-expressing primary recombinant host cells as well as increased protein production or yield in these cells. Importantly, the disclosed STAR elements are human DNA sequences, isolated in the human U-2 OS osteosarcoma cell line. It is, therefore, an important question whether the human STAR elements are functional in a) cell lines derived from species other than man, and/or in b) human cell lines other than the U-2 OS osteosarcoma cell line. In this example, the functionality of STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) in human 293 cells are illustrated.
Materials and Methods
[0228]The tested constructs are the same as described in Example 14. The 293 cell line (ATCC CRL-1573) is derived from human embryonal kidney (immortalized by adenovirus 5 transfection) and is cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium+10% Fetal Calf Serum containing 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/ml penicillin, and 100 micrograms/ml streptomycin at 37° C./5% CO2. Cells are transfected with the plasmids using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) as described by the manufacturer. Selection and propagation of the 293 colonies are as described in Example 14 for U-2 OS cells.
Results
[0229]FIG. 22 shows that flanking a GFP reporter gene that is under the control of the CMV promoter results in a higher number of 293 colonies that express significantly higher levels of GFP protein, as compared to the control without STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element. The STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) element, therefore, conveys a higher degree of predictability of transgene expression in 293 cells. The highest GFP expression level in STAR-shielded colonies is also higher than in STAR-less control colonies. It is, therefore, concluded that STAR7 (SEQ ID NO:7) is able to convey higher expression levels to a transgene in 293 cells, this being another human cell line, distinct from the human U-2 OS cell line.
TABLE-US-00001 TABLE 1 Biopharmaceutical Proteins, Their Tissue or Cell Type of Origin Protein Tissue/Somatic Cells Cell Lines (ATCC #)1 Indications alpha-1 Antitrypsin Liver, leukocytes Hep G2 (HB-8065) Cystic fibrosis, emphysema alpha-Galactosidase A; -Glucosidase Fibroblasts WI 38 (CCL-75) Fabry disease; Pompe's disease Antibodies (monoclonal, Lymphocytes Transfectomas Various therapeutic single-chain, etc) strategies Antithrombin III Liver Hep G2 (HB-8065) Thrombophilia Calcitonin Thyroid (parafollicular cells) TT (CRL-1803) Osteoporosis Ciliary neurotrophic factor Neural tissue (e.g., astrocytes) HCN-1A (CRL-10442) Motor neuron disease Epidermal Growth Factor Kidney G-401 (CRL-1441) Wound healing Erythropoietin Liver, kidney Hep G2 (HB-8065), Anemia G-401 (CRL-1441) Factors VII, VIII, IX Endothelial cells HUV-EC-C(CRL-1730) Hemophilia Famoxin (recombinant gAcrp30) Adipocytes NA2 Obesity Fibroblast growth factor (basic) Cerebral cortex, hypothalamus HCN-1A (CRL-10442) Wound healing, angiogenesis Gastric lipase Pancreas BxPC-3 (CRL-1687) Pancreatic insufficiency, cystic fibrosis Glucocerebrosidase Macrophages U-937 (CRL-1593.2) Gaucher disease Granulocyte macrophage-colony T-lymphocytes J.CaM1.6 (CRL-2063) Chemotherapy neutropenia stimulating factor Human growth hormone Pituitary gland HP75 (CRL-2506) Growth retardation, Turner's (somatotropin) syndrome Human serum albumin Liver (hepatocytes) Hep G2 (HB-8065) Blood replacement (surgery, burns) Insulin Pancreas (Islet beta cells) BxPC-3 (CRL-1687) Diabetes Interferons alpha Leukocytes WBC264-9C (HB-8902) Cancer, hepatitis C Interferons beta Fibroblasts WI 38 (CCL-75) Multiple sclerosis Interleukin-2, -4, -10 T-lymphocytes J.CaM1.6 (CRL-2063) Cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, hepatitis Interleukin-18 Monocytes and macrophages U-937 (CRL-1593.2) Cancer, bacterial infections Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Epithelium HBE4-E6/E7 (CRL-2078) Rheumatoid arthritis Soluble Tumor Necrosis Factor Placenta, spleen, fibroblasts BeWo (CCL-98) Rheumatoid arthritis, receptor multiple sclerosis van Willebrand's factor Endothelial cells HUV-EC-C (CRL-1730) Hemophilia 1These cell lines are offered only as examples of cultured cells corresponding to the tissues and somatic cells; ATCC #: American Type Culture Collection accession number 2NA: Not Available; adipocytes can be differentiated from various other cell types
TABLE-US-00002 TABLE 2 Oligonucleotides used for polymerase chain reactions (PCR primers) or DNA mutagenesis (SEQ ID NOS:134-176) SEQ ID NO: Number Sequence 134 C65 AACAAGCTTGATATCAGATCTGCTAGCTTGGTCGAGC TGATACTTCCC 135 C66 AAACTCGAGCGGCCGCGAATTCGTCGACTTTACCACT CCCTATCAGTGATAGAG 136 C67 AAACCGCGGCATGGAAGACGCCAAAAACATAAAGAAA GG 137 C68 TATGGATCCTAGAATTACACGGCGATCTTTCC 138 C81 AAACCATGGCCGAGTACAAGCCCACGGTGCGCC 139 C82 AAATCTAGATCAGGCACCGGGCTTGCGGGTCATGC 140 C85 CATTTCCCCGAAAAGTGCCACC 141 D30 TCACTGCTAGCGAGTGGTAAACTC 142 D41 GAAGTCGACGAGGCAGGCAGAAGTATGC 143 D42 GAGCCGCGGTTTAGTTCCTCACCTTGTCG 144 D51 TCTGGAAGCTTTGCTGAAGAAAC 145 D58 CCAAGTTGACCAGTGCC 146 D70 TACAAGCCAACCACGGCCT 147 D71 CGGAAGTGCTTGACATTGGG 148 D80 GTTCGTGGACACGACCTCCG 149 D89 GGGCAAGATGTCGTAGTCAGG 150 D90 AGGCCCATGGTCACCTCCATCGCTACTGTG 151 D91 CTAATCACTCACTGTGTAAT 152 D93 AATTACAGGCGCGCC 153 D94 AATTGGCGCGCCTGT 154 D95 TGCTTTGCATACTTCTGCCTGCCTC 155 E12 TAGGGGGGATCCAAATGTTC 156 E13 CCTAAAAGAAGATCTTTAGC 157 E14 AAGTGTTGGATCCACTTTGG 158 E15 TTTGAAGATCTACCAAATGG 159 E16 GTTCGGGATCCACCTGGCCG 160 E17 TAGGCAAGATCTTGGCCCTC 161 E18 CCTCTCTAGGGATCCGACCC 162 E19 CTAGAGAGATCTTCCAGTAT 163 E20 AGAGTTCCGGATCCGCCTGG 164 E21 CCAGGCAGACTCGGAACTCT 165 E22 TGGTGAAACCGGATCCCTAC 166 E23 AGGTCAGGAGATCTAGACCA 167 E25 CCATTTTCGCTTCCTTAGCTCC 168 E42 CGATGTAACCCACTCGTGCACC 169 E57 AGAGATCTAGGATAATTTCG 170 E92 AGGCGCTAGCACGCGTTCTACTCTTTTCCTACTCTG 171 E93 GATCAAGCTTACGCGTCTAAAGGCATTTTATATAG 172 E94 AGGCGCTAGCACGCGTTCAGAGTTAGTGATCCAGG 173 E95 GATCAAGCTTACGCGTCAGTAAAGGTTTCGTATGG 174 E96 AGGCGCTAGCACGCGTTCTACTCTTTCATTACTCTG 175 E97 CGAGGAAGCTGGAGAAGGAGAAGCTG 176 E98 CAAGGGCCGCAGCTTACACATGTTC
TABLE-US-00003 TABLE 3 STAR elements of the invention, including genomic location and length (SEQ ID NOS: 1-66) STAR SEQ ID NO: Location1 Length 1 1 2q31.1 750 2 2 7p15.2 916 3 3 15q11.2 and 10q22.2 2132 4 4 1p31.1 and 14q24.1 1625 5 5 20q13.32 1571 6 6 2p21 1173 7 7 1q34 2101 8 8 9q32 1839 9 9 10p15.3 1936 10 10 Xp11.3 1167 11 11 2p25.1 1377 12 12 5q35.3 1051 13 13 9q34.3 1291 14 14 22q11.22 732 15 15 1p36.31 1881 16 16 1p21.2 1282 17 17 2q31.1 793 18 18 2q31.3 497 19 19 6p22.1 1840 20 20 8p13.3 780 21 21 6q24.2 620 22 22 2q12.2 1380 23 23 6p22.1 1246 24 24 1q21.2 948 25 25 1q21.3 1067 26 26 1q21.1 540 27 27 1q23.1 1520 28 28 22q11.23 961 29 29 2q13.31 2253 30 30 22q12.3 1851 31 31 9q34.11 and 22q11.21 1165 32 32 21q22.2 771 33 33 21q22.2 1368 34 34 9q34.14 755 35 35 7q22.3 1211 36 36 21q22.2 1712 37 37 22q11.23 1331 38 38 22q11.1 and 22q11.1 ~1000 39 39 22q12.3 2331 40 40 22q11.21 1071 41 41 22q11.21 1144 42 42 22q11.1 735 43 43 14q24.3 1231 44 44 22q11.1 1591 45 45 22q11.21 1991 46 46 22q11.23 1871 47 47 22q11.21 1082 48 48 22q11.22 1242 49 49 Chr 12 random clone, and 1015 3q26.32 50 50 6p21.31 2361 51 51 5q21.3 2289 52 52 7p15.2 1200 53 53 Xp11.3 1431 54 54 4q21.1 981 55 55 15q13.1 501 56 56 includes 3p25.3 741 57 57 4q35.2 1371 58 58 21q11.2 1401 59 59 17 random clone 872 60 60 4p16.1 and 6q27 2068 61 61 7p14.3 and 11q25 1482 62 62 14q24.3 1011 63 63 22q13.3 1421 64 64 17q11.2 1414 65 65 7q21.11 = 28.4 1310 66 66 20q13.33 and 6q14.1 ~2800 1Chromosomal location is determined by BLAST search of DNA sequence data from the STAR elements against the human genome database. The location is given according to standard nomenclature referring to the cytogenetic ideogram of each chromosome; e.g., 1p2.3 is the third cytogenetic sub-band of the second cytogenetic band of the short arm of chromosome 1 (WorldWideWeb.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Class/MLACourse/Genetics/chrombanding.html- ).F, forward sequencing reaction result; R, reverse sequencing reaction result.
TABLE-US-00004 TABLE 4 STAR elements convey stability over time on transgene expression1 Cell Divisions2 Luciferase Expression3 STAR6 (SEQ ID NO: 6) 42 18,000 plus puromycin 60 23,000 84 20,000 108 16,000 STAR6 (SEQ ID NO: 6) 84 12,000 without puromycin4 108 15,000 144 12,000 1Plasmid pSDH-Tet-STAR6 was transfected into U-2 OS cells, and clones were isolated and cultivated in doxycycline-free medium as described in Example 1. Cells were transferred to fresh culture vessels weekly at a dilution of 1:20. 2The number of cell divisions is based on the estimation that in one week the culture reaches cell confluence, which represents ~6 cell divisions. 3Luciferase was assayed as described in Example 1. 4After 60 cell divisions the cells were transferred to two culture vessels; one was supplied with culture medium that contained puromycin, as for the first 60 cell divisions, and the second was supplied with culture medium lacking antibiotic.
TABLE-US-00005 TABLE 5 Human STAR elements and their putative mouse orthologs and paralogs NUMBER STAR Human1 Mouse2 Similarity3 SEQ ID NO: 1 1 2q31.1 2D 600 bp 69% 1 2 2 7p15.2 6B3 909 bp 89% 2 3 3a 5q33.3 11B2 248 bp 83% 3 4 3b 10q22.2 14B 1. 363 bp 89% 3 2. 163 bp 86% 5 6 2p21 17E4 437 bp 78% 6 6 12 5q35.3 11b1.3 796 bp 66% 12 7 13 9q34.3 2A3 753 bp 77% 13 8 18 2q31.3 2E1 497 bp 72% 18 9 36 21q22.2 16C4 166 bp 79% 36 10 40 22q11.1 6F1 1. 270 bp 75% 40 2. 309 bp 70% 11 50 6p21.31 17B1 1. 451 bp 72% 50 2. 188 bp 80% 3. 142 bp 64% 12 52 7p15.2 6B3 1. 846 bp 74% 52 2. 195 bp 71% 13 53 Xp11.3 XA2 364 bp 64% 53 14 54 4q21.1 5E3 1. 174 bp 80% 54 2. 240 bp 73% 3. 141 bp 67% 4. 144 bp 68% 15 61a 7p14.3 6B3 188 bp 68% 61 1Cytogenetic location of STAR element in the human genome. 2Cytogenetic location of STAR element ortholog in the mouse genome. 3Length of region(s) displaying high sequence similarity, and percentage similarity. In some cases more than one block of high similarity occurs; in those cases, each block is described separately. Similarity <60% is not considered significant.
TABLE-US-00006 TABLE 6 Oligonucleotide patterns (6 base pairs) over-represented in STAR elements. Ob- Ex- Signif- Number Oligo- served pected icance of SEQ Num- nucleotide occur- occur- coef- matching ID ber sequence rences rences ficient STARs NO: 1 CCCCAC 107 49 8.76 51 177 2 CAGCGG 36 9 7.75 23 178 3 GGCCCC 74 31 7.21 34 179 4 CAGCCC 103 50 7.18 37 180 5 GCCCCC 70 29 6.97 34 181 6 CGGGGC 40 12 6.95 18 182 7 CCCCGC 43 13 6.79 22 183 8 CGGCAG 35 9 6.64 18 184 9 AGCCCC 83 38 6.54 40 185 10 CCAGGG 107 54 6.52 43 186 11 GGACCC * 58 23 6.04 35 187 12 GCGGAC 20 3 5.94 14 188 13 CCAGCG 34 10 5.9 24 189 14 GCAGCC 92 45 5.84 43 190 15 CCGGCA 28 7 5.61 16 191 16 AGCGGC 27 7 5.45 17 192 17 CAGGGG 86 43 5.09 43 193 18 CCGCCC 43 15 5.02 18 194 19 CCCCCG 35 11 4.91 20 195 20 GCCGCC 34 10 4.88 18 196 21 GCCGGC 22 5 4.7 16 197 22 CGGACC 19 4 4.68 14 198 23 CGCCCC 35 11 4.64 19 199 24 CGCCAG 28 8 4.31 19 200 25 CGCAGC 29 8 4.29 20 201 26 CAGCCG 32 10 4 24 202 27 CCCACG 33 11 3.97 26 203 28 GCTGCC 78 40 3.9 43 204 29 CCCTCC 106 60 3.87 48 205 30 CCCTGC * 92 50 3.83 42 206 31 CACCCC 77 40 3.75 40 207 32 GCGCCA 30 10 3.58 23 208 33 AGGGGC 70 35 3.55 34 209 34 GAGGGC 66 32 3.5 40 210 35 GCGAAC 14 2 3.37 13 211 36 CCGGCG 17 4 3.33 12 212 37 AGCCGG 34 12 3.29 25 213 38 GGAGCC 67 34 3.27 40 214 39 CCCCAG 103 60 3.23 51 215 40 CCGCTC 24 7 3.19 19 216 41 CCCCTC 81 44 3.19 43 217 42 CACCGC 33 12 3.14 22 218 43 CTGCCC 96 55 3.01 42 219 44 GGGCCA 68 35 2.99 39 220 45 CGCTGC 28 9 2.88 22 221 46 CAGCGC 25 8 2.77 19 222 47 CGGCCC 28 10 2.73 19 223 48 CCGCCG 19 5 2.56 9 224 49 CCCCGG 30 11 2.41 17 225 50 AGCCGC 23 7 2.34 17 226 51 GCACCC 55 27 2.31 38 227 52 AGGACC 54 27 2.22 33 228 53 AGGGCG 24 8 2.2 18 229 54 CAGGGC 81 47 2.18 42 230 55 CCCGCC 45 21 2.15 20 231 56 GCCAGC 66 36 2.09 39 232 57 AGCGCC 21 6 2.09 18 233 58 AGGCCC 64 34 2.08 32 234 59 CCCACC 101 62 2.05 54 235 60 CGCTCA 21 6 2.03 17 236 61 AACGCG 9 1 1.96 9 237 62 GCGGCA 21 7 1.92 14 238 63 AGGTCC 49 24 1.87 36 239 64 CCGTCA 19 6 1.78 14 240 65 CAGAGG 107 68 1.77 47 241 66 CCCGAG 33 14 1.77 22 242 67 CCGAGG 36 16 1.76 25 243 68 CGCGGA 11 2 1.75 8 244 69 CCACCC 87 53 1.71 45 245 70 CCTCGC 23 8 1.71 20 246 71 CAAGCC 59 32 1.69 40 247 72 TCCGCA 18 5 1.68 17 248 73 CGCCGC 18 5 1.67 9 249 74 GGGAAC 55 29 1.63 39 250 75 CCAGAG 93 58 1.57 49 251 76 CGTTCC 19 6 1.53 16 252 77 CGAGGA 23 8 1.5 19 253 78 GGGACC 48 24 1.48 31 254 79 CCGCGA 10 2 1.48 8 255 80 CCTGCG 24 9 1.45 17 256 81 CTGCGC 23 8 1.32 14 257 82 GACCCC 47 24 1.31 33 258 83 GCTCCA 66 38 1.25 39 259 84 CGCCAC 33 15 1.19 21 260 85 GCGGGA 23 9 1.17 18 261 86 CTGCGA 18 6 1.15 15 262 87 CTGCTC 80 49 1.14 50 263 88 CAGACG 23 9 1.13 19 264 89 CGAGAG 21 8 1.09 17 265 90 CGGTGC 18 6 1.06 16 266 91 CTCCCC 84 53 1.05 47 267 92 GCGGCC 22 8 1.04 14 268 93 CGGCGC 14 4 1.04 13 269 94 AAGCCC * 60 34 1.03 42 270 95 CCGCAG 24 9 1.03 17 271 96 GCCCAC 59 34 0.95 35 272 97 CACCCA 92 60 0.93 49 273 98 GCGCCC 27 11 0.93 18 274 99 ACCGGC 15 4 0.92 13 275 100 CTCGCA 16 5 0.89 14 276 101 ACGCTC 16 5 0.88 12 277 102 CTGGAC 58 33 0.88 32 278 103 GCCCCA 67 40 0.87 38 279 104 ACCGTC 15 4 0.86 11 280 105 CCCTCG 21 8 0.8 18 281 106 AGCCCG 22 8 0.79 14 282 107 ACCCGA 16 5 0.78 13 283 108 AGCAGC 79 50 0.75 41 284 109 ACCGCG 14 4 0.69 7 285 110 CGAGGC 29 13 0.69 24 286 111 AGCTGC 70 43 0.64 36 287 112 GGGGAC 49 27 0.64 34 288 113 CCGCAA 16 5 0.64 12 289 114 CGTCGC 8 1 0.62 6 290 115 CGTGAC 17 6 0.57 15 291 116 CGCCCA 33 16 0.56 22 292 117 CTCTGC 97 65 0.54 47 293 118 AGCGGG 21 8 0.52 17 294 119 ACCGCT 15 5 0.5 11 295 120 CCCAGG 133 95 0.49 58 296 121 CCCTCA 71 45 0.49 39 297
122 CCCCCA * 77 49 0.49 42 298 123 GGCGAA 16 5 0.48 14 299 124 CGGCTC 29 13 0.47 19 300 125 CTCGCC 20 8 0.46 17 301 126 CGGAGA 20 8 0.45 14 302 127 TCCCCA 95 64 0.43 52 303 128 GACACC 44 24 0.42 33 304 129 CTCCGA 17 6 0.42 13 305 130 CTCGTC 17 6 0.42 14 306 131 CGACCA 13 4 0.39 11 307 132 ATGACG 17 6 0.37 12 308 133 CCATCG 17 6 0.37 13 309 134 AGGGGA 78 51 0.36 44 310 135 GCTGCA 77 50 0.35 43 311 136 ACCCCA 76 49 0.33 40 312 137 CGGAGC 21 9 0.33 16 313 138 CCTCCG 28 13 0.32 19 314 139 CGGGAC 16 6 0.3 10 315 140 CCTGGA 88 59 0.3 45 316 141 AGGCGA 18 7 0.29 17 317 142 ACCCCT 54 32 0.28 36 318 143 GCTCCC 56 34 0.27 36 319 144 CGTCAC 16 6 0.27 15 320 145 AGCGCA 16 6 0.26 11 321 146 GAAGCC 62 38 0.25 39 322 147 GAGGCC 79 52 0.22 42 323 148 ACCCTC 54 32 0.22 33 324 149 CCCGGC 37 20 0.21 21 325 150 CGAGAA 20 8 0.2 17 326 151 CCACCG 29 14 0.18 20 327 152 ACTTCG 16 6 0.17 14 328 153 GATGAC 48 28 0.17 35 329 154 ACGAGG 23 10 0.16 18 330 155 CCGGAG 20 8 0.15 18 331 156 ACCCAC 60 37 0.12 41 332 157 CTGGGC 105 74 0.11 50 333 158 CCACGG 23 10 0.09 19 334 159 CGGTCC 13 4 0.09 12 335 160 AGCACC * 54 33 0.09 40 336 161 ACACCC 53 32 0.08 38 337 162 AGGGCC 54 33 0.08 30 338 163 CGCGAA 6 1 0.02 6 339 164 GAGCCC 58 36 0.02 36 340 165 CTGAGC 71 46 0.02 45 341 166 AATCGG 13 4 0.02 11 342 The patterns are ranked according to significance coefficient. These were determined using RSA-Tools with the sequence of the human genome as reference. Patterns that comprise the most discriminant variables in Linear Discriminant Analysis are indicated with an asterisk. (SEQ ID NOS:177-342)
TABLE-US-00007 TABLE 7 Dyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements. Signifi- Observed Expected cance occur- occur- coef- SEQ ID Number Dyad sequence rences rences ficient NO 1 CCCN{2}CGG 36 7 9.31 343 2 CCGN{6}CCC 40 10 7.3 344 3 CAGN{0}CGG 36 8 7.13 345 4 CGCN{15}CCC 34 8 6.88 346 5 CGGN{9}GCC 33 7 6.82 347 6 CCCN{9}CGC 35 8 6.72 348 7 CCCN{1}GCG 34 8 6.64 349 8 CCCN{0}CAC 103 48 6.61 350 9 AGCN{16}CCG 29 6 5.96 351 10 CCCN{4}CGC 34 8 5.8 352 11 CGCN{13}GGA 26 5 5.77 353 12 GCGN{16}CCC 30 7 5.74 354 13 CGCN{5}GCA 25 5 5.49 355 14 CCCN{14}CCC 101 49 5.43 356 15 CTGN{4}CGC 34 9 5.41 357 16 CCAN{12}GCG 28 6 5.37 358 17 CGGN{11}CAG 36 10 5.25 359 18 CCCN{5}GCC 75 33 4.87 360 19 GCCN{0}CCC 64 26 4.81 361 20 CGCN{4}GAC 19 3 4.78 362 21 CGGN{0}CAG 33 9 4.76 363 22 CCCN{3}CGC 32 8 4.67 364 23 CGCN{1}GAC 20 3 4.58 365 24 GCGN{2}GCC 29 7 4.54 366 25 CCCN{4}GCC 76 34 4.53 367 26 CCCN{1}CCC 103 52 4.53 368 27 CCGN{13}CAG 33 9 4.5 369 28 GCCN{4}GGA 64 27 4.48 370 29 CCGN{3}GGA 26 6 4.46 371 30 AGGN{2}GGG 118 63 4.44 372 31 CACN{5}GCG 22 4 4.42 373 32 CGCN{17}CCA 27 6 4.39 374 33 CCCN{9}GGC 69 30 4.38 375 34 CCTN{5}GCG 28 7 4.37 376 35 GCGN{0}GAC 19 3 4.32 377 36 GCCN{0}GGC 40 7 4.28 378 37 GCGN{2}CCC 26 6 4.27 379 38 CCGN{11}CCC 32 9 4.17 380 39 CCCN{8}TCG 23 5 4.12 381 40 CCGN{17}GCC 30 8 4.12 382 41 GGGN{5}GGA 101 52 4.11 383 42 GGCN{6}GGA 71 32 4.1 384 43 CCAN{4}CCC 96 48 4.1 385 44 CCTN{14}CCG 32 9 4.09 386 45 GACN{12}GGC 45 16 4.07 387 46 CGCN{13}CCC 30 8 4.04 388 47 CAGN{16}CCC 92 46 4.02 389 48 AGCN{10}GGG 75 35 3.94 390 49 CGGN{13}GGC 30 8 3.93 391 50 CGGN{1}GCC 30 8 3.92 392 51 AGCN{0}GGC 26 6 3.9 393 52 CCCN{16}GGC 64 28 3.89 394 53 GCTN{19}CCC 67 29 3.87 395 54 CCCN{16}GGG 88 31 3.81 396 55 CCCN{9}CGG 30 8 3.77 397 56 CCCN{10}CGG 30 8 3.76 398 57 CCAN{0}GCG 32 9 3.75 399 58 GCCN{17}CGC 26 6 3.74 400 59 CCTN{6}CGC 27 7 3.73 401 60 GGAN{1}CCC 63 27 3.71 402 61 CGCN{18}CAC 24 5 3.7 403 62 CGCN{20}CCG 21 4 3.69 404 63 CCGN{0}GCA 26 6 3.69 405 64 CGCN{20}CCC 28 7 3.69 406 65 AGCN{15}CCC 67 30 3.65 407 66 CCTN{7}GGC 69 31 3.63 408 67 GCCN{5}CGC 32 9 3.61 409 68 GCCN{14}CGC 28 7 3.59 410 69 CAGN{11}CCC 89 45 3.58 411 70 GGGN{16}GAC 53 21 3.57 412 71 CCCN{15}GCG 25 6 3.57 413 72 CCCN{0}CGC 37 12 3.54 414 73 CCCN{16}AGC * 67 30 3.54 415 74 AGGN{9}GGG 96 50 3.52 416 75 CGCN{12}CTC 28 7 3.46 417 76 CACN{8}CGC 23 5 3.43 418 77 CCAN{7}CCG 31 9 3.42 419 78 CGGN{1}GCA 25 6 3.41 420 79 CGCN{14}CCC 29 8 3.4 421 80 AGCN{0}CCC 76 36 3.4 422 81 CGCN{13}GTC 18 3 3.37 423 82 GCGN{3}GCA 26 7 3.35 424 83 CGGN{0}GGC 34 11 3.35 425 84 GCCN{14}CCC 68 31 3.33 426 85 ACCN{7}CGC 21 4 3.32 427 86 AGGN{7}CGG 33 10 3.31 428 87 CCCN{16}CGA 22 5 3.3 429 88 CGCN{6}CAG 31 9 3.29 430 89 CAGN{11}GCG 29 8 3.29 431 90 CCGN{12}CCG 19 4 3.26 432 91 CGCN{18}CAG 27 7 3.24 433 92 CAGN{1}GGG 80 39 3.21 434 93 CGCN{0}CCC 32 10 3.2 435 94 GCGN{18}GCC 26 7 3.18 436 95 CGGN{15}GGC 27 7 3.15 437 96 CCCN{15}AGG 72 34 3.14 438 97 AGGN{20}GCG 26 7 3.14 439 98 CGGN{5}CTC 26 7 3.13 440 99 TCCN{17}CGA 23 5 3.12 441 100 GCGN{4}CCC 30 9 3.08 442 101 CCCN{2}CGC 30 9 3.07 443 102 CGTN{3}CAG 28 8 3.06 444 103 CCGN{13}GAG 27 7 3.05 445 104 CTCN{6}CGC 28 8 3.04 446 105 CGCN{4}GAG 21 5 3.03 447 106 GCGN{5}GGA 24 6 3.03 448 107 CCGN{1}CAG 27 7 3.01 449 108 CGCN{11}CCG 18 3 2.99 450 109 GCGN{19}CCC 26 7 2.98 451 110 CGCN{18}GAA 21 5 2.98 452 111 GGGN{19}GGA 78 39 2.95 453 112 CCAN{1}CGG 24 6 2.94 454 113 CCCN{7}GCG 25 6 2.94 455 114 AGGN{10}CCC 84 43 2.92 456 115 CCAN{0}GGG 97 52 2.88 457 116 CAGN{10}CCC 82 41 2.87 458 117 CCGN{18}CCG 19 4 2.86 459 118 CCGN{18}GGC 26 7 2.85 460 119 CCCN{2}GCG 24 6 2.84 461 120 CGCN{1}GGC 25 7 2.83 462 121 CCGN{5}GAC 19 4 2.81 463
122 GGAN{0}CCC 52 22 2.8 464 123 CCCN{1}CCG 29 9 2.78 465 124 CCCN{15}ACG 23 6 2.75 466 125 AGCN{8}CCC 66 31 2.73 467 126 CCCN{3}GGC 60 27 2.71 468 127 AGGN{9}CGG 31 10 2.7 469 128 CCCN{14}CGC 27 8 2.7 470 129 CCGN{0}CCG 19 4 2.7 471 130 CGCN{8}AGC 23 6 2.69 472 131 CGCN{19}ACC 21 5 2.68 473 132 GCGN{17}GAC 17 3 2.66 474 133 AGCN{1}GCG 24 6 2.63 475 134 CCGN{11}GGC 31 10 2.63 476 135 CGGN{4}AGA 26 7 2.63 477 136 CGCN{14}CCG 17 3 2.62 478 137 CCTN{20}GCG 24 6 2.62 479 138 CCAN{10}CGC 26 7 2.61 480 139 CCCN{20}CAC 69 33 2.6 481 140 CCGN{11}GCC 27 8 2.6 482 141 CGCN{18}CCC 26 7 2.59 483 142 CGGN{15}CGC 16 3 2.57 484 143 CGCN{16}GCC 24 6 2.55 485 144 CGCN{20}GGC 23 6 2.54 486 145 CGCN{19}CCG 18 4 2.52 487 146 CGGN{10}CCA 28 8 2.51 488 147 CGCN{17}CCC 26 7 2.51 489 148 CGCN{11}ACA 23 6 2.51 490 149 CGGN{0}ACC 17 3 2.5 491 150 GCGN{10}GCC 24 6 2.49 492 151 GCGN{8}GAC 17 3 2.49 493 152 CCCN{15}GGG 84 32 2.44 494 153 CGGN{16}GGC 27 8 2.44 495 154 CGCN{16}CCA 23 6 2.42 496 155 GCCN{3}CCC 73 36 2.4 497 156 CAGN{4}GGG 94 51 2.4 498 157 CCCN{6}GCG 23 6 2.38 499 158 CCGN{16}CGC 17 3 2.38 500 159 CCCN{17}GCA 61 28 2.37 501 160 CGCN{13}TCC 24 6 2.37 502 161 GCCN{1}CGC 29 9 2.36 503 162 CCGN{19}GAG 26 7 2.35 504 163 GGGN{10}GGA 89 48 2.35 505 164 CAGN{5}CCG 32 11 2.35 506 165 CGCN{3}AGA 19 4 2.32 507 166 GCCN{0}GCC 29 9 2.32 508 167 CCCN{8}GGC 61 28 2.31 509 168 CCTN{6}GCG 22 6 2.29 510 169 GACN{6}CCC 48 20 2.29 511 170 CGGN{1}CCC 26 8 2.27 512 171 CCCN{15}CCG 30 10 2.27 513 172 CAGN{9}CCC 84 44 2.26 514 173 CGGN{10}GGC 27 8 2.26 515 174 CGAN{10}ACG 10 1 2.26 516 175 GCGN{3}TCC 21 5 2.26 517 176 CCCN{3}GCC 75 38 2.24 518 177 GCGN{1}ACC 17 3 2.24 519 178 CCGN{9}AGG 27 8 2.23 520 179 CGCN{16}CAG 26 8 2.23 521 180 GGCN{0}CCC 62 29 2.22 522 181 AGGN{12}CCG 26 8 2.19 523 182 CCGN{0}GCG 16 3 2.19 524 183 CCGN{2}GCC 30 10 2.18 525 184 CCGN{11}GTC 19 4 2.17 526 185 CAGN{0}CCC 88 47 2.17 527 186 CCCN{5}CCG 32 11 2.17 528 187 GCCN{20}CCC 66 32 2.15 529 188 GACN{2}CGC 18 4 2.14 530 189 CGCN{6}CAC 23 6 2.13 531 190 AGGN{14}GCG 25 7 2.1 532 191 GACN{5}CGC 17 3 2.1 533 192 CCTN{19}CCG 29 9 2.1 534 193 CCGN{12}GGA 24 7 2.08 535 194 GGCN{9}GAC * 44 18 2.08 536 195 AGGN{10}GGG 94 52 2.07 537 196 CCGN{10}GAG 25 7 2.07 538 197 CGCN{6}GGA 20 5 2.06 539 198 CGCN{7}AGC 23 6 2.04 540 199 CCAN{13}CGG 26 8 2.03 541 200 CGGN{6}GGA 25 7 2.03 542 201 CGCN{19}GCC 24 7 2.03 543 202 CCAN{12}CGC 24 7 2.02 544 203 CGGN{1}GGC 41 16 2.02 545 204 GCGN{3}CCA 25 7 2.01 546 205 AGGN{1}CGC 21 5 2 547 206 CTCN{5}CGC 24 7 1.98 548 207 CCCN{0}ACG 30 10 1.97 549 208 CAGN{17}CCG 29 9 1.96 550 209 GGCN{4}CCC 62 30 1.96 551 210 AGGN{8}GCG 26 8 1.96 552 211 CTGN{1}CCC 88 48 1.94 553 212 CCCN{16}CAG 85 46 1.94 554 213 CGCN{9}GAC 16 3 1.93 555 214 CAGN{6}CCG 29 9 1.92 556 215 CGTN{12}CGC 11 1 1.92 557 216 CTCN{7}GCC 69 35 1.92 558 217 CGCN{19}TCC 22 6 1.92 559 218 CCCN{7}GCC 67 33 1.91 560 219 CAGN{13}CGG 30 10 1.9 561 220 CGCN{1}GCC 27 8 1.9 562 221 CGCN{17}CCG 17 4 1.89 563 222 AGGN{4}CCC 63 31 1.89 564 223 AGCN{10}CGC 21 5 1.89 565 224 CCCN{11}CGG 30 10 1.88 566 225 CCCN{8}GCC 75 39 1.86 567 226 CCGN{1}CGG 22 3 1.86 568 227 CCCN{1}ACC 71 36 1.85 569 228 CGCN{0}CAG 25 7 1.85 570 229 CCGN{19}TGC 23 6 1.82 571 230 GCGN{4}CGA 12 2 1.82 572 231 CCGN{19}GCC 30 10 1.82 573 232 CCAN{10}CCC 85 46 1.81 574 233 CAGN{13}GGG 91 51 1.81 575 234 AGCN{18}CGG 23 6 1.81 576 235 CGAN{8}CGC 11 1 1.81 577 236 AGCN{4}CCC 63 31 1.8 578 237 GGAN{6}CCC 61 30 1.8 579 238 CGGN{13}AAG 23 6 1.8 580 239 ACCN{11}CGC 19 5 1.79 581 240 CCGN{12}CAG 28 9 1.78 582 241 CCCN{12}GGG 76 29 1.77 583 242 CACN{17}ACG 22 6 1.76 584 243 CAGN{18}CCC 82 44 1.76 585 244 CGTN{10}GTC 19 5 1.75 586 245 CCCN{13}GCG 23 6 1.75 587 246 GCAN{1}CGC 20 5 1.73 588
247 AGAN{4}CCG 24 7 1.73 589 248 GCGN{10}AGC 22 6 1.72 590 249 CGCN{0}GGA 12 2 1.72 591 250 CGGN{4}GAC 17 4 1.69 592 251 CCCN{12}CGC 26 8 1.68 593 252 GCCN{15}CCC 65 33 1.68 594 253 GCGN{6}TCC 20 5 1.66 595 254 CGGN{3}CAG 33 12 1.65 596 255 CCCN{3}CCA 88 49 1.65 597 256 AGCN{3}CCC 59 28 1.65 598 257 GGGN{16}GCA 65 33 1.65 599 258 AGGN{8}CCG 28 9 1.64 600 259 CCCN{0}CCG 29 10 1.64 601 260 GCGN{5}GAC 16 3 1.64 602 261 CCCN{9}ACC 60 29 1.64 603 262 CTGN{5}CGC 25 8 1.64 604 263 CGCN{14}CTC 23 7 1.64 605 264 CGGN{14}GCA 23 7 1.63 606 265 CCGN{8}GCC 26 8 1.62 607 266 CCGN{7}CAC 23 7 1.62 608 267 AGCN{8}GCG 21 6 1.61 609 268 CGGN{16}GGA 29 10 1.61 610 269 CCAN{12}CCG 26 8 1.61 611 270 CGGN{2}CCC 26 8 1.6 612 271 CCAN{13}GGG 71 37 1.6 613 272 CGGN{15}GCA 21 6 1.6 614 273 CGCN{9}GCA 20 5 1.58 615 274 CGGN{19}CCA 26 8 1.58 616 275 GGGN{15}CGA 20 5 1.57 617 276 CCCN{10}CGC 26 8 1.57 618 277 CTCN{14}CGC 26 8 1.55 619 278 CACN{11}GCG 20 5 1.55 620 279 CCGN{2}GGC 24 7 1.55 621 280 CTGN{18}CCC 85 47 1.54 622 281 GGGN{13}CAC 58 28 1.54 623 282 CCTN{15}GGC 62 31 1.54 624 283 CCCN{20}CGA 20 5 1.54 625 284 CCCN{8}CGA 20 5 1.53 626 285 GAGN{7}CCC 61 30 1.53 627 286 CGCN{2}CCG 22 6 1.53 628 287 CCCN{0}TCC 98 57 1.52 629 288 AGCN{0}GCC 21 6 1.52 630 289 CCCN{2}TCC 82 45 1.52 631 290 CCGN{5}CCC 30 10 1.52 632 291 CGCN{13}CGC 16 3 1.51 633 292 CCCN{1}CGC 28 9 1.51 634 293 GCCN{16}GCA 53 25 1.51 635 294 CCCN{16}CCA 84 46 1.5 636 295 CCGN{13}CGC 19 5 1.5 637 296 CCGN{17}CAG 28 9 1.49 638 297 CGGN{18}GGC 26 8 1.49 639 298 CCGN{14}AGG 23 7 1.49 640 299 CCCN{5}CGG 26 8 1.49 641 300 CCCN{6}GGA 58 28 1.49 642 301 ACGN{2}CCC 20 5 1.49 643 302 CCAN{9}CCG 27 9 1.48 644 303 CCCN{19}CCA 78 42 1.48 645 304 CAGN{0}GGG 77 41 1.48 646 305 AGCN{1}CCC 58 28 1.47 647 306 GCGN{7}TCC 27 9 1.46 648 307 ACGN{18}CCA 25 8 1.46 649 308 GCTN{14}CCC 61 30 1.46 650 309 GCGN{14}CCC 23 7 1.46 651 310 GCGN{19}AGC 20 5 1.45 652 311 CCGN{8}CAG 29 10 1.45 653 312 GCGN{6}GCC 22 6 1.45 654 313 GCGN{10}GCA 20 5 1.44 655 314 CCTN{7}GCC 69 36 1.44 656 315 GCCN{13}GCC 54 26 1.42 657 316 CCCN{14}GCC 63 32 1.42 658 317 CCCN{15}CGG 26 8 1.42 659 318 CCAN{13}CGC 23 7 1.42 660 319 AGCN{11}GGG 67 35 1.41 661 320 GGAN{0}GCC 64 32 1.4 662 321 GCCN{3}TCC 61 30 1.4 663 322 CCTN{5}GCC 69 36 1.39 664 323 CGGN{18}CCC 25 8 1.39 665 324 CCTN{3}GGC 59 29 1.38 666 325 CCGN{0}CTC 22 6 1.38 667 326 AGCN{17}GCG 19 5 1.37 668 327 ACGN{14}GGG 20 5 1.37 669 328 CGAN{12}GGC 19 5 1.37 670 329 CCCN{20}CGC 24 7 1.37 671 330 ACGN{12}CTG 24 7 1.36 672 331 CCGN{0}CCC 36 14 1.36 673 332 CCGN{10}GGA 23 7 1.36 674 333 CCCN{3}GCG 21 6 1.36 675 334 GCGN{14}CGC 22 3 1.35 676 335 CCGN{8}CGC 16 4 1.35 677 336 CGCN{10}ACA 22 6 1.34 678 337 CCCN{19}CCG 28 10 1.33 679 338 CACN{14}CGC 20 5 1.32 680 339 GACN{3}GGC 46 21 1.32 681 340 GAAN{7}CGC 19 5 1.32 682 341 CGCN{16}GGC 21 6 1.31 683 342 GGCN{9}CCC 64 33 1.31 684 343 CCCN{9}GCC 64 33 1.31 685 344 CGCN{0}TGC 26 9 1.3 686 345 CCTN{8}GGC 67 35 1.3 687 346 CCAN{8}CCC 82 46 1.29 688 347 GACN{2}CCC 42 18 1.28 689 348 GGCN{1}CCC 54 26 1.27 690 349 CGCN{0}AGC 24 7 1.26 691 350 AGGN{4}GCG 28 10 1.26 692 351 CGGN{6}TCC 22 6 1.25 693 352 ACGN{19}GGC 20 5 1.25 694 353 CCCN{8}ACG 21 6 1.24 695 354 CCCN{18}GCC 62 31 1.24 696 355 GCCN{2}CGA 19 5 1.24 697 356 CCCN{8}GCG 28 10 1.23 698 357 CCCN{0}CTC 76 41 1.23 699 358 GCCN{11}CGC 27 9 1.22 700 359 AGCN{9}CCC 59 29 1.22 701 360 GCTN{0}GCC 71 38 1.21 702 361 CGCN{3}CCC 26 9 1.21 703 362 CCCN{2}CCC 117 72 1.19 704 363 GCCN{9}CGC 23 7 1.19 705 364 GCAN{19}CGC 19 5 1.19 706 365 CAGN{4}CGG 32 12 1.18 707 366 CAGN{2}GGG 80 44 1.17 708 367 GCCN{16}CCC 67 35 1.16 709 368 GAGN{5}CCC 60 30 1.16 710 369 CCTN{16}TCG 20 6 1.16 711 370 CCCN{2}GGC 62 32 1.15 712 371 GCGN{13}GGA 24 8 1.15 713 372 GCCN{17}GGC 66 25 1.15 714
373 CCCN{14}GGC 58 29 1.14 715 374 AGGN{3}CCG 31 12 1.14 716 375 CACN{0}CGC 32 12 1.14 717 376 CGGN{18}CAG 28 10 1.14 718 377 AGCN{1}GCC 57 28 1.13 719 378 CGCN{18}GGC 23 7 1.13 720 379 CCCN{5}AGG 64 33 1.11 721 380 AACN{0}GCG 9 1 1.11 722 381 CCCN{10}CCA 88 50 1.09 723 382 CGCN{13}GAG 20 6 1.09 724 383 CGCN{7}GCC 25 8 1.08 725 384 CCCN{9}CCG 28 10 1.07 726 385 CGCN{16}CCC 24 8 1.05 727 386 GAAN{13}CGC 18 5 1.05 728 387 GGCN{3}CCC 49 23 1.03 729 388 TCCN{11}CCA 87 50 1.03 730 389 CACN{0}CCC 70 38 1.02 731 390 CGCN{16}CCG 15 3 1.02 732 391 CGGN{15}AGC 21 6 1.02 733 392 CCCN{12}GCG 21 6 1.02 734 393 CCCN{9}GAG 59 30 1.01 735 394 CCGN{20}TCC 24 8 1.01 736 395 CGCN{0}CGC 17 4 1.01 737 396 ATGN{7}CGG 20 6 1 738 397 GGGN{20}GCA 59 30 1 739 398 CGGN{4}GGC 26 9 0.99 740 399 CGGN{16}AGC 22 7 0.99 741 400 CGGN{5}GGC 25 8 0.99 742 401 GCGN{0}GGA 25 8 0.98 743 402 GGCN{20}CAC 52 25 0.98 744 403 CCCN{9}CCC 97 58 0.97 745 404 ACCN{17}GGC 44 20 0.97 746 405 CCCN{6}CGA 18 5 0.96 747 406 AAGN{10}CGG 26 9 0.96 748 407 CGCN{17}CAC 21 6 0.95 749 408 CCCN{16}CGG 25 8 0.94 750 409 GACN{18}GGC 39 17 0.94 751 410 GGGN{15}GAC 47 22 0.92 752 411 GCCN{4}TCC 66 35 0.92 753 412 GGCN{15}CCC 56 28 0.92 754 413 CAGN{12}CGC 24 8 0.92 755 414 CCAN{3}GCG 22 7 0.91 756 415 CCGN{16}GAG 22 7 0.9 757 416 AGCN{2}CGC 24 8 0.89 758 417 GAGN{4}CCC 54 27 0.89 759 418 AGGN{3}CGC 23 7 0.88 760 419 CACN{13}AGG * 67 36 0.88 761 420 CCCN{4}CAG 88 51 0.88 762 421 CCCN{2}GAA 63 33 0.87 763 422 CGCN{19}GAG 21 6 0.87 764 423 ACGN{18}GGG 21 6 0.87 765 424 CCCN{4}GGC 62 32 0.87 766 425 CGGN{9}GAG 28 10 0.86 767 426 CCCN{3}GGG 66 26 0.86 768 427 GAGN{4}GGC 66 35 0.85 769 428 CGCN{5}GAG 18 5 0.84 770 429 CCGN{20}AGG 24 8 0.84 771 430 CCCN{15}CCC 88 51 0.83 772 431 AGGN{17}CCG 25 8 0.82 773 432 AGGN{6}GGG 89 52 0.82 774 433 GGCN{20}CCC 57 29 0.82 775 434 GCAN{17}CGC 19 5 0.82 776 435 CGAN{11}ACG 9 1 0.81 777 436 CGCN{2}GGA 19 5 0.81 778 437 CTGN{5}CCC 79 45 0.8 779 438 TCCN{20}CCA 77 43 0.8 780 439 CCAN{2}GGG 59 30 0.8 781 440 CCGN{15}GCG 14 3 0.8 782 441 CCAN{5}GGG 69 38 0.79 783 442 CGGN{1}TGC 24 8 0.79 784 443 CCCN{14}GCG 21 6 0.79 785 444 CAGN{0}CCG 27 10 0.79 786 445 GCCN{9}TCC 60 31 0.78 787 446 AGGN{20}CGC 22 7 0.78 788 447 CCCN{6}GAC 42 19 0.77 789 448 CGGN{11}CCA 23 7 0.76 790 449 GGGN{14}CAC 57 29 0.75 791 450 GCAN{15}CGC 19 5 0.74 792 451 CGCN{2}ACA 20 6 0.74 793 452 ACCN{9}CCC 57 29 0.73 794 453 GCGN{9}CGC 20 3 0.73 795 454 CAGN{15}GCG 23 7 0.73 796 455 CCCN{18}GTC 45 21 0.72 797 456 GCGN{3}CCC 24 8 0.72 798 457 CGGN{11}GCC 23 8 0.72 799 458 CCCN{1}CGG 24 8 0.71 800 459 GCCN{4}CCA 70 38 0.71 801 460 CCCN{4}CCG 30 12 0.7 802 461 CGTN{2}GCA 21 6 0.7 803 462 AGCN{7}TCG 18 5 0.69 804 463 CCGN{15}GAA 20 6 0.69 805 464 ACCN{5}CCC 62 33 0.69 806 465 CGCN{14}GAG 19 5 0.68 807 466 CCCN{7}CGC 30 12 0.68 808 467 GAGN{12}CGC 21 6 0.68 809 468 GGCN{17}CCC 58 30 0.67 810 469 ACGN{11}CTC 21 7 0.65 811 470 ACAN{9}CGG 24 8 0.65 812 471 CTGN{7}CCC 82 47 0.65 813 472 CCCN{2}GCC 72 40 0.65 814 473 CGGN{2}GCA 24 8 0.64 815 474 CCCN{0}TGC 83 48 0.64 816 475 CGCN{7}ACC 18 5 0.63 817 476 GCAN{2}GCC 54 27 0.63 818 477 GCGN{8}CCA 20 6 0.63 819 478 AGCN{0}CGC 22 7 0.63 820 479 GCGN{2}GCA 18 5 0.63 821 480 CCGN{2}GTC 18 5 0.62 822 481 CCGN{3}ACA 21 7 0.62 823 482 ACGN{13}TGG 21 7 0.62 824 483 CCAN{8}CGC 23 8 0.62 825 484 CCGN{9}GGC 23 8 0.61 826 485 CCAN{5}CCG 25 9 0.61 827 486 AGGN{3}GGG 97 59 0.61 828 487 CAGN{2}GGC 78 45 0.61 829 488 CCCN{8}CAG 81 47 0.61 830 489 AGCN{5}CAG 80 46 0.6 831 490 CGGN{16}GCC 22 7 0.6 832 491 GCGN{15}CCC 23 8 0.6 833 492 CCCN{11}GCC 59 31 0.59 834 493 CGAN{2}ACG 9 1 0.59 835 494 CGGN{4}GCC 22 7 0.59 836 495 CACN{6}CGC 19 6 0.59 837 496 CGGN{5}ACG 11 2 0.59 838 497 CTGN{4}GCC * 66 36 0.59 839
498 GGGN{18}CGA 18 5 0.59 840 499 CCTN{8}CGC 22 7 0.59 841 500 GCCN{4}CCC 67 37 0.58 842 501 CGGN{10}GCC 22 7 0.58 843 502 GCCN{5}GGA 54 27 0.57 844 503 ACCN{7}GCG 15 4 0.57 845 504 CCCN{8}CGC 24 8 0.57 846 505 CAGN{5}CCC 77 44 0.56 847 506 CACN{14}GGA 63 34 0.56 848 507 CCCN{1}GCC 94 57 0.55 849 508 CCCN{5}AGC 67 37 0.55 850 509 GGCN{5}GGA 59 31 0.55 851 510 CGAN{17}GAG 19 6 0.55 852 511 CGCN{7}ACA 18 5 0.54 853 512 CCAN{13}CCC 87 52 0.54 854 513 CGGN{20}GGC 24 8 0.54 855 514 CCCN{17}GCC 58 30 0.53 856 515 CCTN{10}CCG 30 12 0.53 857 516 CCCN{8}CCG 27 10 0.53 858 517 CGCN{3}GAG 18 5 0.52 859 518 CGCN{7}AAG 17 5 0.51 860 519 CGGN{11}GGA 23 8 0.51 861 520 CCGN{15}CCG 15 4 0.51 862 521 CCCN{3}GCA 57 30 0.51 863 522 CGGN{2}CAG 24 8 0.5 864 523 AGGN{2}CCG 24 8 0.5 865 524 CCCN{4}CAC 69 38 0.5 866 525 GGAN{19}CCC 56 29 0.49 867 526 CCCN{8}CAC 68 38 0.49 868 527 ACCN{6}CCG 18 5 0.49 869 528 CCCN{6}GGC 54 28 0.49 870 529 CCCN{6}CCG 29 11 0.48 871 530 CGCN{14}GCC 26 9 0.47 872 531 CCGN{5}TCC 25 9 0.46 873 532 GCCN{6}GCC 55 28 0.46 874 533 CGGN{7}GGA 24 8 0.45 875 534 GGGN{6}GGA 87 52 0.44 876 535 GCCN{12}TCC 60 32 0.44 877 536 AGTN{16}CCG 17 5 0.44 878 537 GGCN{19}GCC 68 29 0.44 879 538 CCGN{3}CCG 22 7 0.44 880 539 CCCN{8}ACC 58 31 0.44 881 540 CAGN{15}GCC 77 44 0.44 882 541 CCCN{17}CGG 24 8 0.44 883 542 GCGN{1}CCA 22 7 0.44 884 543 CCCN{14}CAG 79 46 0.44 885 544 CCCN{8}CCC 89 53 0.44 886 545 ACAN{12}GCG 23 8 0.43 887 546 AGGN{4}CCG 23 8 0.43 888 547 CGCN{13}GCC 23 8 0.43 889 548 GAGN{2}CGC 23 8 0.42 890 549 CCCN{9}GCG 21 7 0.42 891 550 CGCN{17}ACA 17 5 0.42 892 551 GCGN{17}CCA 23 8 0.42 893 552 AAGN{18}CCG 20 6 0.42 894 553 CGCN{1}GGA 18 5 0.41 895 554 CCAN{1}CCC 90 54 0.41 896 555 CGTN{18}TGC 20 6 0.41 897 556 TCCN{14}CGA 17 5 0.41 898 557 CACN{5}GGG 56 29 0.4 899 558 CCGN{12}GCA 21 7 0.4 900 559 CTGN{6}CCC 77 44 0.4 901 560 CGGN{8}GGC 32 13 0.4 902 561 CCAN{11}GGG 68 38 0.4 903 562 ACGN{19}CAA 21 7 0.39 904 563 GGGN{20}CCC 72 31 0.39 905 564 CGCN{3}CAG 23 8 0.39 906 565 AGCN{17}GGG 58 31 0.37 907 566 CACN{20}CCG 21 7 0.37 908 567 ACGN{17}CAG 24 8 0.37 909 568 AGGN{1}CCC 60 32 0.37 910 569 CGTN{12}CAC 20 6 0.37 911 570 CGGN{9}GGC 23 8 0.37 912 571 CGCN{10}GCG 18 3 0.37 913 572 CCCN{6}CTC 80 47 0.36 914 573 CCGN{10}AGG 23 8 0.36 915 574 CCCN{18}CAG 79 46 0.36 916 575 AGCN{17}CCG 21 7 0.36 917 576 AGCN{9}GCG 18 5 0.36 918 577 CCAN{3}GGC 62 34 0.36 919 578 CCCN{11}GGC 57 30 0.35 920 579 ACGN{5}GCA 23 8 0.35 921 580 CCCN{14}CGG 23 8 0.35 922 581 CCCN{5}CCA 91 55 0.35 923 582 CCGN{1}AGG 22 7 0.34 924 583 GGGN{10}GAC 45 22 0.34 925 584 CGCN{15}CCA 20 6 0.34 926 585 CCTN{19}CGC 22 7 0.34 927 586 CGTN{3}CGC 10 2 0.33 928 587 AGCN{14}CCG 21 7 0.33 929 588 GGCN{2}CGA 17 5 0.33 930 589 CAGN{8}CCC 79 46 0.33 931 590 CCGN{2}GAC 16 4 0.33 932 591 AGCN{19}AGG 70 40 0.32 933 592 CCTN{4}GGC 64 35 0.32 934 593 CCGN{11}AGC 22 7 0.32 935 594 CACN{4}CGC 18 5 0.32 936 595 CCGN{1}CCC 30 12 0.31 937 596 CTGN{13}GGC 73 42 0.31 938 597 CGCN{16}ACC 15 4 0.31 939 598 CACN{18}CAG 79 46 0.31 940 599 GGCN{8}GCC 68 29 0.29 941 600 GGGN{15}GGA 78 46 0.29 942 601 CCGN{16}GCC 22 7 0.29 943 602 CCGN{20}ACC 18 5 0.29 944 603 CGAN{7}CCC 17 5 0.28 945 604 CCGN{6}CTC 23 8 0.28 946 605 CGGN{10}CTC 22 7 0.28 947 606 CAGN{16}CGC 23 8 0.28 948 607 CCAN{3}AGG 77 45 0.27 949 608 GCCN{18}GCC 52 27 0.27 950 609 CGCN{18}GGA 19 6 0.26 951 610 CCGN{20}GGC 22 7 0.26 952 611 ACAN{1O}GCG 17 5 0.26 953 612 CGGN{5}CCC 25 9 0.25 954 613 CCCN{7}TCC 75 43 0.25 955 614 ACGN{10}CGC 10 2 0.25 956 615 CCCN{3}TCC 81 48 0.25 957 616 CCGN{8}CGG 20 3 0.24 958 617 CCAN{15}CGG 22 7 0.24 959 618 CCGN{6}CCG 17 5 0.24 960 619 CAGN{3}GCG 25 9 0.24 961 620 GAGN{1}CCC 62 34 0.24 962 621 CCGN{18}TGC 22 7 0.23 963 622 CCCN{7}CCA 85 51 0.23 964 623 CGGN{3}CCA 24 9 0.23 965
624 ACGN{1}CCC 18 5 0.23 966 625 CGGN{13}TGA 21 7 0.22 967 626 CTCN{6}GGC 53 28 0.22 968 627 GCGN{2}GAC 15 4 0.22 969 628 GGGN{11}ACC 49 25 0.22 970 629 CGCN{4}GGA 17 5 0.22 971 630 CCCN{11}CCG 27 10 0.22 972 631 CCGN{19}GCA 20 6 0.22 973 632 GCGN{0}GCA 20 6 0.21 974 633 AGAN{7}CCC 61 33 0.21 975 634 CGGN{2}CCA 21 7 0.21 976 635 CCCN{7}CCC 89 54 0.21 977 636 ACCN{4}GCG 15 4 0.2 978 637 CCTN{15}CGC 20 6 0.2 979 638 AGCN{9}GTC 44 21 0.2 980 639 CCCN{18}CTC 74 43 0.2 981 640 CGCN{18}CGA 9 1 0.19 982 641 CCCN{15}GCC 62 34 0.18 983 642 ACCN{11}GGC 45 22 0.18 984 643 AGGN{15}CGC 29 12 0.18 985 644 GCGN{0}CCA 27 10 0.18 986 645 GCGN{9}AGC 18 5 0.17 987 646 GGGN{18}GCA 59 32 0.17 988 647 CCCN{17}CAG 77 45 0.17 989 648 CCAN{8}CGG 22 8 0.16 990 649 CCGN{10}GGC 21 7 0.16 991 650 GCAN{0}GCC 76 44 0.16 992 651 CAGN{2}CGC 20 6 0.16 993 652 CGCN{8}GGC 19 6 0.16 994 653 CTGN{17}GGC 65 36 0.16 995 654 GGGN{14}ACC 46 23 0.16 996 655 CCGN{1}TGC 20 6 0.16 997 656 CAGN{8}CGC 22 8 0.15 998 657 AAGN{11}CGC 17 5 0.15 999 658 CCGN{6}TCC 22 8 0.14 1000 659 CCAN{18}CCC 72 42 0.14 1001 660 CCAN{0}CCC 84 51 0.14 1002 661 GAGN{6}CCC 53 28 0.14 1003 662 AGCN{20}GGC 52 27 0.14 1004 663 CAGN{0}CGC 21 7 0.14 1005 664 CCGN{12}CTC 22 8 0.14 1006 665 CGCN{15}ACG 9 1 0.13 1007 666 GGCN{17}CGA 15 4 0.13 1008 667 CCGN{16}AAG 19 6 0.13 1009 668 CGCN{14}TCC 19 6 0.12 1010 669 AGGN{7}CGC 20 7 0.12 1011 670 CGGN{7}CCC 22 8 0.12 1012 671 CGCN{4}GCC 34 15 0.12 1013 672 CGAN{6}CCC 17 5 0.12 1014 673 CCCN{19}GGA 60 33 0.11 1015 674 CCCN{16}GCG 28 11 0.11 1016 675 CCAN{7}CGC 20 7 0.11 1017 676 CCCN{6}GCC 80 48 0.11 1018 677 GCCN{14}TCC 55 29 0.11 1019 678 AGGN{14}GCC 64 36 0.1 1020 679 CGCN{11}GCC 20 7 0.1 1021 680 TCCN{0}GCA 17 5 0.09 1022 681 GCGN{8}CCC 27 11 0.09 1023 682 CCAN{11}GCG 19 6 0.09 1024 683 CACN{4}GGG 51 26 0.09 1025 684 CGGN{7}TCC 20 7 0.09 1026 685 GCGN{5}GCC 20 7 0.09 1027 686 ACGN{12}CAG 26 10 0.09 1028 687 CCGN{19}CGC 14 4 0.08 1029 688 CGGN{8}TGC 18 5 0.08 1030 689 CCCN{1}GAG 65 37 0.07 1031 690 GCGN{19}TGA 18 6 0.07 1032 691 GGCN{15}GCC 70 31 0.07 1033 692 CCGN{7}CCC 27 11 0.07 1034 693 ACAN{19}CCC 63 35 0.07 1035 694 ACCN{16}GGG 47 24 0.07 1036 695 AGAN{1}GGC 64 36 0.07 1037 696 GGGN{17}TGA 64 36 0.06 1038 697 CAGN{5}GGG 83 50 0.06 1039 698 GCCN{13}CGC 22 8 0.06 1040 699 GCGN{7}GGA 19 6 0.06 1041 700 CAGN{14}CCA 94 58 0.06 1042 701 CCGN{4}GTC 16 4 0.06 1043 702 CCCN{13}CGC 22 8 0.06 1044 703 GCGN{14}ACC 15 4 0.05 1045 704 CAGN{20}GGG 81 49 0.05 1046 705 CCGN{4}CCC 27 11 0.05 1047 706 CGCN{5}GGC 18 6 0.05 1048 707 CCTN{6}GGC 57 31 0.05 1049 708 AGGN{3}GGC 67 38 0.05 1050 709 CGGN{11}CGC 14 4 0.05 1051 710 CTGN{18}GGA 77 46 0.04 1052 711 CACN{17}CCA 74 43 0.04 1053 712 CGGN{3}GAG 22 8 0.04 1054 713 CCCN{9}CCA 82 49 0.03 1055 714 CCCN{1}ACG 18 6 0.03 1056 715 CAGN{1}GCC 72 42 0.03 1057 716 AGGN{6}CCG 23 8 0.03 1058 717 AGCN{9}GGG 57 31 0.03 1059 718 CCCN{7}GGC 54 29 0.02 1060 719 CCTN{13}CCC 88 54 0.02 1061 720 CCGN{19}TTC 20 7 0.02 1062 721 CCCN{7}CCG 27 11 0.02 1063 722 CGAN{6}GGC 17 5 0.01 1064 723 CGGN{4}CTC 21 7 0.01 1065 724 CGGN{0}CGC 13 3 0.01 1066 725 CCTN{13}ACG 19 6 0.01 1067 726 GGGN{6}CAC 53 28 0.01 1068 727 CCCN{16}CGC 21 7 0.01 1069 728 CCCN{10}CTC 76 45 0 1070 729 CCCN{0}CAG 92 57 0 1071 730 GCCN{5}CCC 65 37 0 1072 The patterns are ranked according to significance coefficient. These were determined using RSA-Tools with the random sequence from the human genome as reference. Patterns that comprise the most discriminant variables in Linear Discriminant Analysis are indicated with an asterisk. (SEQ ID NOS:343-1072)
TABLE-US-00008 TABLE 8 Candidate STAR elements tested by Linear Discriminant Analysis SEQ ID NO: Candidate STAR Location1 Length 66 T2 F 20q13.33 ~2800 67 T2 R 6q14.1 ~2800 68 T3 F 15q12 ~2900 69 T3 R 7q31.2 ~2900 70 T5 F 9q34.13 .sup. ND2 71 T5 R 9q34.13 ND 72 T7 22q12.3 ~1200 73 T9 F 21q22.2 ~1600 74 T9 R 22q11.22 ~1600 75 T10 F 7q22.2 ~1300 76 T10 R 6q14.1 ~1300 77 T11 F 17q23.3 ~2000 78 T11 R 16q23.1 ~2000 79 T12 4p15.1 ~2100 80 T13 F 20p13 ~1700 81 T13 R 1p13.3 ~1700 82 T14 R 11q25 ~1500 83 T17 2q31.3 ND 84 T18 2q31.1 ND 1Chromosomal location is determined by BLAT search of DNA sequence data from the STAR elements against the human genome database. The location is given according to standard nomenclature referring to the cytogenetic ideogram of each chromosome; e.g., 1p2.3 is the third cytogenetic sub-band of the second cytogenetic band of the short arm of chromosome 1 (WorldWideWeb.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Class/MLACourse/Genetics/chrombanding.html- ).F, forward sequencing reaction result; R, reverse sequencing reaction result. When the forward and reverse sequencing results mapped to different genomic locations, each sequence was extended to the full length of the original clone (as determined by restriction mapping) based on sequence information from the human genome database. 2ND: Not Determined.
TABLE-US-00009 TABLE 9 Arabidopsis STAR elements of the invention, including chromosome location and length (SEQ ID NOS: 85-119) STAR Chromosome Length, kb SEQ ID NO: A1 I 1.2 85 A2 I 0.9 86 A3 I 0.9 87 A4 I 0.8 88 A5 I 1.3 89 A6 I 1.4 90 A7 II 1.2 91 A8 II 0.8 92 A9 II 0.9 93 A10 II 1.7 94 A11 II 1.9 95 A12 II 1.4 96 A13 II 1.2 97 A14 II 2.1 98 A15 II 1.4 99 A16 II 0.7 100 A17 II 1.5 101 A18 III 1.5 102 A19 III 0.7 103 A20 III 2.0 104 A21 IV 1.8 105 A22 IV 0.8 106 A23 IV 0.6 107 A24 IV 0.5 108 A25 V 0.9 109 A26 V 1.9 110 A27 V 1.1 111 A28 V 1.6 112 A29 V 0.9 113 A30 V 2.0 114 A31 V 2.0 115 A32 V 1.3 116 A33 V 0.9 117 A34 I 0.9 118 A35 II 1.1 119
REFERENCES
[0230]Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W. and Lipman D. J. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215, 403-10. [0231]Bell A. C., West A. G. and Felsenfeld G. (2001) Insulators and boundaries: versatile regulatory elements in the eukaryotic genome. Science 291, 447-50. [0232]Berger J., Hauber J., Hauber R., Geiger R. and Cullen B. R. (1988) Secreted placental alkaline phosphatase: a powerful new quantitative indicator of gene expression in eukaryotic cells. Gene 66, 1-10. [0233]Bevan M., Mayer K., White O., Eisen J. A., Preuss D., Bureau T., Salzberg S. L. and Mewes H. W. (2001) Sequence and analysis of the Arabidopsis genome. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 4, 105-10. [0234]Bibel M. and Barde Y. A. (2000) Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 14, 2919-37. [0235]Boivin A. and Dura J. M. (1998) In vivo chromatin accessibility correlates with gene silencing in Drosophila. Genetics 150, 1539-49. [0236]Boshart M., Weber F., Jahn G., Dorsch-Hasler K., Fleckenstein B. and Schaffner W. (1985) A very strong enhancer is located upstream of an immediate early gene of human cytomegalovirus. Cell 41, 521-30. [0237]Bunker C. A. and Kingston R. E. (1994) Transcriptional repression by Drosophila and mammalian Polycomb group proteins in transfected mammalian cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 1721-32. [0238]Chung J. H, Whiteley M. and Felsenfeld G. (1993) A 5' element of the chicken beta-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell 74, 505-14. [0239]Deuschle U., Meyer W. K. and Thiesen H. J. (1995) Tetracycline-reversible silencing of eukaryotic promoters. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 1907-14. [0240]Doll R. F., Crandall J. E., Dyer C. A., Aucoin J. M. and Smith F. I. (1996) Comparison of promoter strengths on gene delivery into mammalian brain cells using AAV vectors. Gene Ther. 3, 437-447. [0241]Foecking M. K. and Hofstetter H. (1986) Powerful and versatile enhancer-promoter unit for mammalian expression vectors. Gene 45, 101-5. [0242]Garrick D., Fiering S., Martin D. I. and Whitelaw E. (1998) Repeat-induced gene silencing in mammals. Nat. Genet. 18, 56-9. [0243]Gerasimova T. I. and Corces V. G. (2001) Chromatin insulators and boundaries: effects on transcription and nuclear organization. Annu. Rev. Genet. 35, 193-208. [0244]Gossen M. and Bujard H. (1992) Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 5547-51. [0245]Graham F. L. and van der Eb A. J. (1973) Transformation of rat cells by DNA of human adenovirus 5. Virology 54, 536-9. [0246]Henthorn P., Zervos P., Raducha M., Harris H. and Kadesch T. (1988) Expression of a human placental alkaline phosphatase gene in transfected cells: use as a reporter for studies of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 6342-6. [0247]Himes S. R. and Shannon M. F. (2000) Assays for transcriptional activity based on the luciferase reporter gene. Methods Mol. Biol. 130, 165-74. [0248]Huberty C. J. (1994) Applied discriminant analysis, Wiley and Sons, New York. [0249]Initiative A. G. (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408, 796-815. [0250]Izumi M. and Gilbert D. M. (1999) Homogeneous tetracycline-regulatable gene expression in mammalian fibroblasts. J. Cell. Biochem. 76, 280-9. [0251]Kain S. R. (1997) Use of secreted alkaline phosphatase as a reporter of gene expression in mammalian cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 63, 49-60. [0252]Kaufman R. J. (1990) Selection and coamplification of heterologous genes in mammalian cells. Methods in Enzymology 185, 536-566. [0253]Kellum R. and Schedl P. (1992) A group of scs elements function as domain boundaries in an enhancer-blocking assay. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 2424-2431. [0254]Kent W. J. (2002) BLAT--the BLAST-like alignment tool. Genome Res. 12, 656-64. [0255]Knofler M., Meinhardt G., Bauer S., Loregger T., Vasicek R., Bloor D. J., Kimber S. J. and Husslein P. (2002) Human Hand1 basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) protein: extra-embryonic expression pattern, interaction partners and identification of its transcriptional repressor domains. Biochem J. 361, 641-51. [0256]Meyer P. (2000) Transcriptional transgene silencing and chromatin components. Plant Mol. Biol. 43, 221-34. [0257]Mercenier A., Wiedermann U. and Breiteneder H. (2001) Edible genetically modified microorganisms and plants for improved health. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12, 510-5. [0258]Morgenstern J. P. and Land H. (1990) Advanced mammalian gene transfer: high titre retroviral vectors with multiple drug selection markers and a complementary helper-free packaging cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 18, 3587-96. [0259]Sambrook J., Fritsch E. F. and Maniatis T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, Second ed., Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview N.Y. [0260]Sanger F., Nicklen S, and Coulson A. R. (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463-7. [0261]Stam M., Viterbo A., Mol. J. N. and Kooter J. M. (1998) Position-dependent methylation and transcriptional silencing of transgenes in inverted T-DNA repeats: implications for posttranscriptional silencing of homologous host genes in plants. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 6165-77. [0262]Umana P., Jean-Mairet J. and Bailey J. E. (1999) Tetracycline-regulated overexpression of glycosyltransferases in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 65, 542-9. [0263]Van der Vlag J., den Blaauwen J. L., Sewalt R. G., van Driel R. and Otte A. P. (2000) Transcriptional repression mediated by polycomb group proteins and other chromatin-associated repressors is selectively blocked by insulators. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 697-704. [0264]van Helden J., Andre B. and Collado-Vides J. (1998) Extracting regulatory sites from the upstream region of yeast genes by computational analysis of oligonucleotide frequencies J. Mol. Biol. 281, 827-42. [0265]van Helden J., Andre B. and Collado-Vides J. (2000) A web site for the computational analysis of yeast regulatory sequences. Yeast 16, 177-87. [0266]van Helden J., Rios A. F. and Collado-Vides J. (2000) Discovering regulatory elements in non-coding sequences by analysis of spaced dyads. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 1808-18. [0267]Vance V. and Vaucheret H. (2001) RNA silencing in plants--defense and counterdefense. Science 292, 2277-80. [0268]Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S, and Axel R. (1978) Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell 14, 725-31. [0269]Yang T. T., Sinai P., Kitts P. A. and Kain S. R. (1997) Quantification of gene expression with a secreted alkaline phosphatase reporter system. Biotechniques 23, 1110-4. [0270]Zink D. and Paro R. (1995) Drosophila Polycomb-group regulated chromatin inhibits the accessibility of a trans-activator to its target DNA. Embo. J. 14, 5660-71.
Sequence CWU
1
10721749DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR1 1atgcggtggg ggcgcgccag
agactcgtgg gatccttggc ttggatgttt ggatctttct 60gagttgcctg tgccgcgaaa
gacaggtaca tttctgatta ggcctgtgaa gcctcctgga 120ggaccatctc attaagacga
tggtattgga gggagagtca cagaaagaac tgtggcccct 180ccctcactgc aaaacggaag
tgattttatt ttaatgggag ttggaatatg tgagggctgc 240aggaaccagt ctccctcctt
cttggttgga aaagctgggg ctggcctcag agacaggttt 300tttggccccg ctgggctggg
cagtctagtc gaccctttgt agactgtgca cacccctaga 360agagcaacta cccctataca
ccaggctggc tcaagtgaaa ggggctctgg gctccagtct 420ggaaaatctg gtgtcctggg
gacctctggt cttgcttctc tcctcccctg cactggctct 480gggtgcttat ctctgcagaa
gcttctcgct agcaaaccca cattcagcgc cctgtagctg 540aacacagcac aaaaagccct
agagatcaaa agcattagta tgggcagttg agcgggaggt 600gaatatttaa cgcttttgtt
catcaataac tcgttggctt tgacctgtct gaacaagtcg 660agcaataagg tgaaatgcag
gtcacagcgt ctaacaaata tgaaaatgtg tatattcacc 720ccggtctcca gccggcgcgc
caggctccc 7492883DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR2 2gggtgcttcc tgaattcttc cctgagaagg atggtggccg
gtaaggtccg tgtaggtggg 60gtgcggctcc ccaggccccg gcccgtggtg gtggccgctg
cccagcggcc cggcaccccc 120atagtccatg gcgcccgagg cagcgtgggg gaggtgagtt
agaccaaaga gggctggccc 180ggagttgctc atgggctcca catagctgcc ccccacgaag
acggggcttc cctgtatgtg 240tggggtccca tagctgccgt tgccctgcag gccatgagcg
tgcgggtcat agtcgggggt 300gccccctgcg cccgcccctg ccgccgtgta gcgcttctgt
gggggtggcg ggggtgcgca 360gctgggcagg gacgcagggt aggaggcggg gggcagcccg
taggtaccct gggggggctt 420ggagaagggc gggggcgact ggggctcata cgggacgctg
ttgaccagcg aatgcataga 480gttcagatag ccaccggctc cggggggcac ggggctgcga
cttggagact ggccccccga 540tgacgttagc atgcccttgc ccttctgatc ctttttgtac
ttcatgcggc gattctggaa 600ccagatcttg atctggcgct cagtgaggtt cagcagattg
gccatctcca cccggcgcgg 660ccggcacagg tagcggttga agtggaactc tttctccagc
tccaccagct gcgcgctcgt 720gtaggccgtg cgcgcgcgct tggacgaagc ctgccccggc
gggctcttgt cgccagcgca 780gctttcgcct gcgaggacag agagaggaag agcggcgtca
ggggctgccg cggccccgcc 840cagcccctga cccagcccgg cccctccttc caccaggccc
caa 88332126DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR3
3atctcgagta ctgaaatagg agtaaatctg aagagcaaat aagatgagcc agaaaaccat
60gaaaagaaca gggactacca gttgattcca caaggacatt cccaaggtga gaaggccata
120tacctccact acctgaacca attctctgta tgcagattta gcaaggttat aaggtagcaa
180aagattagac ccaagaaaat agagaacttc caatccagta aaaatcatag caaatttatt
240gatgataaca attgtctcca aaggaacaag gcagagtcgt gctagcagag gaagcacgtg
300agctgaaaac agccaaatct gctttgtttt catgacacag gagcataaag tacacaccac
360caactgacct attaaggctg tggtaaaccg attcatagag agaggttcta aatacattgg
420tccctcacag gcaaactgca gttcgctccg aacgtagtcc ctggaaattt gatgtccagt
480atagaaaagc agagcagtca aaaaatatag ataaagctga accagatgtt gcctgggcaa
540tgttagcagc accacactta agatataacc tcaggctgtg gactccctcc ctggggagcg
600gtgctgccgg cggcgggcgg gctccgcaac tccccggctc tctcgcccgc cctcccgttc
660tcctcgggcg gcggcggggg ccgggactgc gccgctcaca gcggcggctc ttctgcgccc
720ggcctcggag gcagtggcgg tggcggccat ggcctcctgc gttcgccgat gtcagcattt
780cgaactgagg gtcatctcct tgggactggt tagacagtgg gtgcagccca cggagggcga
840gttgaagcag ggtggggtgt cacctccccc aggaagtcca gtgggtcagg gaactccctc
900ccctagccaa gggaggccgt gagggactgt gcccggtgag agactgtgcc ctgaggaaag
960gtgcactctg gcccagatac tacacttttc ccacggtctt caaaacccgc agaccaggag
1020attccctcgg gttcctacac caccaggacc ctgggtttca accacaaaac cgggccattt
1080gggcagacac ccagctagct gcaagagttg tttttttttt tatactcctg tggcacctgg
1140aacgccagcg agagagcacc tttcactccc ctggaaaggg ggctgaaggc agggaccttt
1200agctgcgggc tagggggttt ggggttgagt gggggagggg agagggaaaa ggcctcgtca
1260ttggcgtcgt ctgcagccaa taaggctacg ctcctctgct gcgagtagac ccaatccttt
1320cctagaggtg gagggggcgg gtaggtggaa gtagaggtgg cgcggtatct aggagagaga
1380aaaagggctg gaccaatagg tgcccggaag aggcggaccc agcggtctgt tgattggtat
1440tggcagtgga ccctcccccg gggtggtgcc ggaggggggg atgatgggtc gaggggtgtg
1500tttatgtgga agcgagatga ccggcaggaa cctgccccaa tgggctgcag agtggttagt
1560gagtgggtga cagacagacc cgtaggccaa cgggtggcct taagtgtctt tggtctcctc
1620caatggagca gcggcggggc gggaccgcga ctcgggttta atgagactcc attgggctgt
1680aatcagtgtc atgtcggatt catgtcaacg acaacaacag ggggacacaa aatggcggcg
1740gcttagtcct acccctggcg gcggcggcag cggtggcgga ggcgacggca ctcctccagg
1800cggcagccgc agtttctcag gcagcggcag cgcccccggc aggcgcggtg gcggtggcgc
1860gcagccaggt ctgtcaccca ccccgcgcgt tcccaggggg aggagactgg gcgggagggg
1920ggaacagacg gggggggatt caggggcttg cgacgcccct cccacaggcc tctgcgcgag
1980ggtcaccgcg gggccgctcg gggtcaggct gcccctgagc gtgacggtag ggggcggggg
2040aaaggggagg agggacaggc cccgcccctc ggcagggcct ctagggcaag ggggcggggc
2100tcgaggagcg gaggggggcg gggcgg
212641625DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR4 4gatctgagtc atgttttaag
gggaggattc ttttggctgc tgagttgaga ttaggttgag 60ggtagtgaag gtaaaggcag
tgagaccacg taggggtcat tgcagtaatc caggctggag 120atgatggtgg ttcagttgga
atagcagtgc atgtgctgta acaacctcag ctgggaagca 180gtatatgtgg cgttatgacc
tcagctggaa cagcaatgca tgtggtggtg taatgacccc 240agctgggtag ggtgcatgtg
gtgtaacgac ctcagctggg tagcagtgtg tgtgatgtaa 300caacctcagc tgggtagcag
tgtacttgat aaaatgttgg catactctag atttgttatg 360agggtagtgc cattaaattt
ctccacaaat tggttgtcac gtatgagtga aaagaggaag 420tgatggaaga cttcagtgct
tttggcctga ataaatagaa gacgtcattt ccagttaatg 480gagacaggga agactaaagg
tagggtggga ttcagtagag caggtgttca gttttgaata 540tgatgaactc tgagagagga
aaaacttttt ctacctctta gtttttgtga ctggacttaa 600gaattaaagt gacataagac
agagtaacaa gacaaaaata tgcgaggtta tttaatattt 660ttacttgcag aggggaatct
tcaaaagaaa aatgaagacc caaagaagcc attagggtca 720aaagctcata tgccttttta
agtagaaaat gataaatttt aacaatgtga gaagacaaag 780gtgtttgagc tgagggcaat
aaattgtggg acagtgatta agaaatatat gggggaaatg 840aaatgataag ttattttagt
agatttattc ttcatatcta ttttggcttc aacttccagt 900ctctagtgat aagaatgttc
ttctcttcct ggtacagaga gagcaccttt ctcatgggaa 960attttatgac cttgctgtaa
gtagaaaggg gaagatcgat ctcctgtttc ccagcatcag 1020gatgcaaaca tttccctcca
ttccagttct caaccccatg gctgggcctc atggcattcc 1080agcatcgcta tgagtgcacc
tttcctgcag gctgcctcgg gtagctggtg cactgctagg 1140tcagtctatg tgaccaggag
ctgggcctct gggcaatgcc agttggcagc ccccatccct 1200ccactgctgg gggcctccta
tccagaaggg cttggtgtgc agaacgatgg tgcaccatca 1260tcattcccca cttgccatct
ttcaggggac agccagctgc tttgggcgcg gcaaaaaaca 1320cccaactcac tcctcttcag
gggcctctgg tctgatgcca ccacaggaca tccttgagtg 1380ctgggcagtc tgaggacagg
gaaggagtga tgaccacaaa acaggaatgg cagcagcagt 1440gacaggagga agtcaaaggc
ttgtgtgtcc tggccctgct gagggctggc gagggccctg 1500ggatggcgct cagtgcctgg
tcggctgcaa gaggccagcc ctctgcccat gaggggagct 1560ggcagtgacc aagctgcact
gccctggtgg tgcatttcct gccccactct ttccttctaa 1620gatcc
162551571DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR5 5agcagagatc ttatttcccg tattcccttg tggcacagca
cctcccacgc caaagcaaac 60caaagcaaag gagcccttga tgaggagggg ccttccccca
acctggtctc ccacaggtcc 120tacatacgta cccaccccag acacacagag ctgcttcctg
ctctcacacc agactgagct 180gtgcccagac atttccccta gcactaacca actctttcaa
aaatacattt ttctctaaaa 240agaacaagtt taaacaaagt tgactcattt taagaactgt
ttagaagata accttgtgtt 300tattaattat gtatttgcag aaattggagg cagaaggtta
ccaacattgc ctggtgtcca 360gccaggaggt agagcgtggt ggcatccaga accttcctcc
aactcctgcc tggcgtggtt 420tttattcatc tttgtattcc caagaaactt ctcagtgtct
caggagtgtt aggcactcag 480tacgtgtttg gtagttacat gaatgaatgc ataatgacta
agtgagttaa tggatgaagc 540taattgtctc tcccttttgc ttttccagag ctttccaagg
tgaaagtgtt ggacactctt 600tcttcatctc agatttaatc aactaagaat gctgcaaatt
gaacaccagt ccacaaaact 660caggaataca tgaaaagcat tgtgccttat ttttaactaa
ctcaaattct atgtcagtct 720cccttttatg ctggatgttg gcgctaaatc tcagtgggtt
cctcattctg ccagacctgt 780gtccagtttg ggggcttcac atagagccac cccatcacag
gagagggaag ggtcttgctc 840ttggttgcca tcactccacc ctcttgtctt ccgagctttg
atgttcactt tccttttcac 900cactcggaag cttcctgcca tgatacattg agacctcaat
gttaatgcca attggggttt 960ggggttctca taaactcaga agtccaggaa aatcgcctgc
tgcctcccac aacactctga 1020gggcattctg gaatcctacc acttacctgg agcctgctgg
cctcaactgt tttgaagtct 1080gtgtctgggc catgcaggta aatgggagga tgttctgtgg
ccataaaaat acccgaagtc 1140ccacctaaag ttgatgcagg gtcttctgca tttcattgca
aaattgttct atcatttcta 1200tagttttcag cctacagtca ggggccagga ctttgcaccc
ttggtaaacc tcaatctctt 1260ctccttcctg gcttctactc ctttctccct caatcccaaa
tcaaggccct tgattgtctg 1320gaggtaggaa agcctggttc tggctcatga tatagtctac
atcatagcct ttgtcatctc 1380atggattcac tcaacaaccg tgtgtggatg gggccaccca
atatgtgcca ggagttgagg 1440acacgcaggg ttatgatgat gaaatagata aggggcccac
actcacggac cctgcaggac 1500agtggagctg tggacccagc atgcgagtaa agacccagtg
agctcaccag acagatcatt 1560taaatcaggt g
157161173DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR6
6tgacccacca cagacatccc ctctggcctc ctgagtggtt tcttcagcac agcttccaga
60gccaaattaa acgttcactc tatgtctata gacaaaaagg gttttgacta aactctgtgt
120tttagagagg gagttaaatg ctgttaactt tttaggggtg ggcgagaggg atgacaaata
180acaacttgtc tgaatgtttt acatttctcc ccactgcctc aagaaggttc acaacgaggt
240catccatgat aaggagtaag acctcccagc cggactgtcc ctcggccccc agaggacact
300ccacagagat atgctaactg gacttggaga ctggctcaca ctccagagaa aagcatggag
360cacgagcgca cagagcaggg ccaaggtccc agggacagaa tgtctaggag ggagattggg
420gtgagggtaa tctgatgcaa ttactgtggc agctcaacat tcaagggagg gggaagaaag
480aaacagtccc tgtcaagtaa gttgtgcagc agagatggta agctccaaaa tttgaaactt
540tggctgctgg aaagttttag ggggcagaga taagaagaca taagagactt tgagggttta
600ctacacacta gacgctctat gcatttattt atttattatc tcttatttat tactttgtat
660aactcttata ataatcttat gaaaacggaa accctcatat acccatttta cagatgagaa
720aagtgacaat tttgagagca tagctaagaa tagctagtaa gtaaaggagc tgggacctaa
780accaaaccct atctcaccag agtacacact cttttttttt ttccagtgta atttttttta
840atttttattt tactttaagt tctgggatac atgtgcagaa ggtatggttt gttacatagg
900tatatgtgtg ccatagtgga ttgctgcacc tatcaacccg tcatctaggt ttaagcccca
960catgcattag ctatttgtcc tgatgctctc cctcccctcc ccacaccaga caggccttgg
1020tgtgtgatgt tcccctccct gtgtccatgt gttctcactg ttcagctccc acttatgagt
1080gagaacgtgt ggtatttggt tttctgttcc tgtgttagtt tgctgaggat gatggcttcc
1140agcttcatcc atgtccctgc aaaggacacg atc
117372101DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR7 7atcatgccag cttaggcgac
agagtgagac tggacataat aacaataata ataaaaataa 60ataaataaaa caattatctg
agaggaaaaa tttgattcat aataaagaga ataaaggttt 120ttggcgtgtt tgttttgttt
tcacctaaga acagctgttc ccctcattgg gttagtttta 180tttgcaagca gaaatcatct
ccgcatgatt tccagggtga tggaaaactg aatatgaatc 240caccttctgc catctattca
cttgtcacat ttaataagac actcatgcct attttagcat 300gttttcttcc ctaccaaatg
agttagtaac atcaagagat taaaataaca caaataagaa 360cattgaaggt attcaaatgt
tacatacaaa tattaaacac aatattatta taattattcc 420tggaaatgac attgcctcta
ctctcaaggt aaaggtcatt tttcttgatt taaacttttt 480tctcaagttt gaaatctcta
agtttcaacc cgtaatctat ttgcaagttt gtgcaaattt 540tagggattga atccatagta
attagtgatt tattgtggtg tagggagaca agtcaaaaga 600atcaggactg ctaggtagat
gactaaggaa aggatggttc acgaggtgac ataaagcact 660cagaagaaaa aggtcaggaa
acggaggaca gaaaaaaacc taagttctgc tgggtgatgc 720tgaatttgtc atcacaaaat
ctgcattgtg gaagctttag ctattgagga gattgctcaa 780gtgtagaact gagaacaata
ggcagtgaac ccgagagaac atcaagagac tgagagaaaa 840tgaaccagac ttccaggtgc
tccatgttcc aaccaacatt ttgtattgtc agaaggaatt 900gagaggcaaa aggaaaccca
ataaaaaata aaacaggaaa gggcatacat gattaccacc 960ccttttctca ccagctgctc
atggaccagc tttctcctag tgctattttc ttggtcactg 1020catcactctg ctaacatagt
ttccccacta gctctgaggc tgtcccagag gggaagccag 1080ctgtcatctc cttcttccac
actctgttgg aggaacctgt cattagcagc tccctactaa 1140acgcatttat gacaaacagg
caggagataa ttaactagaa agtgaacaaa ctcaaacttc 1200agagcctctc atttgtatga
atgcccttgt aaggtcttgg gcctatttta atatttataa 1260atgtgttatt ttcttctaaa
gaaaaccacc aaattgtata agctacagaa tctgcaaaac 1320tgaggtccat ccatgcactc
aggatacatt catagcatct ctgagctgga aaatatctta 1380aaggtcatat atgtcctcca
acactgcaag aatctctctg gcagcattct tttaaaatca 1440tcatctaaaa gagggaaatc
cccagctgtg tttggatttt gctctgtcac ttgtccagtt 1500tccccatcca taaaagggca
acaatatgaa tttcctgata aggtagttgt taatataaat 1560acaaagtgcg tagccacttc
cctaagaaaa atatggggtt tctgcttcac agtctaggga 1620gaggaaaaaa aaggggggtc
agaagtgatt attattatca ttctatattg gaatgttttc 1680agacataaaa agctcaccac
gtcttaggcc agacagatgc attatgaaag ttaagctaag 1740tcttcctcat catgagctgc
acctatatcc ccattacttc ttctagaact gcataattta 1800tttattcttt cttcaaaagt
ttgagagagc cattcttgtc ctctaagatt tttttttttt 1860tttttggaga cagagtctcc
gtctgttgcc caggctggag tgcaatggca ctatctcagc 1920tcactgcaac ctctgcctcc
cagattcaag tgattctcct gcctcagcct cccgagtagc 1980tgggattaca agcacgcacc
accacaacca gctaattttt cgtatttttt agtagagacg 2040aggttttacc atgttggcca
ggctggtctt gaactcctga cctcgggtga tccacccacc 2100t
210181821DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR8 8gagatcacct cgaagagagt ctaacgtccg taggaacgct
ctcgggttca caaggattga 60ccgaacccca ggatacgtcg ctctccatct gaggcttgct
ccaaatggcc ctccactatt 120ccaggcacgt gggtgtctcc cctaactctc cctgctctcc
tgagcccatg ctgcctatca 180cccatcggtg caggtccttt ctgaagagct cgggtggatt
ctctccatcc cacttccttt 240cccaagaaag aagccaccgt tccaagacac ccaatgggac
attccccttc cacctccttc 300tccaaagttg cccaggtgtt catcacaggt tagggagaga
agcccccagg tttcagttac 360aaggcatagg acgctggcat gaacacacac acacacacac
acacacacac acacacacac 420acacgactcg aagaggtagc cacaagggtc attaaacact
tgacgactgt tttccaaaaa 480cgtggatgca gttcatccac gccaaagcca agggtgcaaa
gcaaacacgg aatggtggag 540agattccaga ggctcaccaa accctctcag gaatattttc
ctgaccctgg gggcagaggt 600tggaaacatt gaggacattt cttgggacac acggagaagc
tgaccgacca ggcattttcc 660tttccactgc aaatgaccta tggcgggggc atttcacttt
cccctgcaaa tcacctatgg 720cgaggtacct ccccaagccc ccacccccac ttccgcgaat
cggcatggct cggcctctat 780ccgggtgtca ctccaggtag gcttctcaac gctctcggct
caaagaagga caatcacagg 840tccaagccca aagcccacac ctcttccttt tgttataccc
acagaagtta gagaaaacgc 900cacactttga gacaaattaa gagtccttta tttaagccgg
cggccaaaga gatggctaac 960gctcaaaatt ctctgggccc cgaggaaggg gcttgactaa
cttctatacc ttggtttagg 1020aaggggaggg gaactcaaat gcggtaattc tacagaagta
aaaacatgca ggaatcaaaa 1080gaagcaaatg gttatagaga gataaacagt tttaaaaggc
aaatggttac aaaaggcaac 1140ggtaccaggt gcggggctct aaatccttca tgacacttag
atataggtgc tatgctggac 1200acgaactcaa ggctttatgt tgttatctct tcgagaaaaa
tcctgggaac ttcatgcact 1260gtttgtgcca gtatcttatc agttgattgg gctcccttga
aatgctgagt atctgcttac 1320acaggtcaac tccttgcgga agggggttgg gtaaggagcc
cttcgtgtct cgtaaattaa 1380ggggtcgatt ggagtttgtc cagcattccc agctacagag
agccttattt acatgagaag 1440caaggctagg tgattaaaga gaccaacagg gaagattcaa
agtagcgact tagagtaaaa 1500acaaggttag gcatttcact ttcccagaga acgcgcaaac
attcaatggg agagaggtcc 1560cgagtcgtca aagtcccaga tgtggcgagc ccccgggagg
aaaaaccgtg tcttccttag 1620gatgcccgga acaagagcta ggcttccgga gctaggcagc
catctatgtc cgtgagccgg 1680cgggagggag accgccggga ggcgaagtgg ggcggggcca
tccttctttc tgctctgctg 1740ctgccgggga gctcctggct ggcgtccaag cggcaggagg
ccgccgtcct gcagggcgcc 1800gtagagtttg cggtgcagag t
182191929DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR9
9atgagccccc aaaaatgatc ctctggctta tgacaacctg atgcagccca ggaaatgcct
60gcaacatgcc cactagcagc tgggaacccc tctgtgagga agagaacgtt ttacattaag
120aaaccctttg ttttgcagca gagactattc aggtcacaca tgtgtggcct ctcagttctt
180tgagccattt gaagttctct atccttgctg ggaggctgag ctctccatgg aaacctggtc
240cgatagtgag aggagcagac cctctggaaa caccttttta cacctgacca aagcagccag
300tcatgggcca gtgatgcaac aaggtcaacc ggtgcattct ggcccctcag aaaagcagcc
360cccgggaagg tcaggaggag gctgctgact ccctcttccc ctgcagccgc cccaagcaca
420cccaggagcc ctgcaggttt gggttcacca ggtgccagca ggtcccacga tgctgcattt
480cttacgagct cctggaggat gcagatggtc ctggtcagag gctgcattct gagtatcagg
540agccatgggg caacgtttct gcgattgagg aaggggcatt tctggggtgg gcagaacaaa
600ggtctttggc tgagctggag catccgcctc catcagtgtt ttccggcaac tgtactatcc
660atcgtcttcc cttcccacag ctgaccatgg ctttggaaaa tgctctgaaa ctttcttttc
720agaagagttg actcccaact ccacacttag gggaagtcaa gcctacttct cagaattcag
780agaaggcata aaaaagaatt catttctaaa ggccctttag aagtaacttc aggtctgaca
840gcggccagct aatttctggt cgccttccag gaatcttctg actgcaaaaa aaaagcattt
900accacctgaa cacaaaccca gttacagata gaaaaacata gtcatttaaa tagaatataa
960gcatctggcc tctgcccatc ataatggagt aacacaaaaa tctattttca aaaggaaact
1020aaatattatt gaccaaaaca tgaatgggga gacctcaggg tgatacagct cttgcctgga
1080tggaatttgt aatcaagagg atgagacagg attgtaactt gtgccaatgt gaaagggttt
1140gctcaggtat cattcatttt gcttaaatgc atgggtaatt tccaaagttc tttggagctg
1200aatttcacaa tttagtgcag gtcctggtga gcccaccttg acttatctca cagtacaatg
1260cagtggcgtg gctacaatgc tgggcaagag aagccaatgt caacagccca ggagtggctg
1320ggtccttacc aggctcccag gcatgcttca tggtgggccc tgggctggga ggaacagcac
1380ctttgcctgg tccatgagta tctgggtcaa actctcctgt ggacacagaa ggccatggcg
1440acaggcattc ccaggaaaag aaaagggcag cagctgaaat cgtcaggtgg agaaggcagt
1500catccttgct cagtcaactc taatccggct gcctcctcct cagcttcagg gtgaacctct
1560cctaagctgt gtctttggta tctgatgggc attaggtgct ggtgaaaaag ctggagggtc
1620ctttgggata ttacagaagc ccaatctagc cttgtattca atatctaggc actctcaccc
1680ctgaagttct acgtttccag atttctgaaa acatgggaaa gcatgtgtgt gatgtctgag
1740gtccccctca gcctctggtg tagggttagg agggctctaa agggtggcag ctccagtgtc
1800ccagtggggc ctgaagttgg tcccttccct tcccagctcc catccatggt ttagcccaat
1860cccttccgta cctaagagta ctgcacatgg atgctccacg cagagcctct gctccactcc
1920caggaagtg
1929101167DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR10 10aggtcaggag
ttcaagacca gcctggccaa catggtgaaa ccctgtccct acaaaaaata 60caaaaattag
ccgggcgtgg tggggggcgc ctataatccc agctactcag gatgctgaga 120caggagaatt
gtttgaaccc gggaggtgga ggttgcagtg aactgagatc gcgccactgc 180actccagcct
ggtgacagag agagactccg tctcaacaac agacaaacaa acaaacaaac 240aacaacaaaa
atgtttactg acagctttat tgagataaaa ttcacatgcc ataaaggtca 300ccttctacag
tatacaattc agtggattta gtatgttcac aaagttgtac gttgttcacc 360atctactcca
gaacatttac atcaccccta aaagaagctc tttagcagtc acttctcatt 420ctccccagcc
cctgccaacc acgaatctac tntctgtctc tattctgaat atttcatata 480aaggagtcct
atcatatggg ccttttacgt ctaccttctt tcacttagca tcatgttttt 540aagattcatc
cacagtgtag cacgtgtcag ttaattcatt tcatcttatg gctggataat 600gctctattgt
atgcatatcc ctcactttgc ttatccattc atcaactgat tgacatttgg 660gttatttcta
ctttttgact attatgagta atgctgctat gaacattcct gtaccaatcg 720ttacgtggac
atatgctttc aattctcctg agtatgtaac tagggttgga gttgctgggt 780catatgttaa
ctcagtgttt catttttttg aagaactacc aaatggtttt ccaaagtgga 840tgcaacactt
tacattccca ccagcaagat atgaaggttc caatgtctct acatttttgc 900caacacttgt
gattttcttt tatttattta tttatttatt tatttttgag atggagtctc 960actctgtcac
ccaggctgga gtgcagtggc acaatttcag ctcactgcaa tctccacctc 1020tcgggctcaa
gcgatactcc tgcctcaacc tcccgagtaa ctgggattac aggcgcccac 1080caccacacca
agctaatttt ttgtattttt agtagagacg gggtttcatc atgtcggcca 1140ggntgtactc
gaactctgac ctcaagt
1167111377DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR11 11gattctgggt
gggtttgatg atctgagagt cccttgaata aaaagaattc tagaaaagct 60gtgaaacttc
acctttcccc tattcttaac cttacttgcc tttgggaggc tgaggcagga 120ggatgactta
aggccaggag tttgagaatg tagtgagcta tgaccacacc ggttacactc 180aagcctgggc
gagaccacaa caaaaacctt acctgccaac tgctccatgc tggaaattta 240tttcgtttct
tggattgtgg aaagaactgg cttactgaaa accacacttc tctaaaaccc 300ttcttccagt
taggtgttaa gattttaaca gcctttccta tctgaataaa aactgcacac 360aaagtaaact
taagagatgt caacaactca tctgtttgtt acaagatgag tctccatgct 420tcatcgcctg
tggggaatcc tcatcagcgt ctagtggcaa agactcctgt gtgctcaccg 480aaacgctccc
cttcctccag ggcacacagt cacatggatt tcccatgcac cctggcagct 540cagcaggagt
ccatgactta agaaggccaa tggactgtgg gtgaagtctg tggacgggga 600agccacatgc
gtcacttcca ggcctgggcg tgtgcatcct ccactctctt cccctgtggg 660tgcagaaggc
ggggcagagg gccctgaaac cttggaggtc ggtggagccc aaaatgaagg 720agcgtgggcc
tctgggtctt catgtaaatt taggtaacac tgaactgtca ggtgaacaag 780aaataaacgt
caaatgtatt cagtcgatta gatttggtga tggttgttac agcggttacc 840ctccctcaac
ataataaatt ttcaaacaac tcataatggc tcactcatgt ataaaatatt 900ccatatgaaa
tcccgggata acatgcttat tctagctcaa gcttaatcag agtagtccat 960ctgagggagg
agatagtaga gggcagcaag gggttgtcac tgaagataac tagccttgct 1020aaaagaatgg
ttgaagaagt gagctacaga tagggtaaat ccacatctca gacattctgt 1080gatggtcctg
atattatcct aaagtaaaat gtagagttga accattttaa ttagattcta 1140gaattctatt
aatttataag atgggcattt ccacaaagga ctaaacaaag tacaagagga 1200ttaaataatc
atccacatgg gaggcaccgc cttgcacttt aaaatgatgg agcttatcaa 1260gactggctgt
ggatatctgt ccctgggagg gttttttccc ccattttttt cctttttgag 1320acatgttctc
gctatgttgc ccaggctggt cttgaactcc tgggctcaag tgatcct
1377121051DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR12 12atcctgcttc
tgggaagaga gtggcctccc ttgtgcaggt gactttggca ggaccagcag 60aaacccaggt
ttcctgtcag gaggaagtgc tcagcttatc tctgtgaagg gtcgtgataa 120ggcacgagga
ggcaggggct tgccaggatg ttgcctttct gtgccatatg ggacatctca 180gcttacgttg
ttaagaaata tttggcaaga agatgcacac agaatttctg taacgaatag 240gatggagttt
taagggttac tacgaaaaaa agaaaactac tggagaagag ggaagccaaa 300caccaccaag
tttgaaatcg attttattgg acgaatgtct cactttaaat ttaaatggag 360tccaacttcc
ttttctcacc cagacgtcga gaaggtggca ttcaaaatgt ttacacttgt 420ttcatctgcc
tttttgctaa gtcctggtcc cctacctcct ttccctcact tcacatttgt 480cgtttcatcg
cacacatatg ctcatcttta tatttacata tatataattt ttatatatgg 540cttgtgaaat
atgccagacg agggatgaaa tagtcctgaa aacagctgga aaattatgca 600acagtgggga
gattgggcac atgtacattc tgtactgcaa agttgcacaa cagaccaagt 660ttgttataag
tgaggctggg tggtttttat tttttctcta ggacaacagc ttgcctggtg 720gagtaggcct
cctgcagaag gcattttctt aggagcctca acttccccaa gaagaggaga 780gggcgagact
ggagttgtgc tggcagcaca gagacaaggg ggcacggcag gactgcagcc 840tgcagagggg
ctggagaagc ggaggctggc acccagtggc cagcgaggcc caggtccaag 900tccagcgagg
tcgaggtcta gagtacagca aggccaaggt ccaaggtcag tgagtctaag 960gtccatggtc
agtgaggctg agacccaggg tccaatgagg ccaaggtcca gagtccagta 1020aggccgagat
ccagggtcca gggaggtcaa g
1051131291DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR13 13ctgccctgat
cccttaatgc ttttggccca gagcaccccg ctaagtccaa ccccagaggg 60gcctcatccg
caaagcctcg ggaagaggac agtgacggag gcggctgccc tgtgagctgc 120acggggcaga
atgtcctttt ggcgtcatgt tggatgtcca cacatccata tggggtcagt 180tctattagga
ttccttcggg aagaggtaga gggtaggagg ggttaagcca cgagacgagg 240catgcagagg
ggtggcctgg atgggtctgc actgctgtcc atgcacacgg ggagcgttgc 300aaattgtgct
tcccagccca tagtgccccc acagaggagc ccgggagtcc ctggtgggcg 360tctgtgttcc
tgcaaggagc cagtggagat ggccccgtga actctcatcc cccttgcctt 420ggtggggtct
ctggcaggtt tatggagccg tacatctttg ggagccgcct ggaccacgac 480atcatcgacc
tggaacagac agccacgcac ctccagctgg ccttgaactt caccgcccac 540atggcctacc
gcaagggcat catcttgttt ataagccgca accggcagtt ctcgtacctg 600attgagaaca
tggcccgtga ctgtggcgag tacgcccaca ctcgctactt caggggcggc 660atgctgacca
acgcgcgcct cctctttggc cccacggtcc gcctgccgga cctcatcatc 720ttcctgcaca
cgctcaacaa catctttgag ccacacgtgg ccgtgagaga cgcagccaag 780atgaacatcc
ccacagtggg catcgtggac accaactgca acccctgcct catcacctac 840cctgtacccg
gcaatgacga ctctccgctg gctgtgcacc tctactgcag gctcttccag 900acggccatca
cccgggccaa ggagaagcgg cagcaggttg aggctctcta tcgcctgcag 960ggccagaagg
agcccgggga ccaggggcca gcccaccctc ctggggctga catgagccat 1020tccctgtgat
gttcactctc ctcccaaagc aaaccacagc caagcctgtc tgagctggga 1080gtccccttcc
ccagccctgg gtcagcggca tcctcagtcg ttgttactta ctcagctgat 1140gtcacagtgc
agacatccac cgttccacca cagaaccagt ggctgagcgg accaacgttg 1200ccatgtgcgt
ttgctctgtg gggaacagag cacagagggt gagcgacatg tgcagaacgg 1260ccccttggct
gcagttagga cctcagtggc t
129114711DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR14 14agcaaggacc agggctctgc
ctccccagtc agcatgagca gagcagactc ctttgagcag 60agcatcaggg cagaaataga
acagtttctg aatgagaaaa gacagcatga gacccaaaaa 120tgtgatgggt cagtggagaa
gaaaccagac acacatgaaa attcggcgaa gtcactctcg 180aaatcccacc aagagccggc
tacaaaggtg gtgcaccggc agggcctgat gggcgtccag 240aaggagttcg ccttctgcag
acctcccccg gttagcaaag acaaacgtgc agcccagaag 300cctcaggtcc aaggtcacga
ccacgaccac gcaggagaag gagggcagca caaagccagc 360aacccccacc gcccttcaga
agcagtacag aataaaagtg ggattaaaag gaacgccagc 420accgcaagga ggggaaagcg
agtcacgagc gccgtacagg cgcccgaggc gtccgactcc 480agcagcgacg acggcattga
ggaggccatc cagctgtacc aggtgcagaa aacacacaag 540gaggccgacg gggacccgcc
ccagagggtc cagctccaag aggaaagagc acctgcccct 600cccgcacaca gcacaagcag
cgccacaaaa agtgccttgc cagagaccca caggaaaaca 660cccagcaaga agaagccagt
gcccaccaag accacggacc ctggtccagg g 711151876DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR15 15cagtacatgc agaactgagt ccaaacgaga cggacagcaa
acccggcagt gggctcccag 60acattcctgg gggaaaggga tcctaaccac aggcagttaa
agtcatctcc tccaaccctc 120tatgacacag gctgtgcgct gtcatttaaa agctgagtga
aatttaaccc ttttcccatt 180tagaaaaaca aagcgcagct ggctgccagc actcatttaa
ttttacataa acgtgctctt 240tgaggctgaa gcaaatctga ctgattttca atgtgaaaat
aaaatgtaaa aactgttctt 300ggaattattt ctaaacagaa catcagaatc gtctgaatca
tcagaatcgg ctattttgga 360aaaatcggat tcatcaaacg aatcttcggc caacaactgt
tagagaacga tgttaacacc 420acgcatagga atgttacatt ttctagaatt tgacattttc
attgacggaa aattactgta 480tcttgtatat ggaaatacca ctactaaaaa cataatgcta
taaatagaat gatgtctttt 540gtttccaaag tcaatatact cgagcaatgc aaaaataata
ataaaagtga gatacttcat 600ggcaaagctg ccgcaggata aacattgcag ccacaagtgc
ccccagtatt ctcggggcaa 660actggaaaag ggctaacagg caacattttc atgttattct
actgagtgca gtaattattt 720ttaaaaatat acatgaataa tgaaaaaact gtggtatggt
tttaaagaaa tttccataac 780ctggtgaaac tcttcacaca gggtaatagg ttcataaagc
cttggtcctc tgcaaaacaa 840gcatcaactt gacaatgact aaaagaagca acagcaaaac
tgtcacgcat ttggagccat 900ggcctgggtt gggccggtgt aaagctctcc gccctctgga
gcaagtctgg gccccagcgg 960ctggcatgtg ggcactgcag ggcctgggtt gggcaggtgt
gcagctctcc gtcatctgag 1020cctagtctga ggcctggtgg ctggcacgtg ggccctgcag
ggcctctact tctcacccca 1080gctccacttc cctccctgcc ctcactgggt ctcacagagc
caatgaacac tggggtcaga 1140ttcagggccc agcatccact gcagtgggca ctgcccttcc
acaaggcctg gctccaggaa 1200gcaaccccca cctcagccac acagtagggc aacaggaaat
cccattcccc catgccagtg 1260actacaccag ggaaggggct cacgtgaggc tggccccagg
cctgctgtga gaccgcgttg 1320tctatgagct tggatttaag gaacttggga gcaagaagct
ttctttcatt acgggccacc 1380agcagggaaa aaagttagcc caacgcagtt gacagtcaca
cccccaccag gaccccaggg 1440cacagaagga gggaagagga caacagagga tgaggtgggg
ccagcagagg gacagagaag 1500agctgcctgc cctggaacag gcagaaagca tcccacgtgc
aagaaaaagt aggccagcta 1560gacttaaaat cagaactacc gctcatcaaa agatagtgta
acatttgggg tgctataatt 1620ttaacatgtc ccccaaaagg catgtgttgg aaatttaatc
cccaacaaac cagggctggg 1680aggtggagcc tcatgagagg tggtgaggcc atgagggtgg
agtgaatgga tgaatgccat 1740tgtctcggga atgggcctct tctacaagga cgagttcagc
ccccctttct cttgctcacc 1800ctctctttgc cctttcgcta gggagtgacg taacaagaag
gccctcacaa gatgctggca 1860ccttgatctt ggactc
1876161282DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR16
16cgcccacctc ggctttccaa agtgctggga ttacaggcat gagtcactgc gcccatcctg
60attccaagtc tttagataat aacttaactt tttcgaccaa ttgccaatca ggcaatcttt
120gaatctgcct atgacctagg acatccctct ccctacaagt tgccccgcgt ttccagacca
180aaccaatgta catcttacat gtattgattg aagttttaca tctccctaaa acatataaaa
240ccaagctata gtctgaccac ctcaggcacg tgttctcagg acctccctgg ggctatggca
300tgggtcctgg tcctcagatt tggctcagaa taaatctctt caaatatttt ccagaatttt
360actcttttca tcaccattac ctatcaccca taagtcagag ttttccacaa ccccttcctc
420agattcagta atttgctaga atggccacca aactcaggaa agtattttac ttacaattac
480caatttatta tgaagaactc aaatcaggaa tagccaaatg gaagaggcat agggaaaggt
540atggaggaag gggcacaaag cttccatgcc ctgtgtgcac accaccctct cagcatcttc
600atgtgttcac caactcagaa gctcttcaaa ctttgtcatt taggggtttt tatggcagtt
660ccactatgta ggcatggttg ataaatcact ggtcatcggt gatagaactc tgtctccagc
720tcctctctct ctcctcccca gaagtcctga ggtggggctg aaagtttcac aaggttagtt
780gctctgacaa ccagccccta tcctgaagct attgaggggt cccccaaaag ttaccttagt
840atggttggaa gaggcttatt atgaataaca aaagatgctc ctatttttac cactagggag
900catatccaag tcttgcggga acaaagcatg ttactggtag caaattcata caggtagata
960gcaatctcaa ttcttgcctt ctcagaagaa agaatttgac caagggggca taaggcagag
1020tgagggacca agataagttt tagagcagga gtgaaagttt attaaaaagt tttaggcagg
1080aatgaaagaa agtaaagtac atttggaaga gggccaagtg ggcgacatga gagagtcaaa
1140caccatgccc tgtttgatgt ttggcttggg gtcttatatg atgacatgct tctgagggtt
1200gcatccttct cccctgattc ttcccttggg gtgggctgtc cgcatgcaca atggcctgcc
1260agcagtaggg aggggccgca tg
128217793DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR17 17atccgagggg aggaggagaa
gaggaaggcg agcagggcgc cggagcccga ggtgtctgcg 60agaactgttt taaatggttg
gcttgaaaat gtcactagtg ctaagtggct tttcggattg 120tcttatttat tactttgtca
ggtttcctta aggagagggt gtgttggggg tgggggagga 180ggtggactgg ggaaacctct
gcgtttctcc tcctcggctg cacagggtga gtaggaaacg 240cctcgctgcc acttaacaat
ccctctatta gtaaatctac gcggagactc tatgggaagc 300cgagaaccag tgtcttcttc
cagggcagaa gtcacctgtt gggaacggcc cccgggtccc 360cctgctgggc tttccggctc
ttctaggcgg cctgatttct cctcagccct ccacccagcg 420tccctcaggg acttttcaca
cctccccacc cccatttcca ctacagtctc ccagggcaca 480gcacttcatt gacagccaca
cgagccttct cgttctcttc tcctctgttc cttctctttc 540tcttctcctc tgttccttct
ctttctctgt cataatttcc ttggtgcttt cgccacctta 600aacaaaaaag agaaaaaaat
aaaataaaaa aaacccattc tgagccaaag tattttaaga 660tgaatccaag aaagcgaccc
acatagccct ccccacccac ggagtgcgcc aagacgcacc 720caggctccat cacagggccg
agagcagcgc cactctggtc gtacttttgg gtcaagagat 780cttgcaaaag agg
79318492DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR18 18atctttttgc tctctaaatg tattgatggg ttgtgttttt
tttcccacct gctaataaat 60attacattgc aacattcttc cctcaacttc aaaactgctg
aactgaaaca atatgcataa 120aagaaaatcc tttgcagaag aaaaaaagct attttctccc
actgattttg aatggcactt 180gcggatgcag ttcgcaaatc ctattgccta ttccctcatg
aacattgtga aatgaaacct 240ttggacagtc tgccgcattg cgcatgagac tgcctgcgca
aggcaagggt atggttccca 300aagcacccag tggtaaatcc taacttatta ttcccttaaa
attccaatgt aacaacgtgg 360gccataaaag agtttctgaa caaaacatgt catctttgtg
gaaaggtgtt tttcgtaatt 420aatgatggaa tcatgctcat ttcaaaatgg aggtccacga
tttgtggcca gctgatgcct 480gcaaattatc ct
492191840DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR19
19tcacttcctg atattttaca ttcaaggcta gctttatgca tatgcaacct gtgcagttgc
60acagggcttt gtgttcagaa agactagctc ttggtttaat actctgttgt tgccatcttg
120agattcatta taatataatt tttgaatttg tgttttgaac gtgatgtcca atgggacaat
180ggaacattca cataacagag gagacaggtc aggtggcagc ctcaattcct tgccaccctt
240ttcacataca gcattggcaa tgccccatga gcacaaaatt tgggggaacc atgatgctaa
300gactcaaagc acatataaac atgttacctc tgtgactaaa agaagtggag gtgctgacag
360cccccagagg ccacagttta tgttcaaacc aaaacttgct tagggtgcag aaagaaggca
420atggcagggt ctaagaaaca gcccatcata tccttgttta ttcatgttac gtccctgcat
480gaactaatca cttacactga aaatattgac agaggaggaa atggaaagat agggcaaccc
540atagttcttt ttccttttag tctttcctta tcagtaaacc aaagatagta ttggtaaaat
600gtgtgtgagt taattaatga gttagtttta ggcagtgttt ccactgttgg ggtaagaaca
660aaatatatag gcttgtattg agctattaaa tgtaaattgt ggaatgtcag tgattccaag
720tatgaattaa atatccttgt atttgcattt aaaattggca ctgaacaaca aagattaaca
780gtaaaattaa taatgtaaaa gtttaatttt tacttagaat gacattaaat agcaaataaa
840agcaccatga taaatcaaga gagagactgt ggaaagaagg aaaacgtttt tattttagta
900tatttaatgg gactttcttc ctgatgtttt gttttgtttt gagagagagg gatgtggggg
960cagggaggtc tcattttgtt gcccaggctg gacttgaact cctgggctcc agctatcctg
1020ccttagcttc ttgagtagct gggactacag gcacacacca cagtgtctga cattttctgg
1080attttttttt tttttttatt ttttttgtga gacaggttct ggctctgtta ctcaggttgc
1140agtgcagtgg catgatagcg gctcactgca gcctcaacct cctcagctta agctactctc
1200ccacttcagc ctcctgagta gccaggacta cagttgtgtg ccaccacacc tgtggctaat
1260ttttgtagag atggggtctc tccacgttgc cgaggctggt ctccaactcc tggtctcaag
1320cgaacctcct gacttggcct cccgaagtgc tgggattaca ggcttgagcc actgcatcca
1380gcctgtcctc tgtgttaaac ctactccaat ttgtctttca tctctacata aacggctctt
1440ttcaaagttc ccatagacct cactgttgct aatctaataa taaattatct gccttttctt
1500acatggttca tcagtagcag cattagattg ggctgctcaa ttcttcttgg tatattttct
1560tcatttggct tctggggcat cacactctct ttgagttact cattcctcat tgatagcttc
1620ttcctagtct tctttactgg ttcttcctct tctccctgac tccttaatat tgtttttctc
1680cccaggcttt agttcttagt cctcttctgt tatctattta cacccaattc tttcagagtc
1740tcatccagag tcatgaactt aaacctgttt ctgtgcagat aattcacatt attatatctc
1800cagcccagac tctcccgcaa actgcagact gatcctactg
184020780DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR20 20gatctcaagt ttcaatatca
tgttttggca aaacattcga tgctcccaca tccttaccta 60aagctaccag aaaggctttg
ggaactgtca acagagctac agaaaagtca gtaaagacca 120atggacccct caaacaaaaa
cagccaagct tttctgccaa aaagatgact gagaagactg 180ttaaagcaaa aaactctgtt
cctgcctcag atgatggcta tccagaaata gaaaaattat 240ttcccttcaa tcctctaggc
ttcgagagtt ttgacctgcc tgaagagcac cagattgcac 300atctcccctt gagtgaagtg
cctctcatga tacttgatga ggagagagag cttgaaaagc 360tgtttcagct gggcccccct
tcacctttga agatgccctc tccaccatgg aaatccaatc 420tgttgcagtc tcctttaagc
attctgttga ccctggatgt tgaattgcca cctgtttgct 480ctgacataga tatttaaatt
tcttagtgct ttagagtttg tgtatatttc tattaataaa 540gcattatttg tttaacagaa
aaaaagatat atacttaaat cctaaaataa aataaccatt 600aaaaggaaaa acaggagtta
taactaataa gggaacaaag gacataaaat gggataataa 660tgcttaatcc aaaataaagc
agaaaatgaa gaaaaatgaa atgaagaaca gataaataga 720aaacaaatag caatatgaaa
gacaaacttg accgggtgtg gtggctgatg cctgtaatcc 78021607DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR21 21gatcaataat ttgtaatagt cagtgaatac aaaggggtat
atactaaatg ctacagaaat 60tccattcctg ggtataaatc ctagacatat ttatgcatat
gtacaccaag atatatctgc 120aagaatgttc acagcaaatc tctttgtagt agcaaaaggc
caaaaggtct atcaacaaga 180aaattaatac attgtggcac ataatggcat ccttatgcca
ataaaaatgg atgaaattat 240agttaggttc aaaaggcaag cctccagata atttatatca
tataattcca tgtacaacat 300tcaacaacaa gcaaaactaa acatatacaa atgtcaggga
aaatgatgaa caaggttaga 360aaatgattaa tataaaaata ctgcacagtg ataacattta
atgagaaaaa aagaaggaag 420ggcttaggga gggacctaca gggaactcca aagttcatgg
taagtactaa atacataatc 480aaagcactca aaatagaaaa tattttagta atgttttagc
tagttaatat cttacttaaa 540acaaggtcta ggccaggcac ggtggctcac acctgtaatc
ccagcacttt gggaggctga 600ggcgggt
607221380DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR22
22cccttgtgat ccacccgcct tggcctccca aagtgctggg attacaggcg tgagtcacta
60cgcccggcca ccctccctgt atattatttc taagtatact attatgttaa aaaaagttta
120aaaatattga tttaatgaat tcccagaaac taggatttta catgtcacgt tttcttatta
180taaaaataaa aatcaacaat aaatatatgg taaaagtaaa aagaaaaaca aaaacaaaaa
240gtgaaaaaaa taaacaacac tcctgtcaaa aaacaacagt tgtgataaaa cttaagtgcc
300tgaaaattta gaaacatcct tctaaagaag ttctgaataa aataaggaat aaaataatca
360catagttttg gtcattggtt ctgtttatgt gatggattat gtttattgat ttgtgtatgt
420tgaacttatc tcaatagatg cagacaaggc cttgataaaa gtttttaaca ccttttcatg
480ttgaaaactc tcaatagact aggtattgat gaaacatatc tcaaaataat agaagctatt
540tatgataaac ccatagccaa tatcatactg agtgggcaaa agctggaagc attccctttg
600aaaactggca caagacaagg atgccctctc tcaccactcc tattaaatgt agtattggaa
660gttctggcca gagcaatcag gcaggagaaa gaaaaggtat taaaatagga agagaggaag
720tcaaattgtc tctgtttgca gtaaacatga ttgtatattt agaaaacccc attgtctcat
780cctaaaaact ccttaagctg ataaacaact tcagcaaagt ctcaggatac aaaatcaatg
840tgcaaaaatc acaagcattc ctatacaccg ataatagaca gcagagagcc aaatcatgag
900tgaagtccca ttcacaattg cttcaaagaa aataaaatac ttaggaatac aactttcacg
960ggacatgaag gacattttca aggacaacta aaaaccactg ctcaaggaaa tgagagagga
1020cacaaagaaa tggaaaaaca ttccatgctc atggaagaat caatatcatg aaaatggcca
1080tactgcccaa agtaatttat agattcaatg ctaaccccat caagccacca ttgactttct
1140tcacagaact agaaaaaaac tattttaaaa ctcatatgta gtcaaaaaga gtcggtatag
1200ccaagacaat cctaagcata aagaacaaag ctggatgcat cacgctgact tcaaaccata
1260ctacaaggct acagtaacca aaacagcatg gtactggtac caaaacagat agatagaccg
1320atagaacaga acagaggcct cggaaataac accacacatc tacaaccctt tgatcttcaa
1380231246DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR23 23atcccctcat
ccttcagggc agctgagcag ggcctcgagc agctggggga gcctcactta 60atgctcctgg
gagggcagcc agggagcatg gggtctgcag gcatggtcca gggtcctgca 120ggcggcacgc
accatgtgca gccgccccca cctgttgctc tgcctccgcc acctggccat 180gggcttcagc
agccagccac aaagtctgca gctgctgtac atggacaaga agcccacaag 240cagctagagg
accttgtgtt ccacgtgccc agggagcatg gcccacagcc caaagaccag 300tcaggagcag
gcaggggctt ctggcaggcc cagctctacc tctgtcttca cacagatggg 360agatttctgt
tgtgattttg agtgatgtgc ccctttggtg acatccaaga tagttgctga 420agcaccgctc
taacaatgtg tgtgtattct gaaaacgaga acttctttat tctgaaataa 480ttgatgcaaa
ataaattagt ttggatttga aattctattc atgtaggcat gcacacaaaa 540gtccaacatt
gcatatgaca caaagaaaag aaaaagcttg cattccttaa atacaaatat 600ctgttaacta
tatttgcaaa tatatttgaa tacacttcta ttatgttaca tataatatta 660tatgtatatg
tatatataat atacatatat atgttacata taatatactt ctattatgtt 720acatataata
tttatctata agtaaataca taaatataaa gatttgagta gctgtagaac 780attgtcttat
gtgttatcag ctactactac aaaaatatct cttccactta tgccagtttg 840ccatataaat
atgatcttct cattgatggc ccagggcaag agtgcagtgg gtacttattc 900tctgtgagga
gggaggagaa aagggaacaa ggagaaagtc acaaagggaa aactctggtg 960ttgccaaaat
gtcaagtttc acatattccg agacggaaaa tgacatgtcc cacagaagga 1020ccctgcccag
ctaatgtgtc acagatatct caggaagctt aaatgatttt tttaaaagaa 1080aagagatggc
attgtcactt gtttcttgta gctgaggctg tgggatgatg cagatttctg 1140gaaggcaaag
agctcctgct ttttccacac cgagggactt tcaggaatga ggccagggtg 1200ctgagcacta
caccaggaaa tccctggaga gtgtttttct tactta
124624939DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR24 24acgaggtcac gagttcgaga
ccagcctggc caagatggtg aagccctgtc tctactaaaa 60atacaacaag tagccgggcg
cggtgacggg cgcctgtaat cccagctact caggaggctg 120aagcaggaga atctctagaa
cccaggaggc ggaggtgcag tgagctgaga ctgccccgct 180gcactctagc ctgggcaaca
cagcaagact ctgtctcaaa taaataaata aataaataaa 240taaataaata aataaataaa
tagaaaggga gagttggaag tagatgaaag agaagaaaag 300aaatcctaga tttcctatct
gaaggcacca tgaagatgaa ggccacctct tctgggccag 360gtcctcccgt tgcaggtgaa
ccgagttctg gcctccattg gagaccaaag gagatgactt 420tggcctggct cctagtgagg
aagccatgcc tagtcctgtt ctgtttgggc ttgatcctgt 480atcacttgat tgtctctcct
ggactttcca tggattccag ggatgcaact gagaagttta 540tttttaatgc acttacttga
agtaagagtt attttaaaac attttagcaa aggaaatgaa 600ttctgacagg ttttgcactg
aagacattca catgtgagga aaacaggaaa accactatgc 660tagaaaaagc aaatgctgtt
gagattgtct cacaaacaca aattgcgtgc cagcaggtag 720gtttgagcct caggttgggc
acattttacc ttaagcgcac tgttggtgga acttaaggtg 780actgtaggac ttatatatac
atacatacat ataatatata tacatattta tgtgtatata 840cacacacaca cacacacaca
cacacagggt cttgctatct tgcccagggt ggtctccaac 900tctgggtctc aagcgatcct
ctgcctcccc ttcccaaag 939251067DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR25 25ataaaaaaat aaaaaaccct gctctaattt gcaaaggctc
tatctttcct cccaaccacc 60tgaaatttta gtgaaaacgg ggcttcctgt aggaaggagt
agctagctat cccggtccgc 120tacaggttat cagtgcgtga ataccctgac tcctaaggct
caggatttga ctgggtcgcc 180tcgtccgact gccccgcccc caacgcggac ccacgtcacc
gcgcgccagc ctgcggccgt 240cctgacctcg cgggatttga gcttcggtgc caacaaacac
tcccaccgcg gctgcgtcca 300ctttacctgc cggcggcgac cagcttctga agaaaagtgt
ccaccatggt gtcgaggagc 360ttcaccctcg aaatggtagt gccgggtggc acagattccg
aagacgaccc ctcatgcctt 420ttttcctcac agccgctgcc tagattggcg ctacttgctt
cggccatgtt gaagttgaac 480ctccaaatct aactggcccg gcctccccgc ctgccggagc
tcccgattgg ccgctcccgc 540gaagggtgcc tccgattgga agcagtagaa cgtctgtcac
cgagcagggc gggggcgggg 600aagtcatcgg aggctgaggg cagcggggag gcgaggctct
gcgcggtggg atgtccgcga 660ccggaaaaat acgcgcaagc caaagctcgg gggctcaata
aaaactttta attacatttc 720agagacttcg tacagtgcaa cagtgaatat tcactgttaa
ttttcacaag agtccatttc 780atcaaacgtt cagagagtct gccttttcat tcccttgttc
ctcagtgctc caatcaggtt 840tccagtctcc cagaggtttc ttttagtttt gattaccgac
caaaactcca gtttagggag 900aatggaagtc caccgtccca tccccaccaa aacatatttc
agtcaaaccc aatcccagtc 960cctaaagaat taggaaagta tgggccaagg gtccttttaa
ttatacacac atcaccctta 1020aaactgcgtg tgtgtacgag aaataaagaa aaacacaaga
ggggctg 106726540DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR26
26ccccctgaca agccccagtg tgtgatgttc cccactctgt gtccatgcat tctcattgtt
60caactcccat ctgtgagtga gaacatgcag tgtttggttt tctgtccttg agatagtttg
120ctgagaatga tggtttccag cttcatccat gtccttgcaa aggaagtgaa cttatccttt
180tttatggctt catagtattc catggcacat atgtgccaca tttttttaat ccagtctatc
240attgatggac atttgggttg gttccaagtc tttgctattg tgaatagcac cacaattaac
300atatgtgtgc atgtatacat ctttatagta gcatgattta taatccttcg ggtatatacc
360ctgtaatggg atcgctgggt caaatggtat ttctagttct agatccttga ggaatcacca
420cactgctttc cacaatggtt gaactaattt acgctcccac cagcagtgta aaagcattcc
480tatttctcca cgtcctctcc agtatctgtt gtttcctgac tttttaatga tcatcattct
540271520DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR27 27cttggccctc acaaagcctg
tggccaggga acaattagcg agctgcttat tttgctttgt 60atccccaatg ctgggcataa
tgcctgccat tatgagtaat gccggtagaa gtatgtgttc 120aaggaccaaa gttgataaat
accaaagaat ccagagaagg gagagaacat tgagtagagg 180atagtgacag aagagatggg
aacttctgac aagagttgtg aagatgtact aggcaggggg 240aacagcttaa ggagagtcac
acaggaccga gctcttgtca agccggctgc catggaggct 300gggtggggcc atggtagctt
tcccttcctt ctcaggttca gagtgtcagc cttgaacttc 360taattcccag aggcatttat
tcaatgtttt cttctagggg catacctgcc ctgctgtgga 420agactttctt ccctgtgggt
cgccccagtc cccagatgag acggtttggg tcagggccag 480gtgcaccgtt gggtgtgtgc
ttatgtctga tgacagttag ttactcagtc attagtcatt 540gagggaggtg tggtaaagat
ggagatgctg ggtcacatcc ctagagaggt gttccagtat 600gggcacatgg gagggctgga
aggataggtt actgctagac gtagagaagc cacatccttt 660aacaccctgg cttttcccac
tgccaagatc cagaaagtcc ttgtggtttc gctgctttct 720cctttttttt tttttttttt
tttctgagat ggagtctggc tctgtcgccc aggctggagt 780gcagtggcac gatttcggct
cactgcaagt tccgcctcct aggttcatac cattctccca 840cctcagcctc ccgagtagct
gggactacag gcgccaccac acccagctaa ttttttgtat 900ttttagtaga gacggcgttt
caccatgtta gccaggatgg tcttgatccg cctgcctcag 960cctcccaaag tgctgggatt
acaggcgtga gccaccgcgc ccggcctgct ttcttctttc 1020atgaagcatt cagctggtga
aaaagctcag ccaggctggt ctggaactct tgacctcaag 1080tgatctgcct gcctcagcct
cccaaagtgc tgagattaca ggcatgagcc agtccgaatg 1140tggctttttt tgttttgttt
tgaaacaagg tctcactgtt gcccaggctg cagtgcagtg 1200gcatacctca gctccactgc
agcctcgacc tcctgggctc aagcaatcct cccaactgag 1260cctccccagt agctggggct
acaagcgcat gccaccacgc ctggctattt tttttttttt 1320tttttttttt gagaaggagt
ttcattcttg ttgcccaggc tggagtgcaa tggcacagtc 1380tcagctcact gcagcctccg
cctcctgggt tcaagcgatt ctcctgcctc agcctcccga 1440gtagctggga ttataggcac
ctgccaccat gcctggctaa tttttttgta tttttagtag 1500ggatggggtt tcaccatgtt
152028961DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR28 28aggaggttat tcctgagcaa atggccagcc tagtgaactg
gataaatgcc catgtaagat 60ctgtttaccc tgagaagggc atttcctaac tctccctata
aaatgccaag tggagcaccc 120cagatgaaat agctgatatg ctttctatac aagccatcta
ggactggctt tatcatgacc 180aggatattca cccactgaat atggctatta cccaagttat
ggtaaatgct gtagttaagg 240gggtcccttc cacatggaca ccccaggtta taaccagaaa
gggttcccaa tctagactcc 300aagagagggt tcttagacct catgcaagaa agaacttggg
gcaagtacat aaagtgaaag 360caagtttatt aagaaagtaa agaaacaaaa aaatggctac
tccataagca aagttatttc 420tcacttatat gattaataag agatggatta ttcatgagtt
ttctgggaaa ggggtgggca 480attcctggaa ctgagggttc ctcccacttt tagaccatat
agggtatctt cctgatattg 540ccatggcatt tgtaaactgt catggcactg atgggagtgt
cttttagcat tctaatgcat 600tataattagc atataatgag cagtgaggat gaccagaggt
cacttctgtt gccatattgg 660tttcagtggg gtttggttgg cttttttttt tttttaacca
caacctgttt tttatttatt 720tatttattta tttatttatt tatatttttt attttttttt
agatggagtc ttgctctgtc 780acccaggtta gagtgcagtg gcaccatctc ggctcactgc
aagctctgcc tccttggttc 840acgccattct gctgcctcag cctcccgagt agctgggact
acaggtgcct gccaccatac 900ccggctaatt ttttctattt ttcagtagag acggggtttc
accgtgttag ccaggatggt 960c
961292233DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR29
29agcttggaca cttgctgatg ccactttgga tgttgaaggg ccgccctctc ccacaccgct
60ggccactttt aaatatgtcc cctctgccca gaagggcccc agaggagggg ctggtgaggg
120tgacaggagt tgactgctct cacagcaggg ggttccggag ggaccttttc tccccattgg
180gcagcataga aggacctaga agggccccct ccaagcccag ctgggcgtgc agggccagcg
240attcgatgcc ttcccctgac tcaggtggcg ctgtcctaaa ggtgtgtgtg ttttctgttc
300gccagggggt ggcggataca gtggagcatc gtgcccgaag tgtctgagcc cgtggtaagt
360ccctggaggg tgcacggtct cctccgactg tctccatcac gtcaggcctc acagcctgta
420ggcaccgctc ggggaagcct ctggatgagg ccatgtggtc atccccctgg agtcctggcc
480tggcctgaag aggaggggag gaggaggcca gcccctccct agccccaagg cctgcgaggc
540tgcaagcccg gccccacatt ctagtccagg cttggctgtg caagaagcag attgcctggc
600cctggccagg cttcccagct aggatgtggt atggcagggg tgggggacat tgaggggctg
660ctgtagcccc cacaacctcc ccaggtaggg tggtgaacag taggctggac aagtggacct
720gttcccatct gagattcaag agcccacctc tcggaggttg cagtgagccg agatccctcc
780actgcactcc agcctgggca acagagcaag actctgtctc aaaaaaacag aacaacgaca
840acaaaaaacc cacctctggc ccactgccta actttgtaaa taaagtttta ttggcacata
900gacacaccca ttcatttaca tactgctgcg gctgcttttg cattaccctt gagtagacga
960cagaccacgt ggccatggaa gccaaaaata tttactgtct ggccctttac agaagtctgc
1020tctagaggga gaccccggcc catggggcag gaccactggg cgtgggcaga agggaggcct
1080cggtgcctcc acgggcctag ttgggtatct cagtgcctgt ttcttgcatg gagcaccagg
1140ggtcagggca agtacctgga ggaggcaggc tgttgcccgc ccagcactgg gacccaggag
1200accttgagag gctcttaacg aatgggagac aagcaggacc agggctccca ttggctgggc
1260ctcagtttcc ctgcctgtaa gtgagggagg gcagctgtga aggtgaactg tgaggcagag
1320cctctgctca gccattgcag gggcggctct gccccactcc tgttgtgcac ccagagtgag
1380gggcacgggg tgagatgtca ccatcagccc ataggggtgt cctcctggtg ccaggtcccc
1440aagggatgtc ccatcccccc tggctgtgtg gggacagcag agtccctggg gctgggaggg
1500ctccacactg ttttgtcagt ggtttttctg aactgttaaa tttcagtgga aaattctctt
1560tcccctttta ctgaaggaac ctccaaagga agacctgact gtgtctgaga agttccagct
1620ggtgctggac gtcgcccaga aagcccaggt actgccacgg gcgccggcca ggggtgtgtc
1680tgcgccagcc atgggcacca gccaggggtg tgtctacgcc ggccaggggt aggtctccgc
1740cggcctccgc tgctgcctgg ggagggccgt gcctgacact gcaggcccgg tttgtccgcg
1800gtcagctgac ttgtagtcac cctgcccttg gatggtcgtt acagcaactc tggtggttgg
1860ggaaggggcc tcctgattca gcctctgcgg acggtgcgcg agggtggagc tcccctccct
1920ccccaccgcc cctggccagg gttgaacgcc cctgggaagg actcaggccc gggtctgctg
1980ttgctgtgag cgtggccacc tctgccctag accagagctg ggccttcccc ggcctaggag
2040cagccgggca ggaccacagg gctccgagtg acctcagggc tgcccgacct ggaggccctc
2100ctggcgtcgc ggtgtgactg acagcccagg agcgggggct gttgtaattg ctgtttctcc
2160ttcacacaga accttttcgg gaagatggct gacatcctgg agaagatcaa gaagtaagtc
2220ccgcccccca ccc
2233301851DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR30 30cctcccctgg
agccttcaga aggagcatgg cataggagtc ttgatttcag acgtctggtc 60cccagaatga
tgggagaatg aatttctgtt atttaagcca cccaacctgt ggtgctttgt 120tatagcagcc
tcaggaaact aacacactgc acgtgcccac tattcccttt tccagtatct 180ttcaggactt
gctggcttcc tttgttctgg cgtacaccca tgcatggccc cattccccac 240ttcctaaaac
aacaaccctg acttagtctg tttgggctgc tagaacaaaa tactatagac 300tgggtgactt
ataaacaaca gaaattcatt tctcacattc tggaggctgg gaagtccaat 360atcgaggcac
catcacattt ggtctctgct gaggccccct tcctagctcc tcactgtgtc 420cttacatggc
agaaggggca aggcagctct ctggggtccc ttttcaaggc cacaaatccc 480attcattagg
gctgatgact tcatgactta atcacctcct aatggcccca cctcctaatc 540gcattgggcg
ttaggattca acataaattt tggggggaca cacatattca gaccatagca 600aaccccaaca
ataaaaaacc ttcactttaa ggttccaaat ggactggcag ttaaatcatg 660ttcatattta
cataaaagaa ggagtaagtc aacaaattga taaacgcgtg gagatttgtt 720cggatggatg
ttcaccaaaa tgctggcctt aaagagtgag atgggaaatg ggaactatta 780cattcttctt
catacttttt ggtactgcct gcattgttaa aaaaaaaaaa aaagagcaca 840gagcattttt
acaatcagga aaaaaacaat gaggttatct tcattctgga aaaaaatgga 900aaatgaaaca
gtggagtcac atcatggaaa atgcttatgg tacaatttca tgtgacataa 960aacaatagaa
tagaggacct gttttatgac taaagcactg taaaaatgac aggcctggaa 1020ggagagatga
aaaccactca tttgttaagg tagtcaggtg gcaggtgatt tctcttcttt 1080tgaaaatttc
cattttcatt atatcgcagt ttgtgcattt actaaaactt tcggttggta 1140cacatgcata
aatagataga taaataagta gatagatgat agataaatag acggtaggta 1200gatagataga
tagatatgag aaataagtcc cctgtacttg gccttgcagc cataactagt 1260cattcccctt
cctctgtcca ttgctatgcc tgatggacaa ggcagtctgt gccctctggc 1320cccaattcca
atgtgccctc tgctcctggc tgttagtccc tttccacccc aatacaattg 1380ctccgaggtc
acttctaagt gtgaagcccc cagatcagat ggcttcttct gtgtccttac 1440cttacccaat
ttctaattat aactaaaaca caatgaggct ctagtaaaat accatgagac 1500ttcaggccct
ctgtataact tcactcattt aaacctaaca aggaaaacct accatgaatc 1560cgaggcacag
agcagctaag gaactcacca aggtcacgca gctattggtg atggaaccat 1620gagtcaagct
tcacagcctg ttggctctag aatagggttt cccaacctca gcactgtgga 1680cattttcagg
ctggataatt ctctgttgtg gggggctgtt ctgtgccttg taggatatta 1740ggagcatctc
tggcctctac ccactagacg cagcagcact cccatgccca gttgtgacaa 1800caagcaatgt
ctcccaccat tgccaagtgt cccctgggtg gaaatgcacc c
1851311701DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR31 31cacccgcctt
ggccccccag agtgctggga ttacaagtgt aaaccaccat tcctggctag 60atttaatttt
ttaaaaaata aagagaagta ggaatagttc attttaggga gagcccctta 120actgggacag
gggcaggaca ggggtgaggc ttcccttant tcaagctcac ctcaaaccca 180cccaggactg
tgtgtcacat tctccaataa aggaaaggtt gctgcccccg cctgtgagtg 240ctgcagtgga
gggtagaggg ccgtgggcag agtgcttcat ggactgctca tcaagaaagg 300cttcatgaca
atcggcccag ctgctgtcat cccacattct acttccagct aggagaaggc 360ggcttgccca
cagtcaccca gccggcaagt gtcacccctg ggttggaccc agagctatga 420tcctgcccag
gggtccagct gagaatcagg cccacgttct aggcagaggg gctcacctac 480tgggactcca
gtagctgtag tgcatggagg catcatggct gcagcagcct ggacctggtc 540tcacactggc
tgtccctgtg ggcaggccat cctcaatgcc aggtcaggcc caagcatgta 600tcccagacaa
tgacaatggg gtggaatcct ctcttgtccc agaagccact cctcactgtt 660ctacctgagg
aaggcagggg catggtggaa tcctgaagcc tgctgtgagg gtctccagcg 720aacttgcaca
tggtcagccc tgccttctcc tccctgaact agattgagcg agagcaagaa 780ggacattgaa
ccagcaccca aagaattttg gggaacggcc tctcatccag gtcaggctca 840cctccttttt
aaaatttaat taattaatta attaattttt ttttagagac agagtcttac 900tgtgtggccc
aggctgtagt gcagtggcac aatcatagtt cactgcagcc tcaaactccc 960cacctcagcc
tctggattag ctgagactac aggtgcacca ccaccacacc cagctaatat 1020ttttattttt
gtagagagag ggtttcacca tcttgcccag gctggtctca aactcctggg 1080ctcaagtgat
cccgcccagg tctgaaagcc cccaggctgg cctcagactg tggggttttc 1140catgcagcca
cccgagggcg cccccaagcc agttcatctc ggagtccagg cctggccctg 1200ggagacagag
tgaaaccagt ggtttttatg aacttaactt agagtttaaa agatttctac 1260tcgatcactt
gtcaagatgc gccctctctg gggagaaggg aacgtgactg gattccctca 1320ctgttgtatc
ttgaataaac gctgctgctt catcctgtgg gggccgtggc cctgtccctg 1380tgtgggtggg
gcctcttcca tttccctgac ttagaaacca cagtccacct agaacagggt 1440ttgagaggct
tagtcagcac tgggtagcgt tttgactcca ttctcggctt tcttcttttt 1500ctttccagga
tttttgtgca gaaatggttc ttttgttgcc gtgttagtcc tccttggaag 1560gcagctcaga
aggcccgtga aatgtcgggg gacaggaccc ccagggaggg aaccccaggc 1620tacgcacttt
agggttcgtt ctccagggag ggcgacctga cccccgnatc cgtcggngcg 1680cgnngnnacn
aannnnttcc c
170132771DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR32 32gatcacacag cttgtatgtg
ggagctagga ttggaacccc agaagtctgg ccccaggttc 60atgctctcac ccactgcata
caatggcctc tcataaatca atccagtata aaacattaga 120atctgcttta aaaccataga
attagtagcg taagtaataa atgcagagac catgcagtga 180atggcattcc tggaaaaagc
ccccagaagg aattttaaat cagctttcgt ctaatcttga 240gcagctagtt agcaaatatg
agaatacagt tgttcccaga taatgcttta tgtctgacca 300tcttaaactg gcgctgtttt
tcaaaaactt aaaaacaaaa tccatgactc ttttaattat 360aaaagtgata catgtctact
tgggaggctg aggtggtggg aggatggctt gagtttgagg 420ctgcagtatg ctactatcat
gcctataaat agccgctgca ttccagcttg ggcaacatac 480ccaggcccta tctcaaaaaa
ataaaaagta atacatctac attgaagaaa attaatttta 540ttgggttttt ttgcattttt
attatacaca gcacacacag cacatatgaa aaaatgggta 600tgaactcagg cattcaactg
gaagaacagt actaaatcaa tgtccatgta gtcagcgtga 660ctgaggttgg tttgtttttt
cttttttctt ctcttctctt ctcttttctt tttttttgag 720acggagcttt gctctttttg
cccaggcttg attgcaatgg cgtgatctca g 771331368DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR33 33gcttttatcc tccattcaca gctagcctgg cccccagagt
acccaattct ccctaaaaaa 60cggtcatgct gtatagatgt gtgtggcttg gtagtgctaa
agtggccaca tacagagctc 120tgacaccaaa cctcaggacc atgttcatgc cttctcactg
agttctggct tgttcgtgac 180acattatgac attatgatta tgatgacttg tgagagcctc
agtcttctat agcactttta 240gaatgcttta taaaaaccat ggggatgtca ttatattcta
acctgttagc acttctgttc 300gtattaccca tcacatccca acatcaattc tcatatatgc
aggtacctct tgtcacgcgc 360gtccatgtaa ggagaccaca aaacaggctt tgtttgagca
acaaggtttt tatttcacct 420gggtgcaggt gggctgagtc tgaaaagaga gtcagtgaag
ggagacaggg gtgggtccac 480tttataagat ttgggtaggt agtggaaaat tacaatcaaa
gggggttgtt ctctggctgg 540ccagggtggg ggtcacaagg tgctcagtgg gagagccttt
gagccaggat gagccagaag 600gaatttcaca aggtaatgtc atcagttaag gcagggactg
gccattttca cttcttttgt 660ggtggaatgt catcagttaa ggcaggaacc ggccattttc
acttcttttg tgattcttca 720cttgcttcag gccatctgga cgtataggtg caggtcacag
tcacagggga taagatggca 780atggcatagc ttgggctcag aggcctgaca cctctgagaa
actaaagatt ataaaaatga 840tggtcgcttc tattgcaaat ctgtgtttat tgtcaagagg
cacttatttg tcaattaaga 900acccagtggt agaatcgaat gtccgaatgt aaaacaaaat
acaaaacctc tgtgtgtgtg 960tgtgtgtgag tgtgtgtgta tgtgtgtgtg tgtgtattag
agaggaaaag cctgtatttg 1020gaggtgtgat tcttagattc taggttcttt cctgcccacc
ccatatgcac ccaccccaca 1080aaagaacaaa caacaaatcc caggacatct tagcgcaaca
tttcagtttg catattttac 1140atatttactt ttcttacata ttaaaaaact gaaaatttta
tgaacacgct aagttagatt 1200ttaaattaag tttgttttta cactgaaaat aatttaatat
ttgtgaagaa tactaataca 1260ttggtatatt tcattttctt aaaattctga acccctcttc
ccttatttcc ttttgacccg 1320attggtgtat tggtcatgtg actcatggat ttgccttaag
gcaggagg 136834755DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR34
34actgggcacc ctcctaggca ggggaatgtg agaactgccg ctgctctggg gctgggcgcc
60atgtcacagc aggagggagg acggtgttac accacgtggg aaggactcag ggtggtcagc
120cacaaagctg ctggtgatga ccaggggctt gtgtcttcac tctgcagccc taacacccag
180gctgggttcg ctaggctcca tcctgggggt gcagaccctg agagtgatgc cagtgggagc
240ctcccgcccc tccccttcct cgaaggccca ggggtcaaac agtgtagact cagaggcctg
300agggcacatg tttatttagc agacaaggtg gggctccatc agcggggtgg cctggggagc
360agctgcatgg gtggcactgt ggggagggtc tcccagctcc ctcaatggtg ttcgggctgg
420tgcggcagct ggcggcaccc tggacagagg tggatatgag ggtgatgggt ggggaaatgg
480gaggcacccg agatggggac agcagaataa agacagcagc agtgctgggg ggcaggggga
540tgagcaaagg caggcccaag acccccagcc cactgcaccc tggcctccca caagccccct
600cgcagccgcc cagccacact cactgtgcac tcagccgtcg atacactggt ctgttaggga
660gaaagtccgt cagaacaggc agctgtgtgt gtgtgtgcgt gtatgagtgt gtgtgtgtga
720tccctgactg ccaggtcctc tgcactgccc ctggg
755351193DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR35 35cgacttggtg atgcgggctc
ttttttggtt ccatatgaac tttaaagtag tcttttccaa 60ttctgtgaag aaagtcattg
gtaggttgat ggggatggca ttgaatctgt aaattacctt 120gggcagtatg gccattttca
caatgttgat tcttcctatc catgatgatg gaatgttctt 180ccattagttt gtatcctctt
ttatttcctt gagcagtggt ttgtagttct ccttgaagag 240gtccttcaca tcccttgtaa
gttggattcc taggtatttt attctctttg aagcaaattg 300tgaatgggag tncactcacg
atttggctct ctgtttgtct gctgggtgta taaanaatgt 360ngtgatnttn gtacattgat
ttngtatccn tgagacttng ctgaatttgc ttnatcngct 420tnngggaacc ttttgggctg
aaacnatggg attttctaaa tatacaatca tgtcgtctgc 480aaacagggaa caatttgact
tcctcttttc ctaattgaat acactttatc tccttctcct 540gcctaattgc cctgggcaaa
acttccaaca ctatgntngn aataggagnt ggtgagagag 600ggcatccctg ttcttgttgc
cagnttttca aagggaatgc ttccagtttt ggcccattca 660gtatgatatg ggctgtgggt
ngtgtcataa atagctctta tnattttgaa atgtgtccca 720tcaataccta atttattgaa
agtttttagc atgaangcat ngttgaattt ggtcaaaggc 780tttttctgca tctatggaaa
taatcatgtg gtttttgtct ttggctcntg tttatatgct 840ggatnacatt tattgatttg
tgtatatnga acccagcctn ncatcccagg gatgaagccc 900acttgatcca agcttggcgc
gcngnctagc tcgaggcagg caaaagtatg caaagcatgc 960atctcaatta gtcagcaccc
atagtccgcc cctacctccg cccatccgcc cctaactcng 1020nccgttcgcc cattctcgcc
catggctgac taatnttttt annatccaag cggngccgcc 1080ctgcttganc attcagagtn
nagagnnttg gaggccnagc cttgcaaaac tccggacngn 1140ttctnnggat tgaccccnnt
taaatatttg gttttttgtn ttttcanngg nga 1193361712DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR36 36gatcccatcc ttagcctcat cgatacctcc tgctcacctg
tcagtgcctc tggagtgtgt 60gtctagccca ggcccatccc ctggaactca ggggactcag
gactagtggg catgtacact 120tggcctcagg ggactcagga ttagtgagcc ccacatgtac
acttggcctc agtggactca 180ggactagtga gccccacatg tacacttggc ctcaggggac
tcaggattag tgagccccca 240catgtacact tggcctcagg ggactcagga ttagtgagcc
ccacatgtac acttggcctc 300aggggactca ggactagtga gccccacatg tacacttggc
ctcaggggac tcagaactag 360tgagccccac atgtacactt ggcttcaggg gactcaggat
tagtgagccc cacatgtaca 420cttggacacg tgaaccacat cgatgtgctg cagagctcag
ccctctgcag atgaaatgtg 480gtcatggcat tccttcacag tggcacccct cgttccctcc
ccacctcatc tcccattctt 540gtctgtcttc agcacctgcc atgtccagcc ggcagattcc
accgcagcat cttctgcagc 600acccccgacc acacacctcc ccagcgcctg cttggccctc
cagcccagct cccgcctttc 660ttccttgggg aagctccctg gacagacacc ccctcctccc
agccatggct ttttcctgct 720ctgccccacg cgggaccctg ccctggatgt gctacaatag
acacatcaga tacagtcctt 780cctcagcagc cggcagaccc agggtggact gctcggggcc
tgcctgtgag gtcacacagg 840tgtcgttaac ttgccatctc agcaactagt gaatatgggc
agatgctacc ttccttccgg 900ttccctggtg agaggtactg gtggatgtcc tgtgttgccg
gccacctttt gtccctggat 960gccatttatt tttttccaca aatatttccc aggtctcttc
tgtgtgcaag gtattagggc 1020tgcagcgggg gccaggccac agatctctgt cctgagaaga
cttggattct agtgcaggag 1080actgaagtgt atcacaccaa tcagtgtaaa ttgttaactg
ccacaaggag aaaggccagg 1140aaggagtggg gcatggtggt gttctagtgt tacaagaaga
agccagggag ggcttcctgg 1200atgaagtggc atctgacctg ggatctggag gaggagaaaa
atgtcccaaa agagcagaga 1260gcccacccta ggctctgcac caggaggcaa cttgctgggc
ttatggaatt cagagggcaa 1320gtgataagca gaaagtcctt gggggccaca attaggattt
ctgtcttcta aagggcctct 1380gccctctgct gtgtgacctt gggcaagtta cttcacctct
agtgctttgg ttgcctcatc 1440tgtaaagtgg tgaggataat gctatcacac tggttgagaa
ttgaagtaat tattgctgca 1500aagggcttat aagggtgtct aatactagta ctagtaggta
cttcatgtgt cttgacaatt 1560ttaatcatta ttattttgtc atcaccgtca ctcttccagg
ggactaatgt ccctgctgtt 1620ctgtccaaat taaacattgt ttatccctgt gggcatctgg
cgaggtggct aggaaagcct 1680ggagctgttt cctgttgacg tgccagacta gt
1712371321DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR37
37atctctctct gccaaagcaa cagcggtccc tgccccaacc agactacccc actcagtggg
60gttacggatg ctgctccagc atcctaacac tgcccagctg gtgcctgcct gtgctcaccc
120acaaccccca ggccggcctt ccctgcagcc tgggcttggc caccttggcc tgattgagca
180ctgaggcctc ctgggcaccc agccccatca ctgcacctgc tgcttccagc cccaccccac
240cggctcaggg gttcttccca gcggcgctga tcatgaagtc aacatgcacg caagtcgtct
300caggaaactt tttaatgaaa gtgtcggcca cggtggtgtg taggtggctg agctcagatt
360gcagctgcta agacaccagc cacttaccaa gagaaagcca ggctgcttca aacccagggc
420cggaggcaaa aaagcatcac ttccagccgg ggagtctgga agccacgcct tgtgggaggt
480cacactggca tctaggcctt cgcctgcact gcagaaggag agccgggtcc ccctcctgga
540gaacgctgcg ttccccagcc ccacaccggc tttgccacca cacaggctgt tgaggcagga
600ggcgggtaag acgtagctgt agacccaaag caaccaccag ccctgggacc ctgcgggaga
660ggagcacttt tagaacatgg aaaaatgtgg tcatcccatc attagacagc acacatccta
720cataaataaa aagtcgtatg gggaaggagg ttggggaggg aataaaaaat tggcacagac
780attgatagac tggtttccag tttcaaggta acagatgcac atcatgagac cagaggaggc
840agagacaagg gctgaatttg gcttttctaa gcaacatgtg ttcctgcgca gggctgaatg
900gtcgctgaga cagagatgga agccaggaca agggagccca ccgggcccag ataggtacag
960agagcagagg ctcctgttct gtcctcgcca cccatgaggg tgacactgct tgtaaatggt
1020ggctgtgctc tcccagcaag aaaaaagcac aactaaatcc acactgcaca cagacgcaga
1080cagaaagcct tcaagtggct ctgttttctg ctccctgcct tgccaggtcc acaagcagag
1140aggagtgtca ggcacatggc cccgctgtca ggctccccag tgagctgtag gctcagcagg
1200agctgcccac tgacacacag gggacaccca ctcctgccac cttgggagcg gttgccagac
1260agagccgcac tgggtgctgg tgtcatccag ggaccccaca cacttcctta aatgtgatcc
1320t
1321381445DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR38 38gatctatggg
agtagcttcc ttagtgagct ttcccttcaa atactttgca accaggtaga 60gaattttgga
gtgaaggttt tgttcttcgt ttcttcacaa tatggatatg catcttcttt 120tgaaaatgtt
aaagtaaatt acctctcttt tcagatactg tcttcatgcg aacttggtat 180cctgtttcca
tcccagcctt ctataaccca gtaacatctt ttttgaaacc agtgggtgag 240aaagacacct
ggtcaggaac gcggaccaca ggacaactca ggctcaccca cggcatcaga 300ctaaaggcaa
acaaggactc tgtataaagt accggtggca tgtgtatnag tggagatgca 360gcctgtgctc
tgcagacagg gagtcacaca gacacttttc tataatttct taagtgcttt 420gaatgttcaa
gtagaaagtc taacattaaa tttgattgaa caattgtata ttcatggaat 480attttggaac
ggaataccaa aaaatggcaa tagtggttct ttctggatgg aagacaaact 540tttcttgttt
aaaataaatt ttattttata tatttgaggt tgaccacatg accttaagga 600tacatataga
cagtaaactg gttactacag tgaagcaaat taacatatct accatcgtac 660atagttacat
ttttttgtgt gacaggaaca gctaaaatct acgtatttaa caaaaatcct 720aaagacaata
catttttatt aactatagcc ctcatgatgt acattagatc gtgtggttgt 780ttcttccgtc
cccgccacgc cttcctcctg ggatggggat tcattcccta gcaggtgtcg 840gagaactggc
gcccttgcag ggtaggtgcc ccggagcctg aggcgggnac tttaanatca 900gacgcttggg
ggccggctgg gaaaaactgg cggaaaatat tataactgna ctctcaatgc 960cagctgttgt
agaagctcct gggacaagcc gtggaagtcc cctcaggagg cttccgcgat 1020gtcctaggtg
gctgctccgc ccgccacggt catttccatt gactcacacg cgccgcctgg 1080aggaggaggc
tgcgctggac acgccggtgg cgcctttgcc tgggggagcg cagcctggag 1140ctctggcggc
agcgctggga gcggggcctc ggaggctggg cctggggacc caaggttggg 1200cggggcgcag
gaggtgggct cagggttctc cagagaatcc ccatgagctg acccgcaggg 1260cggccgggcc
agtaggcacc gggcccccgc ggtgacctgc ggacccgaag ctggagcagc 1320cactgcaaat
gctgcgctga ccccaaatgc tgtgtccttt aaatgtttta attaagaata 1380attaataggt
ccgggtgtgg aggctcaagc cttaatcccc agcacctggc gaggccgagg 1440aggga
1445392331DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR39 39tcactgcaac
ctccacctcc caggttcaag tgattctcct gcctcggcct cccgagtagc 60tgggactaca
ggtgcatgac accgcacctg gctagttttt gtatttttag tagagacagg 120gtttcactat
gttggccagg ttggtctcga actcctgacc ttgtgatccg cccacctcgg 180cctcccaaag
tgctgggatt acagagtgag ccactgcgcc tggcctgcac cccttactat 240tatatgcttt
gcattttctt ttagatttga agaacctcat tataaactct agcactaatc 300ttatgtcagt
taaatgcata gcaaatatct cctgacgtgg gagaatatat atttgcaagt 360cttcttgtga
acatatgttt tcagttctag ggagccagac gcctatgagt gaaaagccta 420gtcatcgtgg
agaagtgcat tcaactttgt aagaaactgc caaaccttta ttcataatgg 480ttgtataaat
tttacattac caccaataat gtatgagagt tccagttgct tcacatcctc 540accagcattt
tgttttgtct gtcttttttc ctttggttat tctagtgggc ataagatata 600atagtatccc
ttgtggttta atgtaaattc cactgaagac taataacatt tgcatatttc 660taattaataa
gcctttttaa gtgacttttc aagtctttgc tcatttttat tagatatttg 720ccttcttatt
attgatttga aagaattata tttatatgct tatattctgg ttataagccc 780tttgtcatta
ttttccaaaa caatatttgg ttgtttctgt actactttcc ttgctccttt 840gaattgactt
ggtgccttgg ccaaaaatca attgaccaca tacatgtggg tgcatctcca 900gactaccaca
ttccgtttat ctatttgtct ctccttgtgt caataacact ctgtcttgat 960aatggtaagt
tttgagatca ggttgtgtaa gtcctcctaa tttttcctgg gttttcaata 1020ttgctttgct
ttttaaaaat tttgtatttt catttacatt ttaaaataaa cttgttagtg 1080ggattttgat
tggcattgca ctgaactcgt ggatcaattt ggggagattg gacattctta 1140tatatggatc
ccgtggtcat caactttaag aactctttct catccattag taactcaatc 1200taggttcaga
tgctactcgt tttctgctca gtctgtgtct gagcccctta tgctcttcat 1260tttgtcatcc
aattaacctc agctttgcat caatactatt tcttgctttg gtgcctgtta 1320cctctcctct
aatcaccaat ccacaactta cctccaaatt cagggcttgt ctcattcttc 1380ccaggaggag
tgctgctcag tctatctact tagtattata atttctctgg cttggtatca 1440aggcactccc
atttccggct tccatgagat gtctcagagg gcatgctgcc cggtgtagct 1500gcatggtcaa
gcttcttcat atctcttgcc tcatcactta aactcactat tttgtactcc 1560tgcttcagct
atagggagct actgttagtt tcttgaagac atatgctctc tctctctctc 1620acatctggac
ctgagcacat cctgttactg ctgcttgaaa caatgtgatc cccaggcaca 1680caccattagc
ttagaagcct cccctgattc ttcaaggctg gttgagtccc ttctctgtgc 1740tctcatgaca
acagttggca attcctcgtt gcagcaccta gcccatgatg ctctttggag 1800gcagagactg
agtctttctc actattgaat ttccagcatt catcacagag cctggcatat 1860ataaagccct
ccatcatatg tattaagtga atggataaat gaaaaaaagt tatatatatg 1920tacatatatg
tgtatatatg tatatgtata tatgtgtata tatgtgtgta tatgtgtgtg 1980tatatatgta
catatatatg tatctatgta catatatgta tatatgtata tatatgtgtg 2040tgtatatgtg
tgtgtgtatg tatatatatt acaatgaaat actattcagc cttaaaaagg 2100cagggaatcc
tgtcatttaa cacaatatgg ataaacctag aggactctaa aggcaaatac 2160cacatgttct
cactcacaaa atctaaacaa gttgaactcc tacaagtaga gagtaggatg 2220atggttacca
agggctgggg gacgggagag gatggggaaa gcatagctgt ccatcaaagg 2280gtagaaagtt
tcatttagac aagaggaatc agctttagtg atctatttca c
2331401071DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR40 40gctgtgattc
aaactgtcag cgagataagg cagcagatca agaaagcact ccgggctcca 60gaaggagcct
tccaggccag ctttgagcat aagctgctga tgagcagtga gtgtcttgag 120tagtgttcag
ggcagcatgt taccattcat gcttgacttc tagccagtgt gacgagaggc 180tggagtcagg
tctctagaga gttgagcagc tccagcctta gatctcccag tcttatgcgg 240tgtgcccatt
cgctttgtgt ctgcagtccc ctggccacac ccagtaacag ttctgggatc 300tatgggagta
gcttccttag tgagctttcc cttcaaatac tttgcaacca ggtagagaat 360tttggagtga
aggttttgtt cttcgtttct tcacaatatg gatatgcatc ttcttttgaa 420aatgttaaag
taaattacct ctcttttcag atactgtctt catgcgaact tggtatcctg 480tttccatccc
agccttctat aacccagtaa catctttttt gaaaccagtg ggtgagaaag 540acacctggtc
aggaacgcgg accacaggac aactcaggct cacccacggc atcagactaa 600aggcaaacaa
ggactctgta taaagtaccg gtggcatgtg tattagtgga gatgcagcct 660gtgctctgca
gacagggagt cacacagaca cttttctata atttcttaag tgctttgaat 720gttcaagtag
aaagtctaac attaaatttg attgaacaat tgtatattca tggaatattt 780tggaacggaa
taccaaaaaa tggcaatagt ggttctttct ggatggaaga caaacttttc 840ttgtttaaaa
taaattttat tttatatatt tgaggttgac cacatgacct taaggataca 900tatagacagt
aaactggtta ctacagtgaa gcaaattaac atatctacca tcgtacatag 960ttacattttt
ttgtgtgaca ggaacagcta aaatctacgt atttaacaaa aatcctaaag 1020acaatacatt
tttattaact atagccctca tgatgtacat tagatctcta a
1071411135DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR41 41tgctcttgtt
gcccaggctg cagtgcaatg gcgctgtctc ggctcatcgc aacctccgcc 60tcccagattc
aagtgattct cctgcctcac cctcccaagt agctgggatt accagtatgc 120agcaacacgc
ccggctaatt ttgtatttgt aatagagacg gggtttcttc atgttggtca 180ggctggtctc
aaattcctgc cctcaggtga tctgcccacc ttggcctccc aaagtgctgg 240gattacaggc
atgagccact gtgcccggcc tgggctgggg cttttaaggg gactggaggg 300tgaggggctg
gaaaattggg agagttgatt ggtggggcaa gggggatgta atcatcaggg 360tgtacaaact
gcactcttgg tttagtcagc tcctcgtggg gtccttcgga gcagctcagt 420cagtagctcc
atcagtatac aggacccaaa ggaatatctc aaagggaaaa cagcatttcc 480taaggttcaa
gttgtgatct acggagcagt taggggaact acaatcttgt gacagggtct 540acatgcttct
gaggcaatga gacaccaagc agctacgagg aagcagtcag agagcacgcc 600gacctagtga
ctgatgctga tgtgctgcga gctgggttca ttttcatttc tcccctcccc 660ctgccctcat
taattttgta aagtttatag ggaacatttc acccactctg ctgtggatcc 720ctgtcactta
cggagtctgt catcttggct gtatgggctg tggcctctgc ggtgcccatt 780ctcaggaggt
gtgagaccca tgaggaccgg aggtggacaa ggctagagac cacacccccc 840cgctccatcc
aatcatgttt tcctgggtgc ttggtttcta tgcaggctgc atgtccttag 900tccctgcatg
ggaacagctc ctgtggtgag caggcccctg aggaaggcct tgagcgggaa 960tggagcctag
gcttaggctg cctggtaaga gctggaggga accagccgag gcttgtgcta 1020cttttttttc
cagaatgaaa tacgtgactg atgttggtgt cctgcagcgc cacgtttccc 1080gccacaacca
ccggaacgag gatgaggaga acacactctc cgtggactgc acacg
113542735DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR42 42aagggtgaga tcactaggga
gggaggaagg agctataaaa gaaagaggtc actcatcaca 60tcttacacac tttttaaaac
cttggttttt taatgtccgt gttcctcatt agcagtaagc 120cctgtggaag caggagtctt
tctcattgac caccatgaca agaccctatt tatgaaacat 180aatagacaca caaatgttta
tcggatattt attgaaatat aggaattttt cccctcacac 240ctcatgacca cattctggta
cattgtatga atgaatatac cataatttta cctatggctg 300tatatttagg tcttttcgtg
caggctataa aaatatgtat gggccggtca cagtgactta 360cgcccgtagt cccagaactt
tgggaggccg aggcgggtgg atcacctgag gtcgggagtt 420caaaaccagc ctgaccaaca
tggagaaacc ccgtctctgc taaaaataca aaaattaact 480ggacacggtg gcgtatgcct
gtaatcccag ctactcggga agctgaggca ggagaactgc 540ttgaacccag gaggcggagg
ttgtggtgag tcgagattgc gccattgcac tccagcctgg 600gcaacaagag cgaaattcca
tctcaaaaaa aagaaaaaag tatgactgta tttagagtag 660tatgtggatt tgaaaaatta
ataagtgttg ccaacttacc ttagggttta taccatttat 720gagggtgtcg gtttc
735431227DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR43 43caaatagatc tacacaaaac aagataatgt ctgcccattt
ttccaaagat aatgtggtga 60agtgggtaga gagaaatgca tccattctcc ccacccaacc
tctgctaaat tgtccatgtc 120acagtactga gaccaggggg cttattccca gcgggcagaa
tgtgcaccaa gcacctcttg 180tctcaatttg cagtctaggc cctgctattt gatggtgtga
aggcttgcac ctggcatgga 240aggtccgttt tgtacttctt gctttagcag ttcaaagagc
agggagagct gcgagggcct 300ctgcagcttc agatggatgt ggtcagcttg ttggaggcgc
cttctgtggt ccattatctc 360cagcccccct gcggtgttgc tgtttgcttg gcttgtctgg
ctctccatgc cttgttggct 420ccaaaatgtc atcatgctgc accccaggaa gaatgtgcag
gcccatctct tttatgtgct 480ttgggctatt ttgattcccc gttgggtata ttccctaggt
aagacccaga agacacagga 540ggtagttgct ttgggagagt ttggacctat gggtatgagg
taatagacac agtatcttct 600ctttcatttg gtgagactgt tagctctggc cgcggactga
attccacaca gctcacttgg 660gaaaacttta ttccaaaaca tagtcacatt gaacattgtg
gagaatgagg gacagagaag 720aggccctaga tttgtacatc tgggtgttat gtctataaat
agaatgcttt ggtggtcaac 780tagacttgtt catgttgaca tttagtcttg ccttttcggt
ggtgatttaa aaattatgta 840tatcttgttt ggaatatagt ggagctatgg tgtggcattt
tcatctggct ttttgtttag 900ctcagcccgt cctgttatgg gcagccttga agctcagtag
ctaatgaaga ggtatcctca 960ctccctccag agagcggtcc cctcacggct cattgagagt
ttgtcagcac cttgaaatga 1020gtttaaactt gtttattttt aaaacattct tggttatgaa
tgtgcctata ttgaattact 1080gaacaacctt atggttgtga agaattgatt tggtgctaag
gtgtataaat ttcaggacca 1140gtgtctctga agagttcatt tagcatgaag tcagcctgtg
gcaggttggg tggagccagg 1200gaacaatgga gaagctttca tgggtgg
1227441586DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR44
44tgagttgggg tcctaagcca gaagttaact atgctttcat atattcttgc aagtagaagt
60acagtgttgg tgtaaattcc ccttagatgg atagctaagc ccagaggaaa taatggtaat
120tggaaccata tgaccgtatg caattcatgt gcatatttat atcaagaaaa gaacattata
180ggtcgggtga gaccctattt tgttctgaca atgtcatctg tatttacatg tctgtttcgg
240gagtttggat gtcaagggat tctgtgctgg attgtaaagc atgtgcttct gcttgatgta
300gctactcaat tttgtattct tgactaataa agtcataaac ataattcaac ctctgtgtgc
360gtgctctcct tccattaatt tatactttag caaaaagtat tgaatgtgtg tgttatgtaa
420caatttccta taaattatat taaatgattt attagcttta ttcaataaag ttttaagtgt
480tttcttctat gactacatta tttgttaaca agaaatttct ttaactgaaa acttcaagga
540agactatctg ggtaactctt tcaaaaagaa ttgtccctgt attttgggat tgaatatatt
600aatttcttgt actgttttaa cagcacataa ttttacaaga caagccactt tttcaaagcc
660tgcttctcct cccattttcc ctatctctgt gattgacacc tccaacccct gtagcctgcc
720tctgctctct cttaaccagt cctactgata ctacttccta agtatttttc agccctgtcc
780ttcctctcca tcatgatgga ttcacttcca gttgaaatcc ttatggtacc ctccctggat
840tatggcagta atcagagagc tggtctcctt aactcaggat tcacttcttc tcatctgttg
900ttcacagtga catcagaaag atattttaaa atgatgaact agaattaatt atataaaaca
960cacatacaca cataaataat acttaaattt ttcaatgatg ttccaattat gtaaaatata
1020atataggagg cactttatgt tctggcctca atctttcaat tcaaacttat ctcctgccac
1080tatctccttt gaacattgta ttccagctac tttagaataa taataataca taatattcat
1140agagcccttc ctgggttcct atcaccgtac aaaatacttc acatataaca tttaatcttt
1200gacaacttta ttaggcatgc acaattatta tctatctata tatctatatc tatatatata
1260aaatctatat tttatagata agaaaataga gggtaaaaac ttgccaaaat tacaaagctt
1320agaagtgtag cagttgggat ttgaatctag gcatcctgcc tctatagtct acagtggctt
1380tcttgtgcca aaagccttgc agttccctag acttaacatt tctcaaaatc tgtgtctttc
1440acatgctctt ccaattgtct ggaaaatctt tcccaacctc agtctaactg tggtactcat
1500gttcacccca caagaattga ctccatctgt cccctctcca tgaaaatttc tttgaatctc
1560agcactttgg gaggctgagg caggtg
1586451981DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR45 45cacgccccag
cgtgccctgg actactgctc cgcaggactc ctgttctgct gcaccctgga 60ctacggcacc
agaggaccca gctcccgccg gcctgagcta tggcaccaga ggacccagct 120cccggcagcc
tggactatgg caccagagga cccagccccc cgcttcctgg gctaaggcac 180agtaggaccc
tgcctcatcg tgtactcctg ctcaggagga ccctcgcagg gcggcgcact 240ggactaagct
actgaaggag ccccacccct gcctaaccct ggactaaggc actggagaac 300tcttgctccg
cagagccacg gactcttgca caagagaacc tcagcccagc cgtgccctgg 360actgtggcac
agtagggccc acaccacgcc atggactcct gtattggagg aagagtagtg 420ataaatgtcc
aggtttacaa cttgaaaagt agcaatcaat gtgccacaat agatggatgt 480gatgtaaaat
tataaatgat gaaaacatta tgtgtaattg cctagccaga acagttacac 540aagacaaaga
cgtaaaagaa atccacatag ggaaggaaga ggtaagattg tttctgtttt 600ttgaaaatat
aatcttaaga tagagaaaat cttaaagatt ccaccaaaat aaatggttat 660agctgatgaa
gaaattcaat aaagttaata gttacaaaat caacatacaa atatcattat 720tgtttctatt
aactaatgac aaactattac ctgaaaaata aaggcaattc aatttataat 780agaatcaaaa
cagatatata aatatataaa agacaggagt aaatttaatc aaaaccataa 840aagatttaca
tactgaaaac tatagcacat tgatgaaaaa aattaaaatg gcataaataa 900atggagaaac
atccttcatt gatggattca aaaattagta ttgtaaaagt gtcaatgcta 960cccaaagcaa
tctacagatt aaatgcaacc actatcaaat tccaatgtca ttcttcacag 1020aaatagaaaa
attactgcta aaatttgtat ggaaccacaa aagacctgga ccaaccaaag 1080caatcttgaa
caaaaagaac aaagctggag gcatcagact acctgactcc aaactctatt 1140acaaagctat
aggaattaaa acagcatagc aatggcataa aaacagacat gtaaaacagt 1200acaaagggat
atagaacctg taaataaatc cgtgtgtctg tggtcaattg attttttgat 1260aaaataacta
aaaatacaca gtgaagaaag aaaattattt tcaataaatg gtgtagacaa 1320aactgactat
ccacatacag aagaataaaa tttgactttt attttgctct ttatacaagc 1380atcaaatcaa
aattaaagtt taaatgtaaa actactacaa ggaaatatag aaggagactg 1440tatgacattg
gcctgagcta tgattttctg tagattattc caaaaggcaa caaaagcaaa 1500acacacaaat
gagactgcat aaaacttaaa acttttccac aggaaaagaa gcaatgatag 1560aattaagaga
acccacaaat gggataatat ttttaaacca tacatcaggt aaggggctca 1620tataataata
tataagcaac tcaacctact caaaaataag aaaaaaacta tgcttattaa 1680aaaataagca
aagaatcaga atagacattt cctacatcat acaaaaggcc aaccaggtac 1740atgaaaaaat
cataaacatt cctaattatc agagaagtgc aaatcaatgc cacaatgaga 1800tatcacctca
cacattttac tagggctatt ataaaaaaag atggaagata agtgttggtg 1860aggatgtgga
gaaaaagaaa ccctgtacac tgttggtagg aatggaaatt agtacagcca 1920tcttggaaaa
cagtacgaag ctttctcaag aaattataaa tttatttacc ctatgatcca 1980t
1981461859DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR46 46attgtttttc
tcgcccttct gcattttctg caaattctgt tgaatcattg cagttactta 60ggtttgcttc
gtctccccca ttacaaacta cttactgggt ttttcaaccc tagttccctc 120atttttatga
tttatgctca tttctttgta cacttcgtct tgctccatct cccaactcat 180ggcccctggc
tttggattat tgttttggtc ttttattttt tgtcttcttc tacctcaaca 240cttatcttcc
tctcccagtc tccggtaccc tatcaccaag gttgtcatta acctttcata 300ttattcctca
ttatccatgt attcatttgc aaataagcgt atattaacaa aatcacaggt 360ttatggagat
ataattcaca taccttaaaa ttcaggcttt taaagtgtac ctttcatgtg 420gtttttggta
tattcacaaa gttatgcatt gatcaccacc atctgattcc ataacatgtt 480caatacctca
aaaagaagtc tgtactcatt agtagtcatt tcacattcac cactccctct 540ggctctgggc
agtcactgat ctttgtgtct ctatggattt gcctagtcta ggtattttta 600tgtaaatggc
atcatacaac atgtgacctt ttgtttggct tttttcattt agcaaaatgt 660tatcaaggtc
tgtccctgtt gtagcatgta ttagcacttc atttcttata tgctgaatga 720tatactttat
ttgtccatca gttgttcatg ctttatttgt ccatcagttg atgaacattt 780gcgtttttgc
cactttgggc tattaagaat aatgctactg tgaacaagtg tgtacaagtt 840cctctacaaa
tttttgtgtg gacatatcct ttcagttctc tcaggtgtat atctgggaat 900tgaattgctg
ggtcgtgtag tagctatgtt aaacactttg agaaactgct ataatgttct 960ccagagctgt
accattttaa attctgtgta tgaggattcc acgttctcca cttcctcacc 1020agtgtatgga
tttgggggta tactttttaa aaagtgggat taggctgggc acagtggctc 1080acacctgtaa
tcccaacact tcaggaagct gaggtgggag gatcacttga gcctagtagt 1140ttgagaccag
cctgggcaac atagggagac cctgtctcta caaaaaataa tttaaaataa 1200attagctggg
cgttgtggca cacacctgta gtcccagcta catgggaggc tgaggtggaa 1260ggattccctg
agcccagaag tttgaggttg cagtgagcca tgatggcagc actatactgt 1320agcctgggtg
tcagagcaag actccgtttc agggaagaaa aaaaaaagtg ggatgatatt 1380tttgacactt
ttcttcttgt tttcttaatt tcatacttct ggaaattcca ttaaattagc 1440tggtaccact
ctaactcatt gtgtttcatg gctgcatagt aatattgcat aatataaata 1500taccattcat
tcatcaaagt tagcagatat tgactgttag gtgccaggca ctgctctaag 1560cgttaaagaa
aaacacacaa aaacttttgc attcttagag tttattttcc aatggagggg 1620gtggagggag
gtaagaattt aggaaataaa ttaattacat atatagcata gggtttcacc 1680agtgagtgca
gcttgaatcg ttggcagctt tcttagtagt ataaatacag tactaaagat 1740gaaattactc
taaatggtgt tacttaaatt actggaatag gtattactat tagtcacttt 1800gcaggtgaaa
gtggaaacac catcgtaaaa tgtaaaatag gaaacagctg gttaatgtt
1859471082DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR47 47atcattagtc
attagggaaa tgcaaatgaa aaacacaagc agccaccaat atacacctac 60taggatgatt
taaaggaaaa taagtgtgaa gaaggacgta aagaaattgt aaccctgata 120cattgatggt
agaaatggat aaagttgcag ccactgtgaa aaacagtctg cagtggctca 180gaaggttaaa
tatagaaccc ctgttggacc caggaactct actcttaggc accccaaaga 240atagagaaca
gaaatcaaac agatgtttgt atactaatgt ttgtagcatc acttttcaca 300ggagccaaaa
ggtggaaata atccaaccat cagtgaacaa atgaatgtaa taaaagcaag 360gtggtctgca
tgcaatgcta catcatccat ctgtaaaaaa cgaacatcat tttgatagat 420gatacaacat
gggtggacat tgagaacatt atgcttagtg aaataagcca gacacaaaag 480gaatatattg
tataattgta attacatgaa gtgcctagaa tagtcaaatt catacaagag 540aaagtgggat
aggaatcacc atgggctgga aataggggga aggtgctata ctgcttattg 600tggacaaggt
ttcgtaagaa atcatcaaaa ttgtgggtgt agatagtggt gttggttatg 660caaccctgtg
aatatattga atgccatgga gtgcacactt tggttaaaag gttcaaatga 720taaatattgt
gttatatata tttccccacg atagaaaaca cgcacagcca agcccacatg 780ccagtcttgt
tagctgcctt cctttacctt caagagtggg ctgaagcttg tccaatcttt 840caaggttgct
gaagactgta tgatggaagt catctgcatt gggaaagaaa ttaatggaga 900gaggagaaaa
cttgagaatc cacactactc accctgcagg gccaagaact ctgtctccca 960tgctttgctg
tcctgtctca gtatttcctg tgaccacctc ctttttcaac tgaagacttt 1020gtacctgaag
gggttcccag gtttttcacc tcggcccttg tcaggactga tcctctcaac 1080ta
1082481242DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR48 48atcatgtatt
tgttttctga attaattctt agatacatta atgttttatg ttaccatgaa 60tgtgatatta
taatataata tttttaattg gttgctactg tttataagaa tttcattttc 120tgtttacttt
gccttcatat ctgaaaacct tgctgatttg attagtgcat ccacaaattt 180tcttggattt
tctatgggta attacaaatc tccacacaat gaggttgcag tgagccaaga 240tcacaccact
gtactccagc ctgggcgaca gagtgagaca ccatctcaca aaaacacata 300aacaaacaaa
cagaaactcc acacaatgac aacgtatgtg ctttcttttt ttcttcctct 360ttctataata
tttctttgtc ctatcttaac tgaactggcc agaaacccca ggacaatgat 420aaatacgagc
agtgtcaaca gacatctcat tccctttcct agcttttata aaaataacga 480ttatgcttca
acattacata tggtggtgtc gatggttttg ttatagataa gcttatcagg 540ttaagaaatt
tgtctgcgtt tcctagtttg gtataaagat tttaatataa atgaatgttg 600tattttatca
tcttattttt ttcctacatc tgctaaggta atcctgtgtt ttcccctttt 660caatctccta
atgtggtgaa tgacattaaa ataccttcta ttgttaaaat attcttgcaa 720cgctgtatag
aaccaatgcc tttattctgt attgctgatg gatttttgaa aaatatgtag 780gtggacttag
ttttctaagg ggaatagaat ttctaatata tttaaaatat tttgcatgta 840tgttctgaag
gacattggtg tgtcatttct ataccatctg gctactagag gagccgactg 900aaagtcacac
tgccggagga ggggagaggt gctcttccgt ttctggtgtc tgtagccatc 960tccagtggta
gctgcagtga taataatgct gcagtgccga cagttctgga aggagcaaca 1020acagtgattt
cagcagcagc agtattgcgg gatccccacg atggagcaag ggaaataatt 1080ctggaagcaa
tgacaatatc agctgtggct atagcagctg agatgtgagt tctcacggtg 1140gcagcttcaa
ggacagtagt gatggtccaa tggcgcccag acctagaaat gcacatttcc 1200tcagcaccgg
ctccagatgc tgagcttgga cagctgacgc ct
1242491015DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR49 49aaaccagaaa
cccaaaacaa tgggagtgac atgctaaaac cagaaaccca aaacaatggg 60agggtcctgc
taaaccagaa acccaaaaca atgggagtga agtgctaaaa ccagaaaccc 120aaaacaatgg
gagtgtcctg ctacaccaga aacccaaaac gatgggagtg acgtgataaa 180accagacacc
caaaacaatg ggagtgacgt gctaaaccag aaacccaaaa caatgggagt 240gacgtgctaa
aacctggaaa cctaaaacaa tgcgagtgag gtgctaacac cagaatccat 300aacaatgtga
gtgacgtgct aaaccagaac ccaaaacaat gggagtgacg tgctaaaaca 360ggaacccaaa
acaatgagag tgacgtgcta aaccagaaac ccaaaacaat gggaatgacg 420tgctaaaacc
ggaacccaaa acaatgggag tgatgtgcta aaccagaaac ccaaaacaat 480gggaatgaca
tgctaaaact ggaacccaaa acaatggtaa ctaagagtga tgctaaggcc 540ctacattttg
gtcacactct caactaagtg agaacttgac tgaaaaggag gatttttttt 600tctaagacag
agttttggtc tgtcccccag agtggagtgc agtggcatga tctcggctca 660ctgcaagctc
tgcctcccgg gttcaggcca ttctcctgcc tcagcctcct gagtagctgg 720gaatacaggc
acccgccacc acacttggct aattttttgt atttttagta gagatggggt 780ttcaccatat
tagcaaggat ggtctcaatc tcctgacctc gtgatctgcc cacctcaggc 840tcccaaagtg
ctgggattac aggtgtgagc caccacaccc agcaaaaagg aggaattttt 900aaagcaaaat
tatgggaggc cattgttttg aactaagctc atgcaatagg tcccaacaga 960ccaaaccaaa
ccaaaccaaa atggagtcac tcatgctaaa tgtagcataa tcaaa
1015502355DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR50 50caaccatcgt
tccgcaagag cggcttgttt attaaacatg aaatgaggga aaagcctagt 60agctccattg
gattgggaag aatggcaaag agagacaggc gtcattttct agaaagcaat 120cttcacacct
gttggtcctc acccattgaa tgtcctcacc caatctccaa cacagaaatg 180agtgactgtg
tgtgcacatg cgtgtgcatg tgtgaaagta tgagtgtgaa tgtgtctata 240tgggaacata
tatgtgattg tatgtgtgta actatgtgtg actggcagcg tggggagtgc 300tggttggagt
gtggtgtgat gtgagtatgc atgagtggct gtgtgtatga ctgtggcggg 360aggcggaagg
ggagaagcag caggctcagg tgtcgccaga gaggctggga ggaaactata 420aacctgggca
atttcctcct catcagcgag cctttcttgg gcaatagggg cagagctcaa 480agttcacaga
gatagtgcct gggaggcatg aggcaaggcg gaagtactgc gaggaggggc 540agagggtctg
acacttgagg ggttctaatg ggaaaggaaa gacccacact gaattccact 600tagccccaga
ccctgggccc agcggtgccg gcttccaacc ataccaacca tttccaagtg 660ttgccggcag
aagttaacct ctcttagcct cagtttcccc acctgtaaaa tggcagaagt 720aaccaagctt
accttcccgg cagtgtgtga ggatgaaaag agctatgtac gtgatgcact 780tagaagaagg
tctagggtgt gagtggtact cgtctggtgg gtgtggagaa gacattctag 840gcaatgagga
ctggggagag cctggcccat ggcttccact cagcaaggtc agtctcttgt 900cctctgcact
cccagccttc cagagaggac cttcccaacc agcactcccc acgctgccag 960tcacacatag
ttacacacat acaatcacat atatgttccc atatagacac attcacactc 1020ataccttcac
acatgcacac gcatgtgcac acacagtcac tcatttctgt gttggagatt 1080gggtgaggac
attcaatggg tgaggaccaa caggtgtgaa gattgctttc tagaaaatga 1140ctcctgtctc
tctttgccat tcttcccaat ccgatggagc tactaggctt ttccctcatt 1200tcatgtttaa
taaaccttcc caatggcgaa atgggctttc tcaagaagtg gtgagtgtcc 1260catccctgcg
gtggggacag gggtggcagc ggacaagcct gcctggaggg aactgtcagg 1320ctgattccca
gtccaactcc agcttccaac acctcatcct ccaggcagtc ttcattcttg 1380gctctaattt
cgctcttgtt ttctttttta tttttatcga gaactgggtg gagagctttt 1440ggtgtcattg
gggattgctt tgaaaccctt ctctgcctca cactgggagc tggcttgagt 1500caactggtct
ccatggaatt tcttttttta gtgtgtaaac agctaagttt taggcagctg 1560ttgtgccgtc
cagggtggaa agcagcctgt tgatgtggaa ctgcttggct cagatttctt 1620gggcaaacag
atgccgtgtc tctcaactca ccaattaaga agcccagaaa atgtggcttg 1680gagaccacat
gtctggttat gtctagtaat tcagatggct tcacctggga agccctttct 1740gaatgtcaaa
gccatgagat aaaggacata tatatagtag ctagggtggt ccacttctta 1800ggggccatct
ccggaggtgg tgagcactaa gtgccaggaa gagaggaaac tctgttttgg 1860agccaaagca
taaaaaaacc ttagccacaa accactgaac atttgttttg tgcaggttct 1920gagtccaggg
agggcttctg aggagagggg cagctggagc tggtaggagt tatgtgagat 1980ggagcaaggg
ccctttaaga ggtgggagca gcatgagcaa aggcagagag gtggtaatgt 2040ataaggtatg
tcatgggaaa gagtttggct ggaacagagt ttacagaata gaaaaattca 2100acactattaa
ttgagcctct actacgtgct cgacattgtt ctagtcactg agataggttt 2160ggtatacaaa
acaaaatcca tcctctatgg acattttagt gactaacaac aatataaata 2220ataaaagtga
acaaaagctc aaaacatgcc aggcactatt atttatttat ttatttattt 2280atttatttat
tttttgaaac agagtctcgc tctgttgccc aggctggagt gtagtggtgc 2340gatctcggct
cactg
2355512289DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR51 51tcacaggtga
caccaatccc ctgaccacgc tttgagaagc actgtactag attgactttc 60taatgtcagt
cttcattttc tagctctgtt acagccatgg tctccatatt atctagtaca 120acacacatac
aaatatgtgt gatacagtat gaatataata taaaaatatg tgttataata 180taaatataat
attaaaatat gtctttatac tagataataa tacttaataa cgttgagtgt 240ttaactgctc
taagcacttt acctgcagga aacagttttt tttttatttt ggtgaaatac 300aactaacata
aatttattta caattttaag catttttaag tgtatagttt agtggagtta 360atatattcaa
aatgttgtgc agccgtcacc atcatcagtc ttcataactc ttttcatatt 420gtaaaattaa
aagtttatgc tcatttaaaa atgactccca atttcccccc tcctcaacct 480ctggaaacta
ccattctatt ttctgcctcc gtagttttgc ccactctaag tacctcacat 540aagtggaatt
tgtcttattt gcctgtttgt gaccggctga tttcatttag tataatgtcc 600tcaagtttta
ttcacgttat atagcatatg tcataatttt cttcactttt aagcttgagt 660aatatttcat
cgtatgtatc tcacattttg cttatccatt catctctcag tggacacttg 720agttgcttct
acattttagc tgttgtgaat actgctgcta tgaacatggg tgtataaata 780tctcaagacc
tttttatcag ttttttaaaa tatatactca gtagtagttt agctggatta 840tatggtaatt
ttatttttaa tttttgagga actgtcctac ccttttattc aatagtagct 900ataccaattg
acaattggca ttcctaccaa cagggcataa gggttctcaa ttctccacat 960attccctgat
acttgttatt ttcaggtgtt tttttttttt tttttttttt atgggagcca 1020tgttaatggg
tgtaaggtga tatttcatta tagttttgat ttgcatttcc ctaatgatta 1080gtgatgttaa
gcatctcttc atgtgcctat tggccatttg tatatcttct ttaaaaatat 1140atatatactc
attcctttgc ccatttttga attatgttta ttttttgtta ttgagtttca 1200atacttttct
atataaccta ggtattaatc ctttatcaga cttaagattt gcaaatattc 1260tctttcattc
cacaggttgc taattctctc tgttggtaat atcttttgat gctgttgtgt 1320ccagaattga
ttcattcctg tgggttcttg gtctcactga cttcaagaat aaagctgcgg 1380accctagtgg
tgagtgttac acttcttata gatggtgttt ccggagtttg ttccttcaga 1440tgtgtccaga
gtttcttcct tccaatgggt tcatggtctt gctgacttca ggaatgaagc 1500cgcagacctt
cgcagtgagg tttacagctc ttaaaggtgg cgtgtccaga gttgtttgtt 1560ccccctggtg
ggttcgtggt cttgctgact tcaggaatga agccgcagac cctcgcagtg 1620agtgttacag
ctcataaagg tagtgcggac acagagtgag ctgcagcaag atttactgtg 1680aagagcaaaa
gaacaaagct tccacagcat agaaggacac cccagcgggt tcctgctgct 1740ggctcaggtg
gccagttatt attcccttat ttgccctgcc cacatcctgc tgattggtcc 1800attttacaga
gtactgattg gtccatttta cagagtgctg attggtgcat ttacaatcct 1860ttagctagac
acagagtgct gattgctgca ttcttacaga gtgctgattg gtgcatttac 1920agtcctttag
ctagatacag aacgctgatt gctgcgtttt ttacagagtg ctgattggtg 1980catttacaat
cctttagcta gacacagtgc tgattggtgg gtttttacag agtgctgatt 2040ggtgcgtctt
tacagagtgc tgattggtgc atttacaatc ctttagctag acacagagtg 2100ctgattggtg
cgtttataat cctctagcta gacagaaaag ttttccaagt ccccacctga 2160ccgagaagcc
ccactggctt cacctctcac tgttatactt tggacatttg tccccccaaa 2220atctcatgtt
gaaatgtaac ccctaatgtt ggaactgagg ccagactgga tgtggctggg 2280ccatgggga
2289521184DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR52 52cttatgccat
ctggcggtgc catgtggaac ttcgctgaag aagctaaatt tactgaccat 60ctgtgcctag
agcgggtttc tccaaggaaa ggctctgtaa atctcgtcct tttgaaatct 120aggggaaaac
agcctccttc actgaggatt aatttaaaga aagggggaaa taggaaaatt 180ccatgcgttg
gaagtccatt tagatttcta catgaaccat catatatgtg cactacataa 240ttcttatttt
tttattttta aaaaagggat aatttatatt ccagtgacaa gtttgggaaa 300ggccaaggca
agcaattgag ttgaacatta tgtagcgttt atatagacct tgcagacgtc 360tgtgcaatat
ccaccactga acacgtgagg tcgtactcaa gtctctctgg cccctggtaa 420tgtgactccc
ttcctttatt tgcatgaatc gcctggattg ggtgtcaggt ttttaaaacg 480tcaaggttta
cgcctattgt tgtcaaccaa tcagcatcct actttgacgt gattggcttc 540tactgtaggt
gtcaatcatc caaaatttgc atactactcc tcaggccgcc gggagcctgt 600cagtcggctg
tggcagctgg aagagaagga atcggacgga gaagaatgaa aaatcacttt 660gctttcgcaa
agcgaaagaa aagtattctt ttcctcatta tttttaaata aatttgattg 720tatatttacc
taataaaata aacattcaat taaacaaaaa taagcaacta tcaaagattt 780gtttactaat
tttcgtaatg tttactgttt caataagtag ccaaaggaat attaaaacac 840aaaaatatga
atgctgataa ttttatgtca taaagaccat tttaaaacta aaagtgaaca 900tggggtttct
aaataaaatt accgtggtag cgtaaaaaca ctgctttcaa tacttgggca 960tgctgaaagt
gctgcatcct aagataaaaa atacaccaag ggggggattt caaagaacat 1020tattttgctt
ttaataatcc tgtatttctg tcactttgcc ctttttattt atttaccgtg 1080aactcacaga
cagaatatta cttggagttt ctgaaatact tgtgtttgta catttctcat 1140cttacacgta
cccacacacc ccaaaataaa aaaacaaaga agag
1184531431DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR53 53ccctgaggaa
gatgacgagt aactccgtaa gagaaccttc cactcatccc ccacatccct 60gcagacgtgc
tattctgtta tgatactggt atcccatctg tcacttgctc cccaaatcat 120tcccttctta
caattttcta ctgtacagca ttgaggctga acgatgagag atttcccatg 180ctctttctac
tccctgccct gtatatatcc ggggatcctc cctacccagg atgctgtggg 240gtcccaaacc
ccaagtaagc cctgatatgc gggccacacc tttctctagc ctaggaattg 300ataacccagg
cgaggaagtc actgtggcat gaacagatgg ttcacttcga ggaaccgtgg 360aaggcgtgtg
caggtcctga gatagggcag aatcggagtg tgcagggtct gcaggtcagg 420aggagttgag
attgcgttgc cacgtggtgg gaactcactg ccacttattt ccttctctct 480tcttgcctca
gcctcaggga tacgacacat gcccatgatg agaagcagaa cgtggtgacc 540tttcacgaac
atgggcatgg ctgcggaccc ctcgtcatca ggtgcatagc aagtgaaagc 600aagtgttcac
aacagtgaaa agttgagcgt catttttctt agtgtgccaa gagttcgatg 660ttagcgttta
cgttgtattt tcttacactg tgtcattctg ttagatacta acattttcat 720tgatgagcaa
gacatactta atgcatattt tggtttgtgt atccatgcac ctaccttaga 780aaacaagtat
tgtcggttac ctctgcatgg aacagcatta ccctcctctc tccccagatg 840tgactactga
gggcagttct gagtgtttaa tttcagattt tttcctctgc atttacacac 900acacgcacac
aaaccacacc acacacacac acacacacac acacacacac acacacacac 960acacaccaag
taccagtata agcatctgcc atctgctttt cccattgcca tgcgtcctgg 1020tcaagctccc
ctcactctgt ttcctggtca gcatgtactc ccctcatccg attcccctgt 1080agcagtcact
gacagttaat aaacctttgc aaacgttccc cagttgtttg ctcgtgccat 1140tattgtgcac
acagctctgt gcacgtgtgt gcatatttct ttaggaaaga ttcttagaag 1200tggaattgct
gtgtcaaagg agtcatttat tcaacaaaac actaatgagt gcgtcctcgt 1260gctgagcgct
gttctaggtg ctggagcgac gtcagggaac aaggcagaca ggagttcctg 1320acccccgttc
tagaggagga tgtttccagt tgttgggttt tgtttgtttg tttcttctag 1380agatggtggt
cttgctctgt ccaggctaga gtgcagtggc atgatcatag c
143154975DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR54 54ccataaaagt gtttctaaac
tgcagaaaaa tccccctaca gtcttacagt tcaagaattt 60tcagcatgaa atgcctggta
gattacctga ctttttttgc caaaaataag gcacagcagc 120tctctcctga ctctgacttt
ctatagtcct tactgaatta tagtccttac tgaattcatt 180cttcagtgtt gcagtctgaa
ggacacccac attttctctt tgtctttgtc aattctttgt 240gttgtaaggg caggatgttt
aaaagttgaa gtcattgact tgcaaaatga gaaatttcag 300agggcatttt gttctctaga
ccatgtagct tagagcagtg ttcacactga ggttgctgct 360aatgtttctg cagttcttac
caatagtatc atttacccag caacaggata tgatagagga 420cttcgaaaac cccagaaaat
gttttgccat atatccaaag ccctttggga aatggaaagg 480aattgcgggc tcccattttt
atatatggat agatagagac caagaaagac caaggcaact 540ccatgtgctt tacattaata
aagtacaaaa tgttaacatg taggaagtct aggcgaagtt 600tatgtgagaa ttctttacac
taattttgca acattttaat gcaagtctga aattatgtca 660aaataagtaa aaatttttac
aagttaagca gagaataaca atgattagtc agagaaataa 720gtagcaaaat cttcttctca
gtattgactt ggttgctttt caatctctga ggacacagca 780gtcttcgctt ccaaatccac
aagtcacatc agtgaggaga ctcagctgag actttggcta 840atgttggggg gtccctcctg
tgtctcccca ggcgcagtga gcctgcaggc cgacctcact 900cgtggcacac aactaaatct
ggggagaagc aacccgatgc cagcatgatg cagatatctc 960agggtatgat cggcc
97555501DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR55 55cctgaactca tgatccgccc acctcagcct cctgaagtgc
tgggattaca ggtgtgagcc 60accacaccca gccgcaacac actcttgagc aaccaatgtg
tcataaaaga aataaaatgg 120aaatcagaaa gtatcttgag acagacaaaa atggaaacac
aacataccaa aatttatggg 180acacagcaaa agcagtttta ggagggaagt ttatagtgat
gaatacctac ctcaaaatca 240ttagcctgat tggatgacac tacagtgtat aaatgaattg
aaaaccacat tgtgccccat 300acatatatac aatttttatt tgttaattaa aaataaaata
aaactttaaa aaagaagaaa 360gagctcaaat aaacaaccta actttatacc tcaaggaaat
agaagagcca gctaagccca 420aagttgacag aaggaaaaaa atattggcag aaagaaatga
aacagagact agaaagacaa 480ttgaagagat cagcaaaact a
50156741DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR56
56acacaggaaa agatcgcaat tgttcagcag agctttgaac cggggatgac ggtctccctc
60gttgcccggc aacatggtgt agcagccagc cagttatttc tctggcgtaa gcaataccag
120gaaggaagtc ttactgctgt cgccgccgga gaacaggttg ttcctgcctc tgaacttgct
180gccgccatga agcagattaa agaactccag cgcctgctcg gcaagaaaac gatggaaaat
240gaactcctca aagaagccgt tgaatatgga cgggcaaaaa agtggatagc gcacgcgccc
300ttattgcccg gggatgggga gtaagcttag tcagccgttg tctccgggtg tcgcgtgcgc
360agttgcacgt cattctcaga cgaaccgatg actggatgga tggccgccgc agtcgtcaca
420ctgatgatac ggatgtgctt ctccgtatac accatgttat cggagagctg ccaacgtatg
480gttatcgtcg ggtatgggcg ctgcttcgca gacaggcaga acttgatggt atgcctgcga
540tcaatgccaa acgtgtttac cggatcatgc gccagaatgc gctgttgctt gagcgaaaac
600ctgctgtacc gccatcgaaa cgggcacata caggcagagt ggccgtgaaa gaaagcaatc
660agcgatggtg ctctgacggg ttcgagttct gctgtgataa cggagagaga ctgcgtgtca
720cgttcgcgct ggactgctgt g
741571365DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR57 57tccttctgta aataggcaaa
atgtatttta gtttccacca cacatgttct tttctgtagg 60gcttgtatgt tggaaatttt
atccaattat tcaattaaca ctataccaac aatctgctaa 120ttctggagat gtggcagtga
ataaaaaagt tatagtttct gattttgtgg agcttggact 180ttaatgatgg acaaaacaac
acattcttaa atatatattt catcaaaatt atagtgggtg 240aattatttat atgtgcattt
acatgtgtat gtatacataa atgggcggtt actggctgca 300ctgagaatgt acacgtggcg
cgaacgaggc tgggcggtca gagaaggcct cccaaggagg 360tggctttgaa gctgagtggt
gcttccacgt gaaaaggctg gaaagggcat tccaagaaaa 420ggctgaggcc agcgggaaag
aggttccagt gcgctctggg aacggaaagc gcacctgcct 480gaaacgaaaa tgagtgtgct
gaaataggac gctagaaagg gaggcagagg ctggcaaaag 540cgaccgagga ggagctcaaa
ggagcgagcg gggaaggccg ctgtggagcc tggaggaagc 600acttcggaag cgcttctgag
cgggtaaggc cgctgggagc atgaactgct gagcaggtgt 660gtccagaatt cgtgggttct
tggtctcact gacttcaaga atgaagaggg accgcggacc 720ctcgcggtga gtgttacagc
tcttaaggtg gcgcgtctgg agtttgttcc ttctgatgtt 780cggatgtgtt cagagtttct
tccttctggt gggttcgtgg tctcgctggc tcaggagtga 840agctgcagac cttcgcggtg
agtgttacag ctcataaaag cagggtggac tcaaagagtg 900agcagcagca agatttattg
caaagaatga aagaacaaag cttccacact gtggaagggg 960accccagcgg gttgccactg
ctggctccgc agcctgcttt tattctctta tctggcccca 1020cccacatcct gctgattggt
agagccgaat ggtctgtttt gacggcgctg attggtgcgt 1080ttacaatccc tgcgctagat
acaaaggttc tccacgtccc caccagatta gctagataga 1140gtctccacac aaaggttctc
caaggcccca ccagagtagc tagatacaga gtgttgattg 1200gtgcattcac aaaccctgag
ctagacacag ggtgatgact ggtgtgttta caaaccttgc 1260ggtagataca gagtatcaat
tggcgtattt acaatcactg agctaggcat aaaggttctc 1320caggtcccca ccagactcag
gagcccagct ggcttcaccc agtgg 1365581401DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR58 58aagtttacct tagccctaaa ttatttcatt gtgattggca
ttttaggaaa tatgtattaa 60ggaatgtctc ttaggagata aggataacat atgtctaaga
aaattatatt gaaatattat 120tacatgaact aaaatgttag aactgaaaaa aaattattgt
aactccttcc agcgtaggca 180ggagtatcta gataccaact ttaacaactc aactttaaca
acttcgaacc aaccagatgg 240ctaggagatt cacctattta gcatgatatc ttttattgat
aaaaaaatat aaaacttcca 300ttaaattttt aagctactac aatcctatta aattttaact
taccagtgtt ctcaatgcta 360cataatttaa aatcattgaa atcttctgat tttaactcct
cagtcttgaa atctacttat 420ttttagttac atatatatcc aatctactgc cgctagtaga
agaagcttgg aatttgagaa 480aaaaatcaga cgttttgtat attctcatat tcactaattt
attttttaaa tgagtttctg 540caatgcatca agcagtggca aaacaggaga aaaattaaaa
ttggttgaaa agatatgtgt 600gccaaacaat cccttgaaat ttgatgaagt gactaatcct
gagttattgt ttcaaatgtg 660tacctgttta tacaagggta tcacctttga aatctcaaca
ttaaatgaaa ttttataagc 720aatttgttgt aacatgatta ttataaaatt ctgatataac
attttttatt acctgtttag 780agtttaaaga gagaaaagga gttaagaata attacatttt
cattagcatt gtccgggtgc 840aaaaacttct aacactatct tcaaatcttt ttctccattg
ccttctgaac atacccactt 900gggtatctca ttagcactgc aaattcaaca ttttcgattg
ctaatttttc tccctaaata 960tttatttgtt ttctcagctt tagccaatgt ttcactattg
accatttgct caagtatagt 1020gacgcttcaa tgaccttcag agagctgttt cagtccttcc
tggactactt gcatgcttcc 1080aacaaaatga agcactcttg atgtcagtca ctcaaataaa
tggaaatggg cccatttact 1140aggaatgtta acagaataaa aagatagacg tgacaccagt
tgcttcagtc catctccatt 1200tacttgctta aggcctggcc atatttctca cagttgatat
ggcgcagggc acatgtttaa 1260atggctgttc ttgtaggatg gtttgactgt tggattcctc
atcttccctc tccttaggaa 1320ggaaggttac agtagtactg ttggctcctg gaatatagat
tcataaagaa ctaatggagt 1380atcatctccc actgctcttg t
140159866DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR59
59gagatcacgc cactgcactc cagcctgggg gacagagcaa gactccatct cagaaacaaa
60caaacacaca aagccagtca aggtgtttaa ttcgacggtg tcaggctcag gtctcttgac
120aggatacatc cagcacccgg gggaaacgtc gatgggtggg gtggaatcta ttttgtggcc
180tcaagggagg gtttgagagg tagtcccgca agcggtgatg gcctaaggaa gcccctccgc
240ccaagaagcg atattcattt ctagcctgta gccacccaag agggagaatc gggctcgcca
300cagaccccac aacccccaac ccaccccacc cccacccctc ccacctcgtg aaatgggctc
360tcgctccgtc aggctctagt cacaccgtgt ggttttggaa cctccagcgt gtgtgcgtgg
420gttgcgtggt ggggtggggc cggctgtgga cagaggaggg gataaagcgg cggtgtcccg
480cgggtgcccg ggacgtgggg cgtggggcgt gggtggggtg gccagagcct tgggaactcg
540tcgcctgtcg ggacgtctcc cctcctggtc ccctctctga cctacgctcc acatcttcgc
600cgttcagtgg ggaccttgtg ggtggaagtc accatccctt tggactttag ccgacgaagg
660ccgggctccc aagagtctcc ccggaggcgg ggccttgggc aggctcacaa ggatgctgac
720ggtgacggtt ggtgacggtg atgtacttcg gaggcctcgg gccaatgcag aggtatccat
780ttgacctcgg tgggacaggt cagctttgcg gagtcccgtg cgtccttcca gagactcatc
840cagcgctagc aagcatggtc ccgagg
866602067DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR60 60agcagtgcag aactggggaa
gaagaagagt ccctacacca cttaatactc aaaagtactc 60gcaaaaaata acacccctca
ccaggtggca tnattactct ccttcattga gaaaattagg 120aaactggact tcgtagaagc
taattgcttt atccagagcc acctgcatac aaacctgcag 180cgccacctgc atacaaacct
gtcagccgac cccaaagccc tcagtcgcac caagcctctg 240ctgcacaccc tcgtgccttc
acactggccg ttccccaagc ctggggcata ctncccagct 300ctgagaaatg tattcatcct
tcaaagccct gctcatgtgt cctnntcaac aggaaaatct 360cccatgagat gctctgctat
ccccatctct cctgccccat agcttaggca nacttctgtg 420gtggtgagtc ctgggctgtg
ctgtgatgtg ttcgcctgcn atgtntgttc ttccccacaa 480tgatgggccc ctgaattctc
tatctctagc acctgtgctc agtaaaggct tgggaaacca 540ggctcaaagc ctggcccaga
tgccaccttt tccagggtgc ttccgggggc caccaaccag 600agtgcagcct tctcctccac
caggaactct tgcagcccca cccctgagca cctgcacccc 660attacccatc tttgtttctc
cgtgtgatcg tattattaca gaattatata ctgtattctt 720aatacagtat ataattgtat
aattattctt aatacagtat ataattatac aaatacaaaa 780tatgtgttaa tggaccgttt
atgttactgg taaagcttta agtcaacagt gggacattag 840ttaggttttt ggcgaagtca
aaagttatat gtgcattttc aacttcttga ggggtcggta 900cntctnaccc ccatgttgtt
caanggtcaa ctgtctacac atatcatagc taattcacta 960cagaaatgtt agcttgtgtc
actagtatct ccccttctca taagcttaat acacatacct 1020tgagagagct cttggccatc
tctactaatg actgaagttt ttatttatta tagatgtcat 1080aataggcata aaactacatt
acatcattcg agtgccaatt ttgccacctt gaccctcttt 1140tgcaaaacac caacgtcagt
acacatatga agaggaaact gcccgagaac tgaagttcct 1200gagaccagga gctgcaggcg
ttagatagaa tatggtgacg agagttacga ggatgacgag 1260agtaaatact tcatactcag
tacgtgccaa gcactgctat aagcgctctg tatgtgtgaa 1320gtcatttaat cctcacagca
tcccacggtg taattatttt cattatcccc atgagggaac 1380agaaactcag aacggttcaa
cacatatgcg agaagtcgca gccggtcagt gagagagcag 1440gttcccgtcc aagcagtcag
accccgagtg cacactctcg acccctgtcc agcagactca 1500ctcgtcataa ggcggggagt
gntctgtttc agccagatgc tttatgcatc tcagagtacc 1560caaaccatga aagaatgagg
cagtattcan gagcagatgg ngctgggcag taaggctggg 1620cttcagaata gctggaaagc
tcaagtnatg ggacctgcaa gaaaaatcca ttgtttngat 1680aaatagccaa agtccctagg
ctgtaagggg aaggtgtgcc aggtgcaagt ggagctctaa 1740tgtaaaatcg cacctgagtc
tcctggtctt atgagtnctg ggtgtacccc agtgaaaggt 1800cctgctgcca ccaagtgggc
catggttcag ctgtgtaagt gctgagcggc agccggaccg 1860cttcctctaa cttcacctcc
aaaggcacag tgcacctggt tcctccagca ctcagctgcg 1920aggcccctag ccagggtccc
ggcccccggc ccccggcagc tgctccagct tccttcccca 1980cagcattcag gatggtctgc
gttcatgtag acctttgttt tcagtctgtg ctccgaggtc 2040actggcagca ctagccccgg
ctcctgt 2067611470DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR61 61cagcccccac atgcccagcc ctgtgctcag ctctgcagcg
gggcatggtg ggcagagaca 60cagaggccaa ggccctgctt cggggacggt gggcctggga
tgagcatggc cttggccttc 120gccgagagtn ctcttgtgaa ggaggggtca ggaggggctg
ctgcagctgg ggaggagggc 180gatggcactg tggcangaag tgaantagtg tgggtgcctn
gcaccccagg cacggccagc 240ctggggtatg gacccggggc cntctgttct agagcaggaa
ggtatggtga ggacctcaaa 300aggacagcca ctggagagct ccaggcagag gnacttgaga
ggccctgggg ccatcctgtc 360tcttttctgg gtctgtgtgc tctgggcctg ggcccttcct
ctgctccccc gggcttggag 420agggctggcc ttgcctcgtg caaaggacca ctctagactg
gtaccaagtc tggcccatgg 480cctcctgtgg gtgcaggcct gtgcgggtga cctgagagcc
agggctggca ggtcagagtc 540aggagaggga tggcagtgga tgccctgtgc aggatctgcc
taatcatggt gaggctggag 600gaatccaaag tgggcatgca ctctgcactc atttctttat
tcatgtgtgc ccatcccaac 660aagcagggag cctggccagg agggcccctg ggagaaggca
ctgatgggct gtgttccatt 720taggaaggat ggacggttgt gagacgggta agtcagaacg
ggctgcccac ctcggccgag 780agggccccgt ggtgggttgg caccatctgg gcctggagag
ctgctcagga ggctctctag 840ggctgggtga ccaggnctgg ggtacagtag ccatgggagc
aggtgcttac ctggggctgt 900ccctgagcag gggctgcatt gggtgctctg tgagcacaca
cttctctatt cacctgagtc 960ccnctgagtg atgagnacac ccttgttttg cagatgaatc
tgagcatgga gatgttaagt 1020ggcttgcctg agccacacag cagatggatg gtgtagctgg
gacctgaggg caggcagtcc 1080cagcccgagg acttcccaag gttgtggcaa actctgacag
catgacccca gggaacaccc 1140atctcagctc tggtcagaca ctgcggagtt gtgttgtaac
ccacacagct ggagacagcc 1200accctagccc cacccttatc ctctcccaaa ggaacctgcc
ctttcccttc attttcctct 1260tactgcattg agggaccaca cagtgtggca gaaggaacat
gggttcagga cccagatgga 1320cttgcttcac agtgcagccc tcctgtcctc ttgcagagtg
cgtcttccac tgtgaagttg 1380ggacagtcac accaactcaa tactgctggg cccgtcacac
ggtgggcagg caacggatgg 1440cagtcactgg ctgtgggtct gcagaggtgg
1470621011DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR62
62agtgtcaaat agatctacac aaaacaagat aatgtctgcc catttttcca aagataatgt
60ggtgaagtgg gtagagagaa atgcatccat tctccccacc caacctctgc taaattgtcc
120atgtcacagt actgagacca gggggcttat tcccagcggg cagaatgtgc accaagcacc
180tcttgtctca atttgcagtc taggccctgc tatttgatgg tgtgaaggct tgcacctggc
240atggaaggtc cgttttgtac ttcttgcttt agcagttcaa agagcaggga gagctgcgag
300ggcctctgca gcttcagatg gatgtggtca gcttgttgga ggcgccttct gtggtccatt
360atctccagcc cccctgcggt gttgctgttt gcttggcttg tctggctctc catgccttgt
420tggctccaaa atgtcatcat gctgcacccc aggaagaatg tgcaggccca tctcttttat
480gtgctttggg ctattttgat tccccgttgg gtatattccc taggtaagac ccagaagaca
540caggaggtag ttgctttggg agagtttgga cctatgggta tgaggtaata gacacagtat
600cttctctttc atttggtgag actgttagct ctggccgcgg actgaattcc acacagctca
660cttgggaaaa ctttattcca aaacatagtc acattgaaca ttgtggagaa tgagggacag
720agaagaggcc ctagatttgt acatctgggt gttatgtcta taaatagaat gctttggtgg
780tcaactagac ttgttcatgt tgacatttag tcttgccttt tcggtggtga tttaaaaatt
840atgtatatct tgtttggaat atagtggagc tatggtgtgg cattttcatc tggctttttg
900tttagctcag cccgtcctgt tatgggcagc cttgaagctc agtagctaat gaagaggtat
960cctcactccc tccagagagc ggtcccctca cggctcattg agagtttgtc a
1011631410DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR63 63gcgtctgagc
cgctgggaac ccatgagccc cgtccatgga gttgaggaag ggggttcgcc 60ccacggggtg
ggcgccctct acacagcgcg cttcctcttc tctcgttagc gccgcgggac 120cagcctctgg
ttctgcacct cgcgctctgg gagcagcgcc cggctttggc gagcgcttcc 180ccggggctgc
ccagcctctg ctccgctcgc cccgccaggc ccggctccgc gaagccccca 240gggtccagtc
caaggccccg attccccaag gccagggccc cggggcagca ttggaacagg 300gcgcggacgc
cagtcctccg agcatggagt aactgcagct tttgagaaaa gaaagcggac 360cccaccccat
cgagaacgcg gcgccttgtt tagggacgtt cctgggccgt cacggagtgt 420cgccggctcc
tcggcccctc cctcctccaa gcccccaccc ccgacagcgg cctccctggg 480gacctcccct
cgggctgcgc tttcagccca aacacaggga ggtcttccag gagcctgccc 540agtccccaca
gcagcccaga gacccccact cccacctgta cctgccaagc cttcagagag 600ggcggcctgg
acatgccccg cacgggagga gccccgcctc agcacccctg caagtggcag 660caacccagaa
cacccgtgag aggcctctga gcagcccagg aagtggctgg aagacgcata 720ggcagctcac
tcctctgtaa gagcaaggac cggagaacac atgctgaccc ctgcttttgc 780agaggggcga
tgcttcagga caggcgcgct cagcaggtgt ccatcttatt tcacaccttt 840gtgtttatat
catcttattt tgcattttat gtctaattaa caatatgcag ctggccaggc 900gcagtggctc
aagcctctaa tcccagcact ttgggaggcc gaggcaggtg tatcacttga 960gggcaggagt
tcgggaccgg cctgggcaac atagcaaaac cccattgcta ataaaaatac 1020aaaaattagc
cagccatggt ggcgggcacc tgcagtccca gctactccgg aagctgaagc 1080aggagaatca
cttgaaccca ggaggcggag gtggcagtga gctatcaagc cattacactc 1140cagcctgggc
aacagagaaa gactgtctca aaaaaaaatt aatacgcagc agaatattat 1200gtggtcagcc
caagcagtcc cccccactca gccctctgtc cctacagctc caggcactcc 1260cccagcccct
cccctggaca agaggtaatg cccagagggt gaaaatccac caaggttaag 1320ccagaaacaa
aaagctcaaa gcttcggcat ctccctccgc tcagaccctt agagcagatt 1380cctctcatcg
acagcacgat caggctgtgg
1410641414DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR64 64agagatcttt
taagggctca aaagaccctg cggctcccct gccaatagct ctgccatcgt 60ccccagagct
ttcgaggacc ctccaccatc ggcgccaacc ccagctgagc tgggtgctcg 120tctgcaggcc
tctgctccat ctcagcctga gcatgaggct ctgctgtgct gcttccagca 180gcagggacag
ggctgatgag cctggccctt gcaagcatct tcctgtgccg aatacaattc 240cacagacaga
ggatttaaaa tccaagtgga ggtgacagga aagaaaggaa aacctccagg 300tatcagaaga
aaggaggggg tgtgaagaca gtatgggagg aaggtcaggc tggggctcag 360ctctgggaag
tgccagcctg aacaggagtc acgcccgggt ccacatgcaa gggaatgagg 420accgaggccc
tgcatgtggc agggccttcc gcaggctgcc ccgtctgtga acaggacacc 480agaagaagtc
tgccttccag cctggcaaag tggcaaggaa cctctgggtg ggaaaacaaa 540tcaacaaaca
aattgtcagt aaaaaacaga aacctcacac tttcctttct cttgacctct 600tgaaaaaagc
aaatccactg cagctcacca aaggcaaaga gaaaacctta agaataccca 660gagagaaaag
acacgttact tgcaaaagaa catctaatgc agggagataa tgaaaataca 720gactcttcaa
agggctgaag gaaaaaaacc gtccacctag aattctatcc ccaaactgtc 780atctgagagc
aagggcaaaa caaacgcttt ctcagacagg ctggacgagg tcgctcacgc 840ctgtaatcct
agcactttgg gaggccaagg tgggaggacc gctttaagcc agaagtttga 900gaccagtgtg
ggtaacataa tgagacccca tctctaagaa aaagaaatta aataagacaa 960gactttttca
gacaacaagt gctctgagag ctggcctatc ttggctgtct tgtaaagaat 1020tgctgcgaga
cacctcatta ggaaagagac tgaatctaga aggaaagagc agagcatgag 1080gtacaatgag
gagcaaataa acaggtcacc atataagcaa acccaaatac acattcacta 1140tacgaaacaa
taaaaatgac tcatttgggg ggttaaaaca ctgttgaact aaaatcctgg 1200ataacagcag
catgaaaggt ggggtggtgg tcccaggaaa gcattcaaag gtccatgtct 1260catttgggag
gagggtaggg agactcatga acttgaggct cccttcaggc aagcacagtg 1320caaaaaaatt
ataataatgg gaaacagata cagtagactg tgatgtacaa ctctcagagc 1380agtagaaggg
agggtataaa acaaatctga tcca
1414651310DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR65 65tcgagaccag
cctggccaac atggtgaaac attgtctcta ttacaaatac aaaaattagc 60caggtgtagt
ggtgcatgcc tgcagtccca gccatttggg aggctgaagt tggagaatcg 120cttaaacctg
ggaggtggag gttgcattga gccgagaagc actccagcct ggatgacgga 180gcaagactgt
ctcaaaaaga aaaaaaaaag aagcagcagc aaatatccct gtcctgatgg 240aggctatata
acaaccaaac aagtgaatgc ataagacaat ttcaaggtta tggtagatac 300cataagtggg
agatgaacaa tgagaacaca tggacacagg gaggagaaca tcacacactg 360gggcctctcg
gggggtgggg aaataggggg tgatagcatt aggagaaata cctaatgtcg 420ataacaggtt
agtgggtgca gcaaaccacc atggcacgtg tatatctatg taacacacct 480gcacgttctg
cacatgtatc ccagaactta aagtataata aaaaaagaca ttaaaaaatt 540atgatataaa
atcccaattc aagttgtttt aaaaagagaa aacaattatc tttatataat 600agcggaaaat
atagatggcg gaattaaagc ctcgtcatat tttctaacag aactttctga 660taaacttgat
taaataaaaa ttttaaatat cactaaacac atagaagaaa taaatttaaa 720ccttcacaaa
aaataaagta caatgaatga agacaaggtg tacttgaaaa aagaactgaa 780taaatattct
acatataaaa aaaatctgat gatattgtgg tgattcttta ctttgctact 840agtttctctt
tttttcttct gaaaaatttc ttgggatgta tttggtttca ttagtaaaat 900tctaagtttc
tttgcaatct gaacattgga gcttcatcca tagccagtat gccctaacat 960tatctttgga
caactgtaaa attagaacac tgccagacat atttaatgta tgatgtatat 1020caacactggg
acacatttta tactatcttt attccaaaat caaatgattc actgtggttt 1080ataaatgtac
atggatatat ctctacctaa gcagatagtt aggagagtta gtaaaaatga 1140ggtggaaaat
aggagtcact gtcccttcac agggagagaa ttctgctttt ctcctaatat 1200accctttgct
tgaacagact ccaacccctc atcttttgtc ctttaaatga ccacatttat 1260tttaactttg
ataaacaaca cagaaagata tttgatccat caacattcac
1310662500DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T2F (STAR66F) 66gcaggttgga
tggtgctgac ccctcctcgg gttggcttcc tgtctccagg tggacgtcct 60gtactccagg
gtctgcaagc ctaaaaggag ggacccagga cccaccacag acccgctgga 120ccccaagggc
cagggagcga ttctggccct ggcgggtgac ctggcctacc agaccctccc 180gctcagggcc
ctggatgtgg acagcggccc cctggaaaac gtgtatgaga gcatccggga 240gctgggggac
cctgctggca ggagcagcac gtgcggggct gggacgcccc ctgcttccag 300ctgccccagc
ctagggaggg gctggagacc cctccctgcc tccctgccct gaacactcaa 360ggacctgtgc
tccttcctcc agagtgaggc ccgtcccccg ccccgccccg cctcacagct 420gacagcgcca
gtcccaggtc cccgggctgc cagcccgtga ggtccgtgag gtcctggccg 480ctctgacagc
cgcggcctcc ccgggctcca gagaaggccc gcgtctaaat aaagcgccag 540cgcaggatga
aagcggccag cctcgcagcc tgctcttctt gaaagctggg cgggttgggg 600cggggggctt
ctctggaagg cttggagctg tcccctctgg ccttggggga ctggctgccc 660ccggggcgcc
cgggcctagc cgaggcggtg ctcctgccgg ccagactctc ggtcagtgcg 720ggcacggggt
cccagccact cctagggggc agcgcagccg gcagggtggc cgcccccggg 780tgggacttgg
accctggact ccacgggagg gctccgccac ccagcctggt gttacataag 840gggtggtgga
ggtgggcagt cgagcgttaa agagtaacct gctgccggga agcccgccaa 900gcaatcgcgg
ccccttcccc ggctctggca gctctgcgag cgcgcccgtg gggaacgggc 960cctccccggc
ggggcgcgcg ggcgcgcgag gtgggcggag gcctcggagc tgtgccgggc 1020cgggcctccc
tccctaggcc agcgcgggag cgacccggag ggggcgggcc cggggcgggg 1080cctcgaagcg
ctggccggcg ggagcgcggc cggccgggcc cgcccgcctg cggtgtggac 1140gccgcgcggc
caatgcgcgc gccgggacgg gacgggacgg ggcggggcgg ggcgggacga 1200gacggggcgg
ggcggggcgg gccgggcagc ctccgggcgg cgcggcgcgg gcggcggccg 1260gatccagggc
gggggtcggc ggcccggcca gcccggcccg gcccggggcc gcgtcctgag 1320agtcagccct
cgccgctgca gcctcggcgc ccggccggcc ggccatggag cgccccccgc 1380cccgcgccgc
cggccgggac cccagtgcgc tgcgggccga ggcgccgtgg ctgcgcgcgg 1440agggtccggg
gccgcgcgcc gcgcccgtga cggtgcccac gccgccgcag gtaccgggcg 1500ccggtgggcg
ggggcgccga ccaagtttct ctcgctgcaa agatggcgtc agtgctgccc 1560aaacttcggg
cccccggggg cggggcagcg gggagggcgg ccgcgtcggt ccgcgcgtgt 1620ccgtgggtcc
cgccggggct gcgccgggcg gccggggagc ccttcccgcc gcgccgggct 1680gggggcgggg
ccgggggcgg ggccgcgccg tccacaccgg ccgcagccgg ttttcgaggc 1740gggcgccgag
cggatccgcg gcggaggttg agggaccccc ctcccccggc caccgcctcc 1800gctgagtctg
ccccctcccc atccgcaggg ctcttccgtg ggcggcggct tcgcgggctt 1860ggagttcgcg
cggccgcagg agtcggagcc gcgggcctcg gacctggggg ccccccggac 1920gtggacgggg
gcggcggcgg ggccccggac tccgtcggcg cacatccccg tcccagcgca 1980gaggtgagcg
ggaggcccgg tgcctcggga ctcggtgtgc gcaggggcgg tgggtggggt 2040gcggagacac
cggccccgac ggaggccagg tcagggcccc aggtttgtaa ttaccagcca 2100cccccaagct
cttcagccct ggaggagctg agcagaaatg atcgatgact gggagtccct 2160acacctccct
ccaccgcagt tcctcggggc tagagctcag aacccggagc gggtggctgt 2220gcgtctctgt
gcagaagagg ctgcgcggtc ggcatggggc gactgtccag gaatccctgg 2280ggctcctgac
cgccacctcc caacccctgc caggccggac acctcggtct ggctgccagg 2340gcaggggcgg
gccctggcct ggctcgctgg ggcctgggga gctgcccgtg cttccagccc 2400agtctccccc
tggctgctgc cggctgctgg ccactcccac ctcccaggcc tggcgtgagg 2460cccacagctg
ctgttgcaca accctggtta atgtgtgatg
2500672500DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T2R (STAR66R) 67gtttggggta
gagagaacat actgattatg ggactttgct ttgcagctta gtgctgtcct 60gtcagtggga
agcaacaggg ggcagaactc agcttgtgcc catagaggga atgtttatac 120taggcctgtc
cagaggcaaa tcatccatcc tagcaattgg aacctgactt ttggcaagtc 180ctgccaccat
gggctaaagt gttctggggt tctaaataaa catgaaaggc aacctagacc 240acaaggactg
caattcctgc acaagtcctg gtgctgtgtt gggcttggag ccagggaact 300tggagtgcat
ggaacctagt gagataccag ctgagacaac caaggaagtg cttgtgtcac 360ccctccacca
accccaggca gtacagattg tacctccaag accccttcca tctgcttgag 420gaaggtggag
gggaagagga ctttgttttg caacttggat tccagcccat ccacagtaga 480ataaggcaac
gggcagactc ctaaggcccc catcccagac cctagctcct ggatgacatt 540tctaaacaca
ccatgggcca gaagggaacc cattgccttg aagggaaggg cccagtcctg 600gcagaattta
tcatgtgctg aataaacagc ccttgggccc tgaataatta gtattggtag 660ccaggcagta
tttaccacag gccttgggtg agacccagag ccatgttggc ttcaggtgtg 720acccagcaca
ttcccagctg tggtaacttt ggggagagac cacttctgct tgagaaaagg 780agacagaaga
gtaaaggggt ctttatcttg cagcctggta ccagcttggc cgcagtgggg 840tagagcacca
agagagcacc tgggataaac aaaatcaaaa aacctttagc tagactaaga 900gtaaagagag
aagacccaag taaatataat caaagacaaa aaaggagaga cattacaacc 960aatacctcag
aaattcaaag tatcattagc agctactttg aacaactata tgccagtaaa 1020ttggaaaacc
tagaagaatt atataaattc ctaacatata caacctacca agattgaacc 1080atgaagaaat
ttaaagcctg aataggccaa taacaagcaa tgagattgga gccctaatac 1140aaagtttaca
atgagaaaca ttgctcaaac aaatcataga tgacacaaac aaatggaaaa 1200catccaatgc
tcatggacag gaaaaaatat ttaaatttct atactgccca aagcagttta 1260tacattcaat
gctattcctg tcaaaatacc aatcttattc ttcacaaaaa aaaaattaaa 1320aattacacag
aaccaaaaaa gagcccaaat acccaaggca attttaagca aaaagaacaa 1380agctggaggc
atcacgttac ctgtgatcca cactataggg ctacagtaaa tgaaacagca 1440aggtgctggt
atacaaacag acacataaac caatggaata gaataaagag cttagaaata 1500atgctccaca
cctccagcca tccgatgttt gagaaagtag acataaacaa gcaatgagga 1560gaggactccc
tattcattaa atcaactcaa gacggaccaa aaacctaaat gtaaaacaaa 1620caaacaaaaa
aaataactgc taaaaccctg ggagatgacc taggaaatac cattctggac 1680agtacctggt
gaaaatttca tgctgaagac accaaaaaca attgcagcaa aagaaaaaat 1740tgacatatgg
gatcaaatta aactttagag cttttgcaca gcaaaataaa ctatcaacag 1800agtaaatagg
caccctacag gaagggagaa aatattttca atctgtgctc tgacaaagtc 1860ctaatatcca
gagcctataa ggaacttaaa caaatttaca aacaaaaaac aaacaacact 1920attacgagtt
ggaaaaggac atgaatcgac acttttcaaa agaagacata catgtggcta 1980acaagcatat
gaaaaaaatg ctcaacatta ctaatcatta gagaaatgca aatcaaaacc 2040acaatgagat
accatctcaa ccagtctgaa tggctgttat taaaaaaatc agaaaaaaac 2100agatgctggc
aaggttgtgg agaaaaggaa acacttatac attgttgggg ggagtgtaaa 2160ttaattcagc
cattgtggaa agtattgtgg tgattttcta aagaactaaa aaggaattac 2220tattttacct
ggaaatttca ttattgggta tatacccaaa gaaatatgaa ttattttact 2280ataaagacag
atgcatgcat gtgttcattg tagcactatt cacagtagca aagacatgtt 2340atcaacctaa
atgcccatta acagtaaact ggataaggaa aatatggtac atatacactg 2400tggaatacta
tgcagtcata aaaagaatga gataatgttc attgcagcaa catggatgga 2460actggagacc
attatccttg ggaaactaac aaagcaacag
2500682501DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T3F 68agatttgccc tcaagattac
aactgctggg gctaaagtgg tacagagcct gagttcagta 60ggcttccata gtctcactca
agaatgcaag tttacctctc aatctttcaa tcatcacaat 120tataacaact ttaaaaagag
ccaacatgat atttgcttat cacttttcta ctcacattcc 180agtattaact caaaagtgtc
aacacaacct tcgtgataaa tactattaac gtcatcattc 240ctactgtaca gatgatgata
gtgacacata ggttaagttg cccaaggtct tattattaag 300ggtcatagcc aggatttgat
ctcttcagta aagttctagt caatgctctt aaccattaag 360ccatgcaaca cacccagagc
caactgggtt gtgttgatga ttataatatt tgttttaaca 420aacaataatt tttcctaaat
ataatataga ttttccataa ataccataaa ttcttgatta 480tttatttcac tttattccaa
aaggaagttg aattctgaga tttaaatgaa tagcaaacaa 540cagttgctta atttcactac
ttttgtcact tgtagccagt acttaaaaag agatacataa 600tttatttttg ttgatttgca
tttcacatat aattgtaaga tcctggagaa taaagactat 660atgtgttata ccattttact
ctctcacaca gtgtgtaggc ctaggctttg tgcatagcaa 720gtgttaaaaa gtaatgtgac
tcgtgatagt tattagattt attgaaattc agaaatttag 780ggaaatgcac aataaaatgt
acattttgtg attccggtca aattacttaa aaattatatt 840tttcctatga ataattttta
tttcacttaa attatgtata acaaaataac atgcataatt 900aaacatttac cacaaagaaa
atatttgtac tattgttatc acaataaaga acttgctaca 960taaattcaat tacacttttg
tggaaagtat cttcattata taaaaacaat ctacatttag 1020aataggaaaa ttgtacaaaa
catgaaaata taaacaaatt aagcgagaat tatctaaaaa 1080gcaactcttc agaatttaga
agaattgtct agaataaaaa gaatttagaa gaattatcta 1140agaaacaacc ataaatattc
tgatgtattt aagactcata ttctagaatc ctgactatta 1200ttttttatac ttctatggct
aatctcaagt ttagctttat ttttctaaag caatgaggcc 1260tgtagaatat tttttcagaa
ttctctgagg ttttttcttt tttgtctttc ctgtcatagt 1320atgccaatta ttcatgggtt
tatagaatat gtatgcactg ctaagagcag caaaacaaaa 1380gatatatgtg ctatttatta
attcatgttg ctttatttaa attacttgaa aatgataaag 1440aaaaaactat tgtatttaca
acagcaacca aatatagact acctgtaact acatctaaca 1500gaataaataa aatataacat
acaatatgta gtaaatatat ttataatata tatgttcact 1560aaatagttaa cctgtaactt
acttacagta aatatatata atatctactg agatagtacc 1620acattttatt aaggattaaa
cttttaataa ttcagaagaa taaatataat aaatttcatt 1680tgttctcaaa ctaatttgtt
tttatttgtt tgttttttgt attttaattt gacagtagtt 1740ccaagatatt ttggggtata
taatgaggtg ataattgcaa agaaaattct gaaaaggaaa 1800agactaagcg tgaattgaaa
gtaaaattcg ttaaaaggta taataaactg tgatactgta 1860acaataattg aaaatagata
aagaaaaagg taacatcaat aaatagtcta ttatatatgt 1920gaattatgtt aataaaagtg
acattttatt ttcaatccac aatttctgaa atatatatgg 1980caatattttt ctgttttatt
ttttcaacct ctgattactt tattacattt ttttcttttt 2040ctagaattta cttgtatttt
ctctgtgtct aatatatgat tatttctgaa ctagcatcat 2100tggtcctgga accagactat
attattccca aggtagagca tcaaaatata acaattaaat 2160aaatactttt agttacttta
acaacctttt gtctttcatt ataattttgg aattatagtt 2220tagtacaata cagatagttt
taatatctgt tagagtgaag atatatatat atgtgtgtgt 2280gtttttgaga tggagtctca
ctctgttgcc caggctggag tacagtggtg ccatctcggc 2340tcacggcaac ctctgcgtcc
caggttcaag caattctcct gcctcagcct cccgggtagc 2400tgggactaca ggcgagtgtc
accacgcctg gctaattttt tgtattttta gtagagacag 2460ggtttcacca tattagccag
gatggtctcg gtctcctgac t 2501692511DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of T3R 69cttttggtgc cctgtccctt ataatttcct cgtgtgtcct
ttcccatttg cttatccgat 60gacttgcttc tctcacccat tggattgtga gcctcttgtg
gtcaggggca gtgctctgta 120agctgctgtg tccccagaat ctggcccagt gtaggcactc
agcagctata gactgatgtt 180aagagaaaat gcacatttca tctcagcctc agagcagttc
tgggaaacag ataggaaacc 240aaagctctgc aagaacgtgg gactctctca gggccatcac
aacactgttg ttggtctcat 300gtttggtgac tgggtctcct attcctggtc tctttcctag
gcataatgct tttatataaa 360gtcccttcca ttgttttttt gtttgttttc ttttttcagc
ctaaataact tagtttctct 420aaacttttct cccagggact cttttttaac cctttgaatt
attgctgatt attatcttaa 480taacttttat tttttttcca ttttgcatgt catattttag
caaagcatta aaaggaacac 540ggcacaaagc acacccatat ttttggatgc tgtggatttc
atcatgctgc ttattccatt 600atatctagtc agtacctcca aggcattaat gctgccttac
ctccttcatt cgaagacttc 660cctgtgcaag gtggaatata cgtaaggagg caaacagact
gggttatatg cctgctctgc 720tttacagagg cctcttccag gagtgtaata cgggggttgc
tcatactctg aagaagatag 780tggcaggcta ttactgtcat gagagccaga acgtggctgg
cttcttacag acatggcttc 840ataggggcat gccacgtgat tcctgagtaa gccttctggt
gtgaattccc tgctcactgg 900ggtgattctt cacttcccac agttcaacct gctgtattat
cctcttacct atgcttttct 960gtgatccata gaggtaattt aattttcagt ccatgtacct
accctgccta cttagtttct 1020tctcagtgcc acacttaatt ccttcacatt tactgattaa
ttaaatgaga agactatgcc 1080aggtgaaggt tcagcatctt cagaactcta catgatgcat
tccctgaggc tgcctttcaa 1140taactgaggt gatattcttt gagcagtgtg acctgttaga
ggtgcccagt caggtccgat 1200gaaaagccct ctgatttgtt gaaatagtgc attagtaaag
tattatagtt tattttcaca 1260aagctagatt agttgttaca tgttggtttt tgttttgcct
agccctaaca agtatggagg 1320tgaccttgat gtgtctatag aatatcagga atatctggct
gggtgggtgg ctcacacctg 1380taatcccaac aatttgggag gccgaggtgg gcggatcacc
tgaggtcagg agtttgagag 1440aggcctggcc aacatggtga acccccgtct ctactaaaaa
tacaaaaatt agccaggtgt 1500ggtggcaggt gcctgcaatc tcagctactc cggaggctga
tgcaggggaa tcacttgaac 1560ccgggaggta gaggttgcag tgagccaaga ttgtgccact
gcactccagc ctgggcaaca 1620gagcgagatt ctgcctcaaa aaaaaaaaaa aaaaaaaaaa
aaaaaaaaga atatcaggaa 1680tatccatttt atgtctcaac tcacatacct cacagttttc
tggtccaatt tttaggcact 1740ttatcaggcc ctcatatgtt ttcaaaaata attgctaatg
actttgatga agctaggcaa 1800gatatttttt ggttttaggg cagtttgggc tatagtttgc
agccttccta ctttaataga 1860agaattttta aactagattc tcccccttct cagggtggct
ttctgccttt ccattctagt 1920gcttcacaca gaaatgacaa gctcacaggg gacttatcta
gaaaaggccg agataaaaat 1980aagtacaatg ttaaaaaaat ctatcttata gtatcattta
tttagagctt cctctccttt 2040tctaatgaaa ggctgctgta gtttcctttt gtgctttttt
tgctgaaggc ttttcagtaa 2100tattcccgtg tgtcccctgt gatgctaaaa gcatgagctt
gggggcaggt tgactggcat 2160tcaggtcttt gctcagcctc cagccgcaag acaaggcgaa
taatattgat ctcatggagc 2220tgaaatgaaa attaactttt ctaatctgtg aaaatgcttt
gttataatcc ttaaatacat 2280gaatacatag gttgaaatag caagtaccaa gtgctgacat
tatgtccaca attgccacat 2340gccatgtcct tatgattttt gccagatgtt taataagatt
ataaatgaat aggttattaa 2400atgggcatct cctactctct aggtgtttct gtttctgctt
ctctgttttc tgtttgtatc 2460tccatttatt ttaatgccta ccattatgtg aagtctgcca
ccttcctata c 2511701500DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T5F
70gaactcaata ggggtcttgt acggagcagg ggcttggtcc ctcgtacctc tggccatacc
60tatggagccc aggggatgct tggcagcacc tgggaggtgc caaccccggg tggcaaggga
120gggccggtcc cacgctcaca ttgtcttctg ttctctctct ctctttatct gtgtcgatgt
180ctctctctct tcccccgtgc ccgtgccatc ctctccaccc ctggattcct gtctctgctt
240ggctttcacc cacttctcct ccccacccac ggctgctcct cctcctgtcc ccacctcctc
300cccgggtgca ggacgggcct cttcacacct gacctcgctt ttgaagccac agtgaaaaag
360caggtgcaga agctcaaaga gcccagtatc aagtgtgtgg atatggtagt cagtgagctc
420acagccacca tcagaaagtg tagcgaaaag gtatgacggc cgcctgggcg gggctgggcc
480tggccgtcca ttccttgtgg ccacagcctc ccgtgggcag aaggatctgc tgagccggcc
540tcacggctac ccgcagggac ccagccctag tgtttcctgc cagtttctaa ccctgggtac
600ttgcactcat gacccctcca ggcccccatc ccagaagact tgactccaac ccaagcctcc
660ttggtggcac ctatgctagt gatgaagatg atgttaagga gatggcagct gtttactgag
720cacctactat gtgccaagca cacgctaagt gcttgccctt actatctgac tcagtcctct
780caaccaccct aagacgtggg tagtgttgtt attcccattt tgcagatggc aaaacagagt
840ctcagaaaag agaagcagag tgtgattcag ttttaggaag gacagaggaa ggggtctgag
900gtcagggcct cctgggcagg gggagctgtc ctagttcctc aaaaccaatt tgcctgaaag
960catattggat tactcacttt acagtaatcc gtgcgtgaga gacaggggcg gtctcttttg
1020agttgtctgt gactttttag atgccttttt cctatttgtc tgcttttggg cattttgagg
1080atttttagcc aggttgtcta aagcagttct tcccagggga gtgcgagaga atcagttgcc
1140tgcaggagct tctccagcag gctaaatcag aggtgccagg ggtgagccca gcctcaccta
1200tatctgaagg acttccctat gctggtgggt ggaggcacat ccaccttagc attgagtttc
1260aaataagcat caatcatctc cattcctttt tttttttttt tttttttttg agatggaatc
1320ttgctctgtc gcccaggctg gagtgcagtg gcaccatctt ggctcactgc aacctctgcc
1380tcctgggttc aagtattctc ctgcctcagc ctcccgggtg gctgggatta ctagcatgta
1440ccaccacacc tggctaattt ttgtattttt agtagagatg gggttttgcc acgttggcca
1500711500DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T5R 71gattacaggc gtgagccacc
acacctggcc cagtggggtc cttctaaaat gcaaagctga 60tcatgtctct tcttccaggc
ttaaagccct cccatggctt cctgcagccc tggtgcacgc 120cttacgccaa gcctgaaaac
actctgcaca cccacccctt ccctgcacaa acgggcctct 180gcacactacc tgccccggcc
atgcccccgc aaccagccct ctctgcttat ctaccttggc 240cttctctctg gtcaagcccc
aggcccgtcc ctgcccctag gccttcactt agagcctcag 300aagcacttct tgcaggaagc
cctccagact ccagaatggg tccagaacct acttcctttt 360cgtggcattt ctgtattctt
tttttttttc ttccatagag ccagggtctc actgtgtttc 420ctaggctagt ctcgaactcc
tgggctcaac tgatcctcct gccttggcct tccatagtgc 480tgggattaca ggcatgagtc
attgcacccg gcctccacag tcttaattaa ttggttggag 540cattatttgc attaatatct
ctcaccaccc tccccattcc tgtccaagac ctcagggagg 600gccaggccag atgtatcatc
tgcaccaggg agtcccctgc aggggcttcc agatgtctgc 660taaatgaaca cacagctctc
tctggccagt ccaaggcacc ccaggaggcc accagaagcc 720tgcagcctcc ctccctccct
cctgctaagc ccaaggaatg agcactgagc agggaatggt 780aatctggaca catccatact
ctgcccttca gaaactacct agctgtcacc ctgcacgaaa 840caggcaccag cctgagagtc
aggaggcctg ggctctgggt ccacctagac agctgtgggg 900cgcaggacca accgcacccc
aatctctaag cctgggtttt tccatacgta aaaaaatgag 960ggcagggcgg gttagacact
agaccagatc tgtgatgaca ggcccgttgg aaggctggag 1020gcggggcccc tcgctgaagg
aaaatgcctt acctccagaa gtggcccgcc ctggagtggc 1080cagcaaaggg ggcattgccc
ctgcgctgga atacacccag aagcagggtg tgagcaggag 1140ctgcggagac cttcagggac
aggacagtct agggaggggg tgagcccttt gcagatctcc 1200tgcttatgcc aggagaaagg
taaacacctc tcaaacacac aaggagccag ggggctgtgg 1260gctggaacct atagccggca
acagcgtata gcttaggatt ttatagcatt gttctaccct 1320agttatgttt cctatacttt
tgtttgtttg tttgtttgtt tgtttgtttg tttgaaatgg 1380agtctcactc tgtcgcccag
gctggagtgc aatggcacga tcttggctca ctgcagcctc 1440tgtcttccag gttcaagtga
ttctcctact tcagccttcc tgagtagctg gaattacagg 1500721199DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of T7 72ccatcttata aatatatcat aatttactga aaaatatttc
agtaatgttg aaaggcctct 60gtgccatttc cagcttgagg ctattcctaa aaatccttgc
acatgtcttt cagtgcacac 120atgtatacat ttcggttggg tatgcctagg agtggaatga
ctggttatag ggtacactta 180cgttgagctt tggtagatac taccaactgc cagttttcca
aagttgtacc aatttacatt 240cctaccacca gtacatgagg gttccagatg ctgaacgtcc
tcactaatgc ttggtaatgt 300ctgccttttt cattttagtc attctggagg tagtgtgata
atatctcatc gtggttattt 360gctttagcct gatgattaac gatcctgacc attttttgga
acatttggag atcatctttt 420gtgaagtaac tactcaaata ttttgcccat tttgctactg
ggttgttcaa aagattcatt 480aaaagaactt cttttatata tgggtttgta gttgttattt
agatattcta gagactagcc 540agatccctat actacaaata ctttctccta ctttgtagtt
tgccttttta ctttctttta 600tatacatata atttttcccc ctccaaaaga cagggtcttg
ctctgttgcc caggctggag 660tgtagtggtg caatcatagc tcactgcagc cttgaactcc
taagctcaag caatcctcct 720tcctcagact ctggagtagt tggaacaata ggcacatggc
attatgcgca gtcaacttta 780aaaaaaaaaa aaattgtaga gatgaggtct tactatgttg
ttgcccaggc tgatctttaa 840ctcctggtct aaagcaatcc tcctgcctca gcctccctcc
caagtagcta agaatacagg 900tgtgcaccac cacatctagc tttactttct taatggcgtc
ttttaatgaa cagataattc 960ctaagtttga tgtagtcaaa tcatcatttt ttcctttata
gtcagcattt atatccagtt 1020caagtaaaga atatcatgaa aacattcttc tttgttttct
tttagaaact ttcataaagt 1080agcatttaaa atgtgaattt tcctataatc ctagcacttc
aggaggctgt gccaccgcac 1140tctagcctgg gcaacagagc gagaccttgt ctcaaaataa
aaaattaaaa aaaaaaaat 1199731602DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T9F
73tgagcatctc tgaactattg cgccatgtat ttccaatttt catattgtgt atttgtatat
60tttatatgta atagtatagg tgtaatatgt aaatatattt tatatgtatt taaaatcttt
120atattttgaa gggttttgtt tcaactatta cttgttaatt tcacagtccc tttctttgat
180gttagcaaat agtaccttca tgaacctcag aggacttgga tctgaatgtg caatgccctc
240tagtatttca aataatagtt cagttggtat agtatttttt taatctgcaa aaaacaatac
300ttgctaatat agctatgtta gagtaaacaa taaatcgaga ataaatttat agcctttgaa
360acaaaacaaa ccaaaaattt tactcctttt tggctttcat ccctgcactg gtatcttaac
420ttctgtttgt ataaaagaat accatttttt cacagaagac aaagaacaat cagccaatct
480aataattatt ttatggccat gctctgaaat acaattaaaa ttatgattgt ggacaatatg
540ccttttcggg acctggctga tggtatttct ggtgtgaccc caactttcca gtcagttcag
600ggcaataaac attggataca ggacagcttt ggggatgaaa tagaattaaa tttagtgtag
660tttttgccac ttttagctgg atgcctggcg aggggttttg tgccctctga gagcctccgt
720cttctcaact gaggggtggt tgtgagtttt gggtcaaatg cttggtgttt agtagatgct
780tggagcttcc atgaaacatg caaccacggc gttgctgcta tttgttcaga tgcgagagga
840acatgacttt tggctgcctg agtgttctca tagcatctgg gccttccttg tgagatcgtc
900agaaagtgtt tcctgcacaa agcctgtact gcggccctgg cgtggggctg attgtcccgc
960tactctgctg tgatggctga attcaaagag tggccgatag gagcacgtat ggtgggtgcc
1020ttgttaacag ctcatagcag aaacgtgaca agcgggagag ggctttgggt tgtcctgaac
1080ttcaaacacc tgtaactgct gcgggaagag cggcacgtgg atgaaacgga cacagagggg
1140gaataggcag gaaaggacgc gggctctttt cgaagcagca ggtctcaagg cggccagcca
1200ctggcgcagc tgcagctgaa gccacggcag agtctccatc cttcccacta tctgctgaat
1260cagagaaagt ggcaggcaac atttttagtg ccttaaattt agaacgcttg ctcaaaatca
1320gaccctactt aaaataagga gcgataccct catttcttaa atagtaaaaa tgccctcagc
1380agaattaacg ggagtatctt ccaacttcat atcctgaatg gaaaagtctg tccaccatcc
1440cgaggacgtg tttgaagcgc agtgtgaaaa tccagcacgt cgtggaccgg ccagacccct
1500gtgccgtgag aggcggggcg gcggggccgt ggggcgctcg cactcccgag ctcatcgtgg
1560catgcgctga gccgaaaacc acgaggtaga gggaatgaga tc
1602741602DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T9R 74gagcttgatt gtctggccgc
gaaaacaggg caggcccgtg tccaacatga tagtgaccag 60ggagacgacc acatccatgt
agggcctggg gagagacagg agggagcggt gggctgaggc 120cagcctaggt ggtggccctg
cctgtagtcc tgtggactgg ctgatgccaa cagcctcagg 180tgtgggctcc tgccacccac
ctcgcctgcc acatcttgca catccccgag gcaactttcg 240atctgctgca ctcggtcacc
cgtactgccc aggcaagggc tgcccatacg cactctggac 300aggctgagtg tcctgccctg
tcccccacat aaggctgccg gccatggctt ctgcacctgg 360gtgggatgca gacacgctga
cctgcctttc tctgcggggc agtggggatg aacccaggtt 420ggactgtggc cttggccaag
tgacctgtat atgaaactgg gacaaagccc atctttggca 480cgtagcctgt ggggtggcag
gtgctcaggc tttggtgaca aggtggatgg gatgcccaga 540aagggagagc ccatggctga
aggcgtgggc aggattgtgg ggaaggtggt tggaattaga 600tgcccagagc aagaatttat
tggcacaggt gggcagacag aggtgaccaa aggacaggtg 660taggtcagca ggtggctgct
agcacctacc tcactctctg gaacccgatt cccttcatcc 720taaaggggat ctcagaacgt
tccacacacc ccctccgcct ccaccctggc cctcacccag 780gctcaccgca cagccaggta
gcctggacac acatctccat gaaccacttg aagggtgtgg 840cctccatctt gccccccatg
atcatcacca tctcatccgt cagcttgatg tcgggttccc 900agccgagatt gccgcccggc
gagctttcaa acatgaagcc aaagtctgca aaaccccaaa 960gagctgcctg tgactgggta
ggagccaggg cgggcaagga cgagtggtct gttttgagga 1020gtggaaaagg actcttcaac
aggagcaccc cctccacccc caaaaggcag gttgtgtttt 1080cttggagaca gtgatggggt
gggtggtggg gcagcaggca gagaaagaga agggaggaag 1140tggaggaagg agccaagctg
gggcactgaa cctggaccag ccccactccg cccagctcca 1200gcttctgact cagagcaatg
gcggctctcg ccccagctcc ctggggccgg ggccaggcac 1260cctctacagc agaacagctt
ggtggccgac agttcggacc tcagagctgg accctgacac 1320tcctggcagg gtggtcctgg
gcattctcct ctctgtgggg tggggatccc tatccacccc 1380tgggtgccgg ggtgaaggga
gaggagggtg gcgctgtggc tggctgaccg atgtggatga 1440tatggccctt cttgtccagc
ataatgttgc cgttgtgtct gtccttgatc tgcagcagga 1500acagcaggag gctgtaggcg
gccatgcttc ggatgaagtt gtagcgggcc tgtgcagaga 1560gcgccctggg ctcaaaaagg
ccctggggcc tgtgggcatt ct 1602751301DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of T10F 75aatcaaactg gacccttatc ttccaccata tacaaaaatt
aatgcaaggt ggattaaaga 60tttaattgta aggcctcaaa ctataaaatc ttaaaaggaa
acctaggaaa taccatctgg 120acatcagcct tgggacataa tttataacta agtcctcaaa
agcaattgca acaaaaaaca 180aaaactgaca agtgagacct aattaaacta aagaactttt
gcacagcaaa agaaactatc 240aacagaataa acagacaacc tacagaatgg gagaaaatac
ttgcaaacta tgcatccaac 300aaaggtttaa tatccagaat ccataaggca cttaaacaac
tcaacaaaca aaaaacaaat 360aacttcattt aaaaaaagac atgaacagac acttctcaaa
agaagacata caagtagaca 420aaaaacatag gaaaaaaata cttaccatca ctaatcatca
gaaaaatgca aatctaaacc 480ataatgagat atcatctcac accagtccaa atggccatta
ataaaaagac aaaaaacaac 540agaagctggc aaggctgtgg agaaaaagga acacttatac
acttttggtg ggaaagtaaa 600ttagttcagc cactgtggaa agcagtttgg agatttctca
aagaactaaa aatagaacta 660ccatatgacc caacaattcc attactggtt agatacccag
aggaaaataa attgttctac 720aaaaaagaca tgtgcacttg tatgttcatt gcagcactat
tcacaatagc aaagacatga 780aatcaaccta ggtgcctgtc agcagtgaat tggataaaga
aaatgtggta catatacacc 840atggaatact acacagccat aatagaagaa tgaaatcatg
ttctttgcag caacatggat 900ccagctggag gccatcatcc taagcgaatt aacagaggaa
caaaaaacca aataccacat 960gtcctcactt gcaaatgaga ggtatatata gacataaaca
tgggaacaat ggacactggg 1020gactcctgga ggagggaaag aagtggcagg caaagggttg
aaaaactact tattgggtac 1080tatactcact acctgggtaa tccgctagta gggatcattt
gttccccaaa cctcagtatc 1140acataatata cccatgtaac aaacctgcac atgtaccccc
gaatctaaaa taaaagttgc 1200aattattaaa ataaaataaa aataaagcta gcaatgagcc
ctatacatga aaatcaataa 1260aacataatca tggctgtata gaggggcttg tcatttatag c
1301761300DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T10R
76aattttacac acacacacac acacacacac acacacacac acaatatcgc tcagccttaa
60aaacatgcta ctaatcggct ttaagaaaag aagaaaattc tgtcatttct gacaccatgg
120aagaacttca acattacgtt aggtgaacta attcaggtac agaagaatac tacagtatct
180cacttatata tggaatgtaa aaatgttgaa ctcaaaagta gagaatggaa tggtggttac
240caggccttga gagagagggg taaaggttgg tcaaaagatg caaaatttca gttaagagga
300aggagtacaa gagatttatt gtacatcatg gtgactataa ttgataacaa tgtgcttttt
360tcttgacaat tgctaagagt agaatttgtt tatgggcacc aagcttgatt ccaagtcttt
420gctattgtga atagtgctgc catgaacatg caaatgcgtg tgtctttttg gtagaatgat
480ttgttttctt ttggatatat acccactaat gggattgctg ggtcaaatgg tagttctaag
540ttctttgaga aatctacaaa ctgctttctg tggtggccaa actaatttac actcccatta
600actgtgtcta agtgttccct tttctccatg tcctcaccag catctgttgt ttttttgact
660ttttaataat agccattctg actggtgtaa ggaggtatgc cattgtggtt tgatttgcat
720ttctctgatt agtaaaatga agcatttttt gtatgtttgt cagccatgta tatgtcttct
780tttgagaaat atctgttcat ttattttgcc cacttttaaa tgaggttatt tggttttgct
840tgttcaattg tttaaattct ttatcgatgc tgtatattag acctttgttg aatgtgtagt
900tttgagaata ttttctctcc ttctgtaggt tgtctgttta ctcttttgat agtttatttt
960gctgtgcaga aactctttag tttaattggg cctcatttgt caatttttgc tttcgttgta
1020cttgcttttg gtgacattgt cacaaattct ttcctaaggt caatgttcaa aatggtgttt
1080cctaggtctt cttctaaaag tcttatagtt tgagggttta catttaaatc tttaatctat
1140cttaagttaa tatttgtata tggtgagaga aaggggtcca gtttaattct tttgcatatg
1200actagccagc tatcccagca ctatttatta aatagggagt actttcctca ttgcttattt
1260ttgtcgactt tgttcaagat cagatggctg taggtgtgtg
1300772001DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T11F 77tctttggggt atgattatat
gtctaggtaa aactctttta agaagatgaa gcagagagga 60ttgaattgac aaagacagct
ctttaaaaat taaggttatt tcaagactaa gaacataact 120gcttaattgc aggtaataac
agaaaaaact tggaaataaa catcccatta tttgacctcc 180aaggcagaag actggcacca
aggaaatggc agcttcgtcc ctttcctgtc ttgggcattg 240gtaaaaggag ttgtctagac
atgtttgatt tctgtttcag cccttattag tagttatgcc 300atggcaaatt attcaatttc
tctgactcag tttccttatt cagaaaatgg aagcataatt 360cttgcctcat agggccatga
agattaaatg aggggtgtct tgaagtgtct gggacataaa 420tcttcaataa aagctaattc
ctttttttta cagttatctc aaacctttta gtgaattggt 480gcttatcagt gagcttttta
ggtgatgcaa agaccctgct ttgctcattt taaggaacag 540ttatttttct ttctccattt
tgaagtttct tgtttgctgc ctggttgata tggtttggct 600gtgtccccac ccatatctca
tcttgaattg tagttcccat aatccccaca tgtcatggga 660gggacctggt gggaggtaat
tgaaccatgg gggtggttac cctcatgctg ttcttgtgat 720agtgagtgag ttctcacaag
agctgatggt tttataaggg gcttccccct tcgcttggca 780ctcattctct ctcctgttac
cctgtgaaga ggtgtctcct gccgtgattg taagtttccc 840gaggcctccc ggccatgtga
aactgtgagt caattaaacc tcttttcttt ataaattacc 900aagtcttggg tattccttca
aagcagcatg agaacagact aatacattgg tttaaattag 960aatgccaaaa tttaaataat
ttttatcttg aatagtagat ggaattaact ttctcttgaa 1020agatatattt taaaaaattg
aacttacaca gacagttttg aaatggtctt attttagttt 1080tatttattta tttattttga
gacagagtct cacagtgtcg cccaggctgg agtgcaatgg 1140cacaatctcg gctcactgca
acctccacct ccagggtcaa gcgattctct tgcctcagct 1200tcctgagtag ctgggattat
aggcgcccac caccatgccc agctaatttt tgtgttttta 1260gtagagacgg ggtttcacca
tgttggccag gctggtctcg aactcctgac atcgtgattc 1320tcccacctcg gcctcccaaa
gtctcaggat tacaggcatg aaccaccgcg cctggctgaa 1380attgttttta ttatagatgt
tgcttgtgca gttttgttag aagttcgtga cttttaacag 1440tgatgaaaat acttcgtcat
tcaacaggtt atttttctgc tggttgtagg ttatttgtaa 1500ggaactgtta gtctcctatc
tgggtggaca tgtaatagta tcagttactg aaccagaact 1560ttaaacacct ttctgatact
cacactggga ggtcaccaag tatctcagaa taaaatgtcc 1620caaactgaac ctaccatgtt
cccagaaacc cagcccttct caaattccca gacttggtga 1680atgggagcct gtccttgcag
tcttgtagcc caaaacctag ggcttaagaa caccttcttc 1740cttactccca tatgcaaccc
atcaagttcc atgcatttca tctcctaatc tcaaatccct 1800tcacccatct ccacagccac
cccgctagtc cgggctgcca ttgtctctca cttaaaatgt 1860tgttattgtc taactgacct
tcctgaaccc tttcttgcct ctttccagtt tattttccac 1920actacagcca gaaaaagctt
ttcaaaatac gcatctggtc acctgcatac ctgtctccag 1980accacataca ataagccttc a
2001782001DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of T11R 78tctgccagcg gctcccgcgc caggtcctcg aagcgcacca
ggcggtagcg gccgcgcagg 60aagggtggcg gcttgagtgt ggcggcctcg gcgatgcgca
cgtggctgcg gcacacctcg 120cgaatcaggc gcaggtgagg gtcggcctcc acccacttgc
cgttggtgcc cagcacgatg 180ccgttgtcgc gtgccagtat cgggcccgcc gcctcccggg
agcgcagcac ggcccgcggg 240tcgcgcacca ggtgcacgat gcgcaggttg agcgcggggt
cgctgagcag cgggtagagc 300acctgcaggt tgaagaagcg cacctccttg agcaccacgt
ggctgtagga gcggcaggcc 360tcccgggcca ggctgaatgg ctgccgcgtg cacagtgtct
tgcatacgtc ctgcttgctg 420atggtgcctc ggggaaaggc gctgcaggcg ggcggcgagc
acagcgcgcg gctcgttgcc 480cagttgaaaa aggcggacag gtttcggctc tgtggcatgt
aggcatcaaa cacgtccatg 540tcgcacaaaa agatagagcg catcaggtcg cgcacggcca
tgtgcagcgt tgccgcgctg 600ccctgcgaca gggtggtcca cacatgccac gcgggctcca
tcaggtagaa gacgtcgggg 660tgctggctga agagctggcc caagaaggat gagcccgagc
gccacgagga cagcaccagc 720acgtgcacac gatcctcgcc gccggctggg gatgagggcc
ctggccggga gatgatgaag 780agcaggaggc aggtggtctg tgccaggagg agcactgtca
ctgtcttgct ggagaaccgt 840ggcagccaca tgcgggcggc tgggggcctt cgggtggagt
gggcaacttt agggacccgg 900gccctcatgc ccatcccatg ccccaattac tgcccagtgc
cctcagggat cagccctcag 960attcggctac cctacccatt ggacttccca agactcccaa
ggtctcagtc gagcactttc 1020ccaggaatac ggagtcaaga cataggccag aatatagtct
gtgctcacag cagaagtcca 1080gttgcagaat aatgtgggat atcatcaaac tgtctaccta
cccacccacc cacctactta 1140catacctaca ggctatctat ctgtagagag aaatactatg
tttcaaagag aactcctgtc 1200ttttgcttca ggatacctct tagagagacc cttttaggtt
gtggagctaa aagggcttga 1260tgggggcttc ggtggatgtc agagcaccac caggctcgcc
gaggttgaat cctggctctg 1320ccacttccta gcctatgatc ttgcttatga agatcactta
aatctctctg tgacggatca 1380ctttacccgt gtgtgaaaga gggataattc cggtacctgg
ctcacaggat ctggggggat 1440tggggggtta ttataatgaa gatgggggaa gggaacacgc
agtcatgccc ataactgagg 1500attgcacctt ttacaaggtg tgcttctgta ttatataatt
tttttaacag gcaggtataa 1560aacttttgtc agccaggcgc ggtggctcac gcctgtaatc
ccagcattat gggaggccga 1620ggcgggcgga tcacgaggtc aggagatcga gaccatcctg
gctaacacag tgagacccca 1680tctctactaa aaatacaaaa aattagccag gcgtgatggt
gggcgcctgt agtcccagct 1740actcgggagg ctgaggcagg agaatggcgt gaacctggga
ggcagaggtg gcagtgagct 1800gagattgcgc cactgcactg cagcctgagt gaagagtgag
actccgtttc aaaaaaaaaa 1860aaaaaaacaa caaaaaaaaa acttttgtca ttaaagataa
acaagtaaat aaagtggaca 1920aagaacagca actgttgtca tcactggtgg ggagtgaagt
gctgtaggca gcatgggctc 1980cagaaggagg gtgtcctgga g
2001792100DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T12
79tggcatccag catggagccc acagcttccc tttgtagaat tgcccagttg ttgcagagtg
60ctttggtctc aatgggtcta aagctcttga tgatataaga gcttcaactt ccttttccct
120ctcctccccg caggctgcac aatgtcctgg tgaatcacct gggacttcag agctctgcca
180ccctgggtgt gaagctcagg tctgctcttg gtagcttggt cagtgtgaag tacaccgtga
240ttttgggcaa gctgcttaac ctccctggcc ctccgtttcc tcatctgtag aatggggata
300ttcacagaac ctacttgtag ggccatggtg aggattaaat gatgaacagt gctggcaaac
360aggaaatgct atataagtgt ccctagcaat atacacaccg cacatcctca gtcaccacgt
420gtgttcactg aggtatgggc catgtgtggg tggaattgtg ttccctaaaa agatatgttg
480atgtgctaac ttgaggtccc tgtgaatgca ggaaaccaaa atatttcttc tcaaaatagt
540gaggattgtt aagttaaaga cactgaaaat gcaggggaac actgccttgg cctctacttg
600cctgatgaca ggcacgaatc cttccttact taagacacat cacttgctta tcagcccaga
660gaaagcacct gcaggcacca ggaaaatcta ggaacagatt ttactctctt cccacatttt
720cccacttttt caaacactga aactgctctc tcctttgtct tgtcactaga taggatttat
780ggctctttgt taaaatattg tttaagcaag gcttctacgc cactagcttg agagagaaat
840acttttgaac tgaggcctct tccgcatgat aggcagagca tgcattaata catttctgct
900tgtttctctt ttgttaatct gacttttgtt ttccagagtg tctcaaataa gaacataaaa
960gggaggggag aaattatagt ttctccccta catgaactta ttcggatata gggtctttgc
1020agatgtaatc aagttaagat gaagtcatat ttgattagga taggccctaa ttaaatatgg
1080ttgctgtctt tataaaatga gaagaagaga ccaggtgtgg tggctcacac ctataatccc
1140agaactttgg gatgccaagg caggaggatt gcttgaggcc aggagtttga gactagcctg
1200ggcaacacag caagactcca tctccaaaaa aattaaaaat tagctgggca tggtggcatg
1260cacctgtagc cccagctact tggtgggctg aggcaggagg atcaattgat cccaagagtt
1320caaagctgca gtgagctatg atggcaccac ggcaacctgg gtgacagagc gagaccctgt
1380ctcttaaaga agaaaaaaag aggagaaaaa aacagagaca cagaaaaaag tccttgggat
1440gataaatgca gaaattggag ccatatatcc acaagacaag gaaccaccag gattcttggg
1500aactccagaa gctaagaaga gggcatggaa caggttctac cctagggcct tcagagggag
1560cgcagccctg cagacaccct gagttcagac ttctggcctc cagaactgcg aaagaataac
1620tttctgttgt tacagcagcc ctaaggcact agtacaggtg acatgtattg ctcttctgaa
1680gagcagggtg tctacagcgg cagaggtctg ggtcctggca cgtgcccttt aggattccaa
1740tatccttagg ggcctgctgg tgctgacagt tccagaacca taagacagaa ttcctgcggg
1800ccagtttgga agcagagaca ggaaactgga agagccctta gcctgtgctt gggcttaaag
1860ccctttagct tgtggcttta actctgaaac ttctagaggg catcttgcag gtcagtgtga
1920ggtacagaag ttgtcacaag cttcctggct caaagaaagt gagacttcac gaacttttct
1980ggacatcaca ccagcactta tgaagttatc ttgttaagca cagatgaaat cagaaataca
2040ggcattcacc atcacttaaa caaagctcag attgtagagt gcgaggaaga atcggtggga
2100801700DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T13F 80cagatctcta aagtattggg
tgtggactag agctctggac ggcctaaagg aaaggaatgt 60gccggttcac agggacccgc
ggctaagctc aagggtaaaa tacagcttta caaagcatct 120ttaggctgtt ccttcccaaa
cgtgcttaga agggaacagg gaaaggcggg tgtgttttct 180cactgaggtt cttctagtgg
ctggaatctg atagagtacc aagttgtagg gatatggata 240tattttccct ttggcactcc
ataaagctaa atgttgggct gaaaaaagga tgcagcctat 300aaacaagtat ttttcctgaa
accaactgca tgaggaaacg ctgcgctccc cctcagggag 360cagtttctga agccagctga
gcacagctgg cactggccag agggagccct ccaccctccc 420accacgtatg cccacctgca
aacctgggtt ctgagtcccc atgcagggga cagacctgaa 480aattccagtt tgtgtccttt
caggtcatcg acaggaatga cagcctggca agctgcagtg 540actgcacaca gctaccctgt
gagctccact tgtgtgggtg caggtgggcg acaggagtgt 600gtgacacaga caggcactcc
accaggagga aacccacagc agacgtcaac catcgcttta 660ttaaggctgc gagtcggggg
gctgagtcat gcactccaca gacaccccca ctgctcccaa 720ggtccacttt tggatgaccc
tgaaggcaga gactcctgag atctgggcca caatctaggg 780tgagccaccc acagtgccct
gctggacagg ggggtatgcg gactgcacgg gggggccctc 840agcaggggtc ttcctgccta
gggtggggct ggctccagtg ggtcctgggc tcaggcaggg 900ggggtggcag ggaggcaggg
acatcccccc gccctctggc ctatggcttt gttgccctat 960tgccaccagc gcagaagcaa
tgtgctatac cgtgaggtga tgaagaagag ccccgggagg 1020gagcaggcag ctctgtgcct
ggggcctggc cagacctcag gggtgctgtg gccctgctcc 1080tgttccccct cagctcctcc
cagcaatggg tctcctccag tggaggtcag tcactcagaa 1140gtggacccgc agcacgtctt
ggctagcaac cggccgctgg caggctgtgc acgtcatggg 1200cagggagcgt tgcttctcac
ccaggcaggg tcggcacagg aggtggccgc agggcagctg 1260gtacaccggc tcctttttga
agtagggaga aaatactctt ttgcaggagg cacattcggg 1320gcccaggatg ctcccaggct
gctctggtaa atcaggaagg aaaacaggcc agggttagga 1380aagctgctcc atggtccagg
ctgctctgag gggcagagcc ttcccaccgt gctgctgcag 1440catctggctt catccctccc
gagtccatcc cagtctgatc aggtagggga gtggaagcgg 1500gagagggagc ctgggaaccc
gggaggcctc ttctctatca tctttgacca aatctcagtg 1560cctctacgaa tgcttgagaa
gagctggctt ctgagggcag caggcaggac tgggcccttc 1620ctcctggtct cccagcaagg
tttactttcc cctgcgatag gtggccaagg ctggagcaag 1680gcacagctca ctctgacaag
1700811701DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of T13R 81gaatctgacc actcagtccc acatcccagg attcagagaa
aaagaattcc agtgagggct 60ctggacccca cacagctaag gcttccaggg tttaggcaag
ccctgaggga cacccatcat 120aattacccag acgggggccc agcatcccgc cccagcattc
tgccttgcaa ggagctccct 180caccagggct cagggaaggg acagcctgca gttccagcaa
gggaggcctg cagagtcagc 240cacaggtggc cactatcggt tgcttggtgc caacttagtg
tgagggggca gggcccagac 300tcgagggtgc cattaccgtc ccccatcgtg tacttctttt
cctcgtagct tgagtctgtg 360tattccagga gcaggcggat ggaatgggcc agctgggaga
gatggcccac agctcgggtc 420agagatggag ggtccctgac tttgtgacga ctctgcacaa
ggggagcccc atctcctcct 480ctcgttcctg cctcacccgc ccccaccccg cacgcccagc
cacacgcaca gacagcggca 540agcacagacc ccgctgtcag ggacagccct gaagaggaac
cgtccctaga gcccgtcctg 600cagctgctcc acacttcccc gcccccacgc acccccgtcc
caccgcccag cggaccctgg 660ctcaccccgc ggatgttcca gtaccccagt gtcatgggca
tggtgctggt tgctgtggat 720tctgcagaca ggcctcagcg gggcggggct cagcgtttgt
gagaggccca gagagggtag 780aggggaagcc ttgctgcgac cccgccccac ggcccgccct
gcccccgaaa cgggccaatc 840tggaggcctg gagcgcgctc atggggctag gagtaggatc
tcctcccacc tcccagcccc 900gtgggtttca ggagagagat caggacgccc agaagcccag
ggcgggggag aactggttga 960gtccaggggt tcaagactga actgagctat gatcgcgccg
ctgcactcta ggttaggcaa 1020gaaagaaagg ctctctctaa aacagagaga ttctgaataa
agtaataata gcctaataaa 1080gaaaaataac acaaaagaac atttggtgct cagggattca
ctggataagt tttcaaaact 1140tttcaatgta tgatagagat tgttataaac tgcggacata
cgtggcatga cagacctaac 1200gtgggaagga caacacaggc aaggatgatt ataactcact
gtcacttatc agcctaaatc 1260caaacgtcag gaataccgcc tcagagaaaa gaaaatgatg
tttttgtcat aagtggtgct 1320gtgctcctag ggagcttgct gggtgggaag agagacagaa
aggtggggag caggggctgg 1380tggacttggg gagggaggag aaagcccatg tggaaacgtt
agaatctggg gtaatcagag 1440gtctttgtat tcattcgttt tgtaaatttc tcaaactctc
atgttaaatc aaaataaaaa 1500gttaaaaaaa aaaaactacc aggacagaca tacacaaata
ttattaactg aaataaatgt 1560tccatcaaaa aggacttacc ttaactacat gagttatatt
atgatttcta ttattattat 1620tattattatt ttaatattag tatccatcca gcacaccact
ggtcttcaag tggaggtaac 1680tttgcccctc aggggacatg t
1701821482DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T14
82atcagccccc acatgcccag ccctgtgctc agctctgcag cggggcatgg tgggcagaga
60cacagaggcc aaggccctgc ttcggggacg gtgggcctgg gatgagcatg gccttggcct
120tcgccgagag tnctcttgtg aaggaggggt caggaggggc tgctgcagct ggggaggagg
180gcgatggcac tgtggcanga agtgaantag tgtgggtgcc tngcacccca ggcacggcca
240gcctggggta tggacccggg gccntctgtt ctagagcagg aaggtatggt gaggacctca
300aaaggacagc cactggagag ctccaggcag aggnacttga gaggccctgg ggccatcctg
360tctcttttct gggtctgtgt gctctgggcc tgggcccttc ctctgctccc ccgggcttgg
420agagggctgg ccttgcctcg tgcaaaggac cactctagac tggtaccaag tctggcccat
480ggcctcctgt gggtgcaggc ctgtgcgggt gacctgagag ccagggctgg caggtcagag
540tcaggagagg gatggcagtg gatgccctgt gcaggatctg cctaatcatg gtgaggctgg
600aggaatccaa agtgggcatg cactctgcac tcatttcttt attcatgtgt gcccatccca
660acaagcaggg agcctggcca ggagggcccc tgggagaagg cactgatggg ctgtgttcca
720tttaggaagg atggacggtt gtgagacggg taagtcagaa cgggctgccc acctcggccg
780agagggcccc gtggtgggtt ggcaccatct gggcctggag agctgctcag gaggctctct
840agggctgggt gaccaggnct ggggtacagt agccatggga gcaggtgctt acctggggct
900gtccctgagc aggggctgca ttgggtgctc tgtgagcaca cacttctcta ttcacctgag
960tcccnctgag tgatgagnac acccttgttt tgcagatgaa tctgagcatg gagatgttaa
1020gtggcttgcc tgagccacac agcagatgga tggtgtagct gggacctgag ggcaggcagt
1080cccagcccga ggacttccca aggttgtggc aaactctgac agcatgaccc cagggaacac
1140ccatctcagc tctggtcaga cactgcggag ttgtgttgta acccacacag ctggagacag
1200ccaccctagc cccaccctta tcctctccca aaggaacctg ccctttccct tcattttcct
1260cttactgcat tgagggacca cacagtgtgg cagaaggaac atgggttcag gacccagatg
1320gacttgcttc acagtgcagc cctcctgtcc tcttgcagag tgcgtcttcc actgtgaagt
1380tgggacagtc acaccaactc aatactgctg ggcccgtcac acggtgggca ggcaacggat
1440ggcagtcact ggctgtgggt ctgcagaggt gggatccaag ct
1482831680DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of T17 83ggcgccacta cgggattaag
cctgaaaccc gagcggcccc ggcccccgcc acggccgcct 60ccaccacctc ctcctcctcc
acttccttat cctcctcctc caaacggact gagtgctccg 120tggcccggga gtcccagggg
agcagcggcc ccgagttctc gtgcaactcg ttcctgcagg 180agaaggcggc agcggcgacg
gggggaaccg ggcctggggc agggatcggg gccgcgactg 240ggacgggcgg ctcgtcggag
ccctcagctt gcagcgacca cccgatccca ggctgttcgc 300tgaaggagga ggagaagcag
cattcgcagc cgcagcagca gcaacttgac ccaagtaagt 360gcaaaagaaa ttgccccctg
atttattgct gaaacctgta aggctcgaat gtgcaaaact 420gatagtttta ctaacctata
aaaacgtcta gacgcctacc caagcctagg cgaacaacat 480gcatccataa aaagagcttc
ccataaccac ctaccctggg cgctcagtta gtacggtaaa 540cagagcgcga gcattaaggc
tttttatgat aattccccac aagttgtgaa aagcgaccat 600ccttggtgaa attaatttaa
cgacctctct tccccaccct gtggtctctc cctgcctccc 660ctcctctcct ctctccccgt
ctccaaacct ccctctttgt agacaacccc gccgcgaact 720ggatccacgc tcgctccacc
cggaaaaagc gctgtcccta caccaaatac cagacgcttg 780agctggagaa agaattcctc
ttcaacatgt acctcacccg ggaccggcgc tacgaggtgg 840ccaggattct caacctaaca
gagagacagg tcaaaatctg gtttcagaac cgtaggatga 900aaatgaaaaa gatgagcaag
gagaaatgcc ccaaaggaga ctgacccggc gcggtgctgg 960cgggagcgct caagggcagc
ggatttgttg ttgttgctgt tttcctttgt gggtgtttgg 1020tgcttgattt ccagaaactc
tccagcgact tggacttctt cttctttttt tttttctttt 1080tagatagaag tgactgtgtg
gttggtctct gaggtatttg ggggactctg tatttgctcg 1140tttacgtgtt ggaaaaacca
agtggctttg gggtttcgcc ctatcccact ccctctcttt 1200cctgctccat tggttcctta
agaaatgcta tattttgtga gtgcaagctg gcttggggag 1260ccctctcttg tgtaaatgtc
ccccatgttt ctgaaaagtg ctgtagttta gtcccctcac 1320ccccagcact gcccaaacag
gggccaagtg cgccccaatt ccaagaatga aggcagagcg 1380acaacagtgc ggacaccccg
gctgctagcc cacggtgaag cccggcgggg ttgcccacca 1440gttgcgaaag ccccctttcc
tcagggagca cgcgggacct cggtggagat ctccagtgag 1500gcttagagga gcccagggcc
tcgggcgggt tggggtttgt cctcagtgca ttggacgcgc 1560tgctctctcc cctgaaggct
gggctcgcgt gggcggccgc gggtggtggc cctcccggtt 1620cctgcccgag gaccagttgt
aaatgttact gcttcctact aataaatgct gacctgatca 168084919DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of T18 84gatcatctac taggttgaaa ggagagaata tgacttccag
aacagcactg atgcttaaaa 60aggatgcctc tggaagaaaa ggaggaagag gagcaagtga
tgggagaata cagtgggact 120ttgggcacca tagggtcatc ctgagttttt caccaaaatc
aggaacagcg gcaaaactgg 180tttcactgaa gaagacacac gtttggagac atgtgtagtc
tccaaggatt ctcacttaac 240aaagcctatt tctgttgtta aaaacccctg cataatgcac
ccacacacaa acacaaggct 300tggtctgtgt tcctggccac ctaaagaaac tgattcccag
taagtttaaa cctgaatgaa 360atgtttctgc aaattcagcc tcaaaattcc tcctctacct
ggcatccctg gcttgtaaac 420tatgtgtctc attagttcat aaacaaagca gccctgactt
tgccttgtac tcaaccacag 480ccctaggagc cagtagaatt tgtccagagg tgctgggctt
tggagcccaa gtggacaaag 540tcagaccccc tttcctcagg gcaaagccct cccacagggc
tgggacccca aaggctatgc 600tggaagcagg ttcagcagca ggatatcaag gggcaaagct
cctaattcaa aatcttcctg 660gcttctgaac aaccattagg atggacagag aaaacttttg
ccctgctctg agagggtccc 720acagggcttt tggaagcaga gccaccattg agaaatccct
ttcaacctga gtagtaattc 780agatttttct cccactcctg cacaacttaa tttgctgaat
ggaaaattca gccagaagtg 840atgggctgct tgaaatcaac aaaacttgac acattcttcc
cattttcatt ttactttatt 900gttaaacaca taattgatc
919851174DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A1
85gatcaataga agaatggagt ttgtgtttgc tagccatagt tttgacgtgt gggagagttg
60gagtctagaa ggttctctgg acgaatgtcg gcttgttaac tgcaggaatt cctctgtaag
120tctctgtcct tacagaaaat ggcccgaaat tgaaaaaccc tacttcttgg aaaacagaaa
180taatttgtgt aatgaatgtt gcaggcggtg ttggacgttc gtgtggagat attggcaatg
240gtaggagacg atggtatcac acgttggatc gattaaaaag aaaaacagag tctctccatt
300tgtgagtttc tctcttttaa ttacttttgt tactttaaca tccttaggat tcacagacga
360aaaacagaga cacccaattt ttgtgtttcg agactgtgtc gtgtgttgtg tagttggtat
420caaccaactt atatctgtaa tcattgtttc tttttattta ttctcggttt gcagaaacat
480ccgatgagct tgtcttagag ggacgtttgt tgttgttttc tgggtctggt cgtgatgaac
540tcgaaagcat tgtgtgtttg gttagtagtt tgaaataggt gtgtgtattg tatttgtata
600tgctgcgttt gtgttttaga gatcatcgta cataaaacac atcatcgtac ataactaaaa
660tttgagctaa actacaaaag aaagtaacct tcatttttag tcgaaccagg ccccagctag
720gcagctatct cgtaaataag attgctggct tacgatcgta ttccacgtgg caatttatgt
780gccgtggatt taaatttgta cgtggcatga gtgttaggag aatgtccaca tggcttgtag
840ttgttagtcc cacgctctga accagagcaa ccggctcctt acacgtgttc ggcttaaatc
900catttttcga atgagattac acttctaacc ttgtctccct ctcccgctta taccaccacc
960actctcacac aagtctctca agtcacaaac tctgtttcaa accaaaaggg aactttgtgt
1020gtgttgtcga gttttatggt gactgtaaac cctagccaag ctcattgttt gcctatgaaa
1080atgagtctac cgggtttcaa tactcttccc cacacggcaa caacgatacc ggtttccata
1140cggagcaata ggacgatgtc gttttttgag gatc
117486910DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A2 86gatcaaaatt
ttggtttctt cgctttgatt ttcttcttct tcttcttctt cttccctcaa 60gttccttaga
atatctttct catccatttt ttttggttct tgttttgtta agtgaacatt 120ttagttgatt
ttaaagtgct aaacttaaat gcagcatttt actaatataa aattacgctc 180cattattgac
cttatataca tagaacaaaa taatgttata atcttcgact tttttctaac 240aaatattaac
caatcatgtc actaagaaat taaaaaatac tagtatatag gaatctagtc 300cattgtatat
atcgtaaaca tggacacttc accaacgaac atgcatgggg tctttttata 360aggttcttta
taccgaaacc attgttttgg tttttatgat aattgagtta gttttgtggc 420ttttccgttc
aactaaaagt ctcattatgt caactgctat taaaccggcg cacatggcat 480gttttatgaa
attaaggtca attggactcc aacttttcaa ttattaaaaa aaaagaaaaa 540tgattgttgt
atgccttggc gaagaagaaa agccgctagc tttattcatt atcaaacgaa 600acaaaaacaa
caacacatca ctaagaatct taaactctta accttacatc aaagtaactt 660ttattacatt
gcatacaaga aaagaacaaa ccagcattat taggtttgag attaaacctg 720ttcccacaca
tatacataga gatatgaact ctacaatttc aaaccagagc cttgaagttt 780ctcctcaaca
atcatgtcga ttttgttttc catttcagga gtcatataac tcttccaatc 840accaacttcc
cctttacgga aaaaactctt gaaacttact ccttccgaca agcttcctgt 900tttgttgatc
91087906DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A3 87gatcattaat cgcagatttt
tacaagacag cagcttggag agcaacttac aagtgtgtta 60taaactctga actcaacttg
gaagatgttg acgttccaaa tgaaattgga agacaaacta 120tcttcccacc aaggacaaga
aggccgtctg ggaggccaaa aaggctacgt atcaaatcca 180ttggcgaata tccggttcgt
atttgtagga gtcccatttt ttcgacttta tctttattcc 240gtatttaatt ttcaatttta
tgtggtttaa cagaaatcaa agagcgtgaa ggtgaagatt 300aacaggtgtg gcagatgcaa
aaagactgga cacaacagga caagctgtag taatccaatc 360tgaagatgtt ttaaaatcgg
ctatattgat agaacgatga ccattttatt attgtttttg 420tgtttggaaa tggttatttt
tggataaaat atgttgcatt ctattttata attttagttt 480cgacttatta catataaatc
tagtaaggta atatattagc aaattacaga taatgatgaa 540aaacatggac aggtataggt
ggataagata taaataaggt aggactgaat tgttacccgt 600taataatgaa agaatatacg
aaatactaaa cattaaataa ggaagttact aattattgga 660caacaaaaag tttaattcct
ttaaaaagaa attggaatac agacagtttc attgacctaa 720ttaagtactt ctttgaaaaa
aatcaaacta ggagaataga agttgtaaat aattgaaggg 780aaacgtcgat tcggtgaaaa
ggttttttaa ttagtattta aagggaaata tcttctctta 840tacagaatat cttgccccag
aacaaatcgc ctcaaatact aaaagtgtgt acatcttctc 900ttgatc
90688782DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR A4 88gatcaaattc atatgcttat ttgtgattat actttgcttt
gattcaggaa atcaaagaag 60atagctccac cttacagggt gatactacac aatgacaact
tcaacaagag ggaatatgtg 120gttcaggtgt tgatgaaggt aatacccggc atgactgtag
acaacgcggt taacattatg 180caagaagctc atatcaacgg tttggcagtt gtgattgttt
gtgctcaggc tgatgcagag 240caacactgta tgcagctgcg cggtaacggc cttctcagtt
ctgttgaacc tgatggtgga 300ggctgctgaa actaattaaa ctcagtatag attttcccac
cttccaggac tctctattta 360gtcaaaaaca tttgttgttt taatgtatat aatatcagaa
atttggtaca agactgttac 420tatatgcaat gaaccttgcc cctacataga tctgttgtga
gttttaagtg ttttcatttg 480gaacttcaga atgcaaataa acaaaacttt attgaagtca
aatggtgtta cagatgaatc 540tttctgattc tgtaatcact aatgtaaatg tatctaagca
attgtaaggg agtgacgtgt 600ttcggtttca tctcgcccaa aaaagcattc aaacccaaga
aacctgcagt ttcaagacat 660tgatgggata ccatatagat gtatcaagca tcaaccggag
taagaagcga ctgaatgccg 720aagataatga aaagcattcc accggaaaga gccacctgca
acaacataag agctatttga 780tc
782891356DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A5
89gatcctgtaa aacataaagt tagagataat tgtccgattt gtttgccctt ttaatttgga
60gagatatgaa ccaaaaacat atttcggaat gggtcccttt ttcatcgtgt gtaacagttt
120taccaaacag taatactttg tgaaagtttt gattaattaa tgcaaaaaga ttagaaaaaa
180gcgaaactaa tttttggatt acactagaaa aaggttaaaa tcaataacca aaaaaagaaa
240aaggttaaag ttacaaaaca caccggttta tagagtgaaa tgattattgt tctgttgaat
300tgacgtgcca gcttagcatc accttactat tatcagtcac ctatatatca caattcacag
360gcttcttgct ttctctcatt ggctcgtctt cttccctttc ttctccaatc accttagctt
420gctgatcagg taaactagat tggtgtttcg tgttgttttc ttctcaactt aggtgtttga
480tttgagaagt ttttctatgt atgttggcat gttgcgttcg tagcattgca tatcaacgga
540taggtttgaa taggtagaat taatttgatt gatatatgaa agaatgtttg tatatatact
600ctaggtctag gttattgaat attgagaaat ttattttgtt aggtttagat gaattattct
660tcgatgagtg gttcaaagtt caattggcaa gtcttttcaa tgattgtagt attttggtga
720tgataagtaa gttgttaatg actctcaagt ctgaattcat gttttggttt tgtttccttg
780taaaaatgtg aacgtttttc ttacagaagc tttcacaaac aaagtatggt taattgagtg
840actaatccac taattctctt ttgttgtttt atatcgttta ttaggtaatg tttttttttt
900ttgggtgtgt aaaatatgat actgactcaa gattttatca tatttctgaa tccataagct
960aaagtacatt tgagagaagc aagagagata gaatggggcg tggagttagt gcaggtggag
1020gacaaagttc tttgggatat ctttttggga gcggagaggc tccaaagcta gcagccgtta
1080acaaaactcc agctgaaact gagtcttctg ctcatgctcc acctactcaa gctgctgctg
1140caaacgctgt tgatagcatc aaacaagttc ctgctggtct caatagcaac tctgcaaaca
1200attacatgcg tgcagaagga caaaacacag gcaatttcat cacggtatgt ctttaattct
1260ttcgctgaat cgagtcctgt gtgctggtta tcggatagca aaaacatctg tatctttact
1320tttcttagat tagttgtctg aaaatgaaag aagatc
1356901452DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A6 90gatcgactgg
tacaatgcta gaagccctag aggttgtagg tgatagccac gatacatcct 60taggtgatgt
aagtcaactg aatataaatg gccatttacg tagacttcat gtcctagatg 120atccctccta
ttataacgtg aatctcggtt tcttggtgtg gaaaacgaaa tgattgatat 180gtttttgtca
gggatttgag gtggtgaaca gtcgttatat gactagttat gatgatgaag 240atacaccgcc
aggaagtgga ttcaggacaa aactaagaga gttccataag aggtaaatga 300cgcattaact
catgcctctc aacattttgt cggcattcaa acagatgcat tcaagtctct 360tttaataaac
acaagaatcc catttgttta ttgttttgtt tgtatgcagt gcggcatcat 420tcacagaact
agataggaat tacctaacac cgttcttcac aagtaacaac ggagattatg 480atgatgaggg
taacatggag caacaccatg gtaacaacat aattctctga tctcttgttt 540cactattatt
tttgttgtta ttccgcaccc aaaaccatga aatttacaat tggggttatt 600gcagaagaac
gaatcccatt tactagaaga ggaaatctaa ataaccgcgg ctaagtttcc 660gagatgagaa
atctaatagt gttttttcag cggcatatat atgtacataa aacaaactgg 720atgtatggga
ggaggtagtg acaaaggatt tgttctaagc taggtttctc tataatatgg 780tactgtgttg
ttggtgtaaa cctgaatgga tattgttagg ttgaaactaa ttacattcac 840acaaagaaag
aaaaaaactt gaagaaggcc atggctggtt tatactgaac cacgaatttt 900gttagtttta
aactcttagg gaaaatgcta taatgccttt tttgtcttgt agtcgtgttt 960ggtttgaatt
aaaaaaaaaa tagagaacgt cacggcacgc caaaagtgtg gaccttgttt 1020attcgccgga
agtaagtaac caaaaacgct tctaatcttt cgtttacaac aaatatctct 1080ctctctctcg
ctctctctcg ctctctcttt cttcttcttc atcttctttc atggctgtta 1140ctggctgggc
aatcacaatc tgaattcttt cttcctcctt gtctctctga ttttcgccga 1200gttttggggg
ctcttgttgt tacacgatga gtctggtggt tggtcagtct ctgggtttaa 1260ctctagtcgg
tgatggtctt tcgttacgca attccaaaat aaatgtcgga aaatcaaagt 1320ttttctcggt
aaatcggagg agattggcgc gtgcggccct ggtacaagct aggcctaagg 1380aagacggagc
ggcggcaagt ccttccccat cgtcgagacc ggcgtcagtt gtgcagtacc 1440gacgagctga
tc
1452911085DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A7 91gatctatctt
atattgttag ttcatgtttg tttttaaaga ctgtttttat gtttcaatgg 60tatattactg
actggggcag taatattgtt gaagtctgta gattatggtc gcatggctga 120aatactggtg
cagagggctg cttctcctga tgaattcact cgattaacag ccatcacgtg 180ggtaagcaga
ataaaccatg cttctgcttg gcgtcttcca gttatataga ttggtactat 240tttgacttct
cgggagattc atatactaag aatatctgct ttttattaaa tgttgtagat 300aaacgagttc
gtaaaacttg ggggagacca gctcgtgcgt tattatgctg acattcttgg 360ggctatcttg
ccttgcatat ctgacaaaga agagaaaatc agggtggtaa gtttgcttct 420cctcctcagt
gatggaaact gtaggttttg tatgcatctt tttactttct ttgttttttg 480atttttattt
gcataaggtt gctcgtgaaa ccaatgaaga acttcgttca atccatgttg 540aaccctcaga
tggttttgat gttggcgcaa ttctctctgt tgcaaggagg ttagtttttc 600tctattgttg
tttttatatc cgtttgaata ttattaaatc gcgcctgttt atttgtgagt 660ttttgcattg
agcaggcagc tatcaagtga gtttgaggct actcggattg aagcattgaa 720ttggatatca
acacttttaa acaagcatcg tactgaggtg aagaaactgg tttttgcttg 780ggcatcattc
ttttctagtt agcctttttg tttatcgcgt tatagctaaa ttggtaatgc 840tgcaacaggt
cttgtgcttc ctgaatgaca tatttgacac ccttctaaaa gcactatctg 900attcttctga
tgacgtaagt tctatctccc tgactgttcg tttgattggt tggtgaactt 960tataatataa
aggtttggtt ttgtctagta ataaacttat ttgatatttg aactatctgg 1020acttggaaat
atactttagg tggtgctctt ggttctggag gttcatgctg gtgtagcaaa 1080agatc
108592696DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A8 92gatcatcttt
ttctaggtag ggaattgctt atctcggtaa gctaagaatg ttagaaacaa 60agaactagga
cagaacggga aatggagaag gaggttagaa tcaaagaaca gtaaatggag 120aaggaggtta
atgtgtattt cattctatct acattttaac taattgagtg tatccagtct 180tatccattaa
tgtaattaca agaagaatag taccaagcat gtaggttata gttttcactt 240tactgggtga
aggtttctgt agttcaagtg ggtcaaaagt ggtttgcgga aacatatctc 300taataatttg
attgagaggc tcctcgcact cacatggact taaacttttg tgtattatac 360aaacatgatt
cacatacaca tctcgtgtat attgcaatac atttggtaaa ttatctgaaa 420ataataatga
aggtttcttc aaaagaggtc caggagctat ttccattaac actgttatac 480tgaacagtat
acaaaagaag actgcagtgc gagaatttat ggaggatgat aatgcatttg 540agatattctt
ctgaacactt tcatatcttt tatgtaaaac atttttgatg agaaaatcac 600cagtagtatc
caaacacttt aatccagatg atgggaaaat gctttgttta aacctactac 660gaagtatgct
taatacttca ttattaccag ttgatc
69693925DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A9 93gatctggttt cggtaattgt
tgtttccggg aattgagtat agaaacacaa atacatattt 60aaccctgatg aaagagggtg
taaacttgtg cagatagatg cgaaaacaac gcacgacaaa 120cttgtgaagt tggtgctcga
tgataaagtt agacgaaatg ttgtatctct tattgttttg 180cgacaaattt acatgtcacg
gctgagttat atgcttaagg gaagatgaaa agttcagtca 240atttacatgt caccactgag
ttatacgttc caggaaagac gaaaggttcg atagaattac 300attacggttg agttatatgc
ttaagggaga acgaaacgtt cagtcaattt acatgtcacg 360gctgagttat atgttccagg
gaagacgaaa ggttcggtaa aattacatta cggatgagtt 420atatgtttaa gggaagacat
ctataaattt acatgtcacg gctgagttat atgttcaagg 480gcaaacgaaa gatgagtgta
aattatatgt tacggctgag ttatatgctt caaggaagac 540gaaaggttcg gtaaattaca
tgtcacggct gagttatcat tcagggaaga cgaaaggttg 600tgtaaattat atgttacggc
tgaggtacat cacgttaagg ctgagttata atacagatcg 660gaaaacaaca tttttctggg
gaagacaata tgaaatttat tggccaaaga acaacaatca 720aattaagaaa cgtaagaata
tgtttgaggg atacatagga ggaagacgaa actatatgaa 780tcaaaacatt gatagaagta
gaaatatctc taaatagatc gattgagagg aaaactaaac 840gagagacata taaaatcaaa
gtaaaagagt agttattctt gattcaactc aaacctgtaa 900caaatcatat aaaattctat
agatc 925941753DNAArtificial
Sequencesequence of STAR A10 94gatctgaatg agatgtgttg gcgaacgcat
atagtttttg tttcttgctg ttcataactt 60tgcttatgga attttattta tgtctttctc
tatacctctt tggaccagtg ttccatttgc 120aatagagagt cactcgtgaa aaaaacaaat
aatgtgtgtg tatcaattat tccctctcgg 180ccttatattt tgtcttcttt ttgctaatta
tatactattg atttagatat ttacttatat 240tcatgacgtc ttcttcttat attcttattt
aatttgaagt tagaaaatta acgttacaac 300ttacaactat taaattattg ttaattggtt
ttataataag tatcgctctt gtctccattc 360acttgtcttt tattgtcccc agtaccaaac
taccaaatac aattcatatt cactaattaa 420ttagtttgat gcaaaggatg atgcaatgtt
aagaaaattg aaactctacc acattctaaa 480atgaagcaac tctaccatat ttaatttctt
tagacttgga atagtcacaa tatgaatgct 540taggtagtta cggttagtta ggagtatcac
acagaattga aaataccaaa ccacaatttt 600aatcaggtga ttcggtacta atttttatta
atgaataaaa acataaccga accaactcaa 660agcagatatt aacctgaaaa tgaactcacc
aaaacaataa tagaaagact caaatcgagc 720cggaaaccag attgagcaac gaactcatgg
gaatatcata tctatttatg tccagactat 780taatatacat acctatgaca aaatactatg
catgcaatgc aagactgaag taaccatatt 840tttttgggta aaccattgat aagctaaact
tgaatatcca tagtacttca tcgtactatg 900tatcaatagt atagtaagtt tgacacaatt
acattcagtt tgatttttat catataaacc 960tcccaacaat atttaaaacc gtatctatat
ataaatttat ttgattaaat cagcctagaa 1020gtttatagtt cagtgcagat aaattcaaat
tttgatatat atcttaattg aattaaccgt 1080cttttggtta aattattgtt acaagcttac
aaaatccact atacaccaag ttggacttag 1140atatcatata tgagattaac agccgattac
acttgtacat tgacctgacc tatacaaacg 1200actacaactt tatgtatata tatttctcta
tttttggaaa ctcgtttgat ttgttttcac 1260atgtcgtgaa atttacagct ttgtttccta
ctctcaaaaa tagagcatag agctggctga 1320tcacacttca aattaaaacc aacaacgtat
ataaactata acccatgtga acacaaaaat 1380ttagaccttt tttcaaaacc attccaattt
ctaacaaaaa caaaattaga aatcctaaaa 1440tctgcaaggt gtatggaagg caaaaaaggc
taacaggatt aaaaacagtt tacattagtt 1500attctcttta aaatagaaag aagattttcg
ataaaaacgt cgtcgtatct tcgtcgacgt 1560ctccgtcttt aatgggggag caaagggcaa
gcggtgcttc ctcctccacc gactcatatt 1620caactccttc gccgtctgcg tcaccgtctc
catctccggc tccacgtcaa catgtcacgt 1680tactcgaacc atctcatcaa cacaagaaga
aaagcaaaaa agtcttccga gtttttcgtt 1740cggttttccg atc
1753951908DNAArtificial Sequencesequence
of STAR A11 95gatctcactc aagctcatgc tcacgttcaa ggactttcca accgcaaggt
tatcttcaac 60ttgtactcat taaggcctct caatattcat gtgttatgtt catgtagatg
tccggtccag 120ttcaacaact gtttcattgc tttagttgtc acgagaaata tttgtatata
ttattatggt 180gtgcaaaaca tagtaaaatg ttgttcaatt ggcagatgat gatgatgaaa
atggaaagtg 240aatgggttgg agcaaatgga gaagcagaga aggcaaagac gaagggttta
ggactacatg 300aagagttaag gactgttcct tcgggacctg acccgttgca ccatcatgtg
aacccaccaa 360gacagccaag aaacaacttt cagctccctt gacctaatct cttgttgctt
taaattattt 420catattgtaa attactttct gctttatcgg ttttaccatt tcgggagtct
tttttgtgtg 480caatctgttt cgtttggtaa gcttgtagtt tcatgaaagt gaatgtaaga
tatgcattac 540gtttgttgct gaagtgaatg taagatacgc actattatat ctcatgattt
tctaagaaaa 600ccctcttaaa acgaagatgt ctatagcatt acgtttctat ttccatataa
tacgttaaaa 660tttatggttt ttacgtataa aatgcaaaat aaagacacaa gtatatctcc
aaagcaatgt 720accgttggga aaatttatta gtacgttttc aattgtcaat gcaaataatt
aatggatgtg 780atagtcacaa ttaaacatac aataataaaa atgatgatga tgattcgatg
atgtggtggg 840aaggataaat taaaccgact ttggggcagt gacaggcagt gtcagtgtca
aagacaacca 900tttgtagtca ctatttctat cgaaggttgc aaattgaatg gtggaggagt
atcaaaacga 960cacacatact tgaaaagata ttttaataat ataaaaaaat tggtgatggc
gtaataacaa 1020acctagagct aattattatc cttaatgata ccaaatctat atgatacgat
atttgtttta 1080aaaagagtaa agactgacac ttgagatgtg acactggcga tttcgctcac
gtcaccactt 1140ttcccacctc aaataacgct tacggcttta tccattaatt ctaagtataa
ttttaagtgt 1200attttttctt gccaaattca aatatatctt actaaatgga tgaacattat
aaaattgtta 1260tcaaaaccat taaatgttct tataatttct ttcgttcctc caatgtcatc
ccaagacttt 1320ttgacctaat atatgatata tctaacttgc tttggaatcg tatgacatat
atcttcaaat 1380acatatttcg tatttttttt tcacgaaaac taatttagaa agtagaaaac
cagctatttt 1440aaagaaaata aagtgtgttt atatatattc taaaacaatg ctataagaac
ataagaccaa 1500gatatataca atgttatttt atatttatta ttaagcatta acattgaaat
taaaaatatt 1560aaacatgtat accaaagtaa tcaacattgt agttattact actctctctg
ttcatttttg 1620tttgattgtt tagaaaaaac acacatatta agaaaacata ttaaatattg
attataaatg 1680tattattttt aatgttttac agttttctat aactttaaac caatgataat
taactatttt 1740tttaaaaaat taccattcac ctatactaac caataaagat tacatagaaa
actaaaaaaa 1800ttaatctttt aaaaacaaat tttttttcta aacaatcaaa caaaaaggaa
cagaggggga 1860atattatttt aatttaattt agattaccat tgtagttagt aattgatc
1908961403DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A12
96gatctattgc tgtttatggc aggctgtcat ttcagaaaag aatggtggtt tgggatgtaa
60tgttggtgaa gatggtggtc ttgctccaga tatctcgagg tacatatatt tttcctctct
120gatgctaatc tgcttgcatc tgtagattgt cgaaactgag aaaaccatgt tatggtttga
180tggcttagtg cctaatatgt gtaattgcaa ctgtatgcag cctcaaggaa ggtttggagc
240ttgtaaaaga agctatcaac cgaacagggt acaatgataa gataaagata gccattgata
300ttgccgccac taatttttgt ttaggtaatt ttctgcttcc tggctaactg attttttgcg
360gcttcttgta gtcatggata gtcttggttt ggttctcggc attgtcattc acaattggct
420agtgagacga ataagatgtt aaatcatcaa atgtgtagcc tatcaatatc ttgctcttgc
480aagtttcaac tatgttatac gtttttgtgt attatttctt accttgtgga actgttcttt
540cctgaacagg taccaagtat gatttagata tcaagtctcc aaataaatct gggcaaaatt
600tcaagtcagc ggaagatatg atagatatgt acaaagaaat ttgtaatggt atgtctggct
660cgtctgaaca atattttttg tgtctatctt agtactcttg cagtattgta acgaccagat
720tctctgtttg gtctccttgt gggtttagat tatccaattg tgtctataga agaccctttt
780gacaaggagg actgggaaca caccaagtat ttttcgagtc ttggaatatg tcaggtccaa
840ctcggttccc ctactattaa cggttcacat agattttgtg ttctttcaga tcacactgtc
900ttctgattct tttctcagag tcaaatatct aaagagagag acccttaaat cttcttgtac
960aatcattttc cttgtctaaa ttctcagtgt taaactcttg taggtggtag gtgacgattt
1020gttgatgtca aattcaaaac gagttgagcg tgccatacag gagtcttctt gtaatgctct
1080tcttctcaag gtatttcgtc cgtcctattt tgtttattac tatgtattac ctgtgcacat
1140attgtatgtt tactgcctaa gaacgacaaa gacataatgt gcatacggtg atacaggtga
1200atcagattgg tacagtaaca gaagccattg aagtagtgaa aatggcaagg gatgcccagt
1260ggggtgtggt gacatctcat agatgtggag aaacagagga ctctttcatc tctgacttat
1320ctgtgggtct cgcaacaggt gtgattaaag ctggtgctcc ttgcagagga gaacgtacta
1380tgaagtataa ccaggtctgg atc
1403971140DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A13 97gatccatttc
atatacatat taccaatttt ggcttttata ggtttgtatc cagaaggcct 60tttcgtggct
acgattaagg aaaatacgaa aacaaaagtg aattttacta cttttgtagc 120atggtttatt
ctactttata tacctaagaa atatgagcaa caattacttc tgtaatgact 180ttttactact
tcgtagttgg tacaaactac aaaagattgt gttgttttta catgatactt 240tataatatct
atattaatat atttagtcgt gtttaatcaa aaaagcacca gtggtctagt 300ggtagaatag
taccctgcca cggtacagac ccgggttcga ttcccggctg gtgcattgag 360ctatgatgat
ataggcttca gcattggttg ggtccattgc attcttctga actatcagtt 420gatgtatgcc
acacctctga gctcttcttt ttttttcctc gtcaattaat tttttaaagt 480tttgtctgcc
taaaaacttt cttctttttg attaatcata ttaagcatct cggctataaa 540aaccacggtc
tactaactta acatgcattg gactagtttt agtggagagt gttcgagtta 600aaatgagaag
ctcacgattg cataacggaa catttgattc gctaggcatc tccatttgta 660aaagtagcca
ctccaataca aaatggtcga tgatggtgag tgggtgagac aaacccacca 720ccacctcaag
aagatatatt tctctggtta agaatttgaa tggttgacaa agaaacggtc 780actctatata
cttagaaaat atagtcatac atagacacca tcggtctagt tataataata 840accactggat
taatgcccag tgaaaataat tgagtagcca aaacatgaat ataacaatat 900cccaatttac
atacaacaac acaaaggagg ttttacacga ttctatagta caaactcata 960acaacaaaaa
atcacacttt tgtttaacag ttgcctttat ggctttacta cagtatcttg 1020tccagggttt
tcacacataa caatcacagt aaatcgtttc cttttctttg catcttccat 1080tccttttgta
cacgtaacat ctccggcttc ccgaccatca gctaagaacc agatgcgatc
1140982125DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A14 98gatccagcaa
ctaagtctta tgctcaagtg tttgctcccc accatggatg ggctatacgg 60aaagctgttt
ctcttgggat gtatgctctt cccacaaggg ctcacctact taatatgctc 120aaagaggatg
gtgagttcat caactagtta atatgctcaa agtggatggt gtgtttgata 180aactagtagt
ttaagtagtc agattagttt caaggtcttc acaggattag gtagatatca 240cggcaatatt
tggcctgtat aagtcctggt atcataagag agaactcttt gagattcaca 300ttggttttaa
gttcatttgg cagtaggata ttagattttg aattttccaa tactatctct 360gtttgagatt
tcataaatcg agtttcttct tcattatgtt cgctgacgat attgtttttt 420tcatttattt
atgaatgttg ttacagaggc ggcggctaag atacatatgc aaagctatgt 480caattcatcg
gcaccattaa tcacgtatct tgataatcta ttcctctcca agcaactcgg 540tattgattgg
tgaagagcct gaaaaaaagg cataactatt gttactcttt agacaaaata 600acctatgttc
tcacatcaag ctatgtaatg tcataacaac agcgacgaaa tacattggaa 660taaattgagt
atgtccttaa tctgtcgttt tatctcttct tttaataaac acagtttatc 720tcatagtaag
cagaagaagc tttacacggg ttgtaggaac gtattaaacg gtttgtttca 780atttcactct
ctttggtttt gaaattctag tataaaccaa agtagttggt gcttcaagtt 840gtgttactta
ttcaacaaaa aaatatatta tttttaattt ttaattttcg taggtaagat 900tacatagtaa
caaaatgtta aatttaacaa tgtaagatta ctatgtaaat gcatgggcac 960cagtaatcac
gtatcttgat gatatatatc cctaatccaa gcgagtcggc atttattggt 1020gaagaatctc
aagactcata gtcatcgcta gttaacaatc tttttcggac aaaagcgtct 1080tcgttaaaat
tcggcattat taaccttttt gcccttttaa aatcagaaaa tttctgtttt 1140actggtattt
ttctttgacg attcaatttt ttagttgtat tatatatatg aaagaagctt 1200aactctctct
cacagcttga tatgtcagta tctaaaacaa gcaatacata atttaattaa 1260tttatcataa
aatatttatg attaaaaagt aaagaagata aatattaaaa agctaaatgt 1320ctcttataat
ttaaaaataa aaattaaaaa ggattgaaaa gtaaagaaga taaatataaa 1380gaaactatta
gtatcttata aataaataaa taaactaaaa attgaaatat aattatttta 1440gttttgaatt
aagaaaatat taaatataaa aaaaattaaa cataaagaaa ctatatatat 1500cttgtaatta
aaaaattaaa aaaaaatgaa aaatgagaaa aaaaatataa actcttcatc 1560atataattaa
tgaaatttaa aaacttattg cttttaattt tttgtacaat aattaaggaa 1620atttagaaat
taattattaa ttttagaaga aaaatgttaa aatagtttaa tagttttgat 1680tcactaaata
catgtgtaca tatatgatgg tatgaggatc aagaaagtgc cgtaaaatgt 1740aaaacttcca
atgttcctta gtgaaaaatg ttaacttttc tgttgacaag acgtgtatat 1800aaacatcacc
tataccggag aagaagaaga cacaaaacaa agttaaaaag aagaaatttt 1860tggtgcagtg
aattcgaaga gcaatatgaa gaatattggt tacattatta tagccacctt 1920gcttgttggt
ctcctcctca tcatggctct agtggcgagt ttctattggg ccaaacgaca 1980tgtcaaatgt
tgtggcggag agggactgtc gtcaaaggat gtgttcaatt tacttataca 2040attggttgct
tttattctgc tttgtggttt atttgcttat ttggtatttt tggtttagat 2100tagtaaccta
aagccatagc agatc
2125991196DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A15 99gatcagcaat
tacagttgga tggaaaaaga gagacgagaa tgtatctgct gctggtgact 60ttaaggtagg
ctgagtacca aattgcattc tgactgttct tacctcgacc acctttctta 120ctttccctag
ctctaatctt gctattacta gattgaatct ggtggactcg gagcatcagc 180tcgttatact
cgtaaacttt catccaaatc tcatggtcgc attgtgggta gaatcggaag 240gtatgtttta
ttgacaatcc cgagcaacct aatgtatgat gtgcgagagg atagaaatca 300ttttttaagt
tgtctttaca tgtgtggcgc aatcattgtt ctcattttac tttggaattt 360tttttttaac
ttattcagca atgctcttga gattgagctc ggtggtggaa ggcaaatttc 420tgagttcagt
acagtaagaa tgatgtatac agtaggactc aaggtaaact actctttaaa 480actttcggag
ccatcttagc cattatgcaa tctgcttatt tccggtactc ttatactttg 540tttgtagggt
attttctgga aagtagagct acaccgtggt agccaaaagc tgattgttcc 600cgtgagtgtt
actttcttcc tttcttttct tgtggtgtca tgtctgctgt cttcggataa 660gaaccgaaca
gattgtgtct taatctgtgg agtagaatat attaaaaaag cataaaccaa 720tagaaccaaa
gaccaatcct aaaagcctag ggatggattc tagagcatta tccttgactc 780tctgaaacct
ttacccaact caattatgga caaagacaaa catccgtatt actctgggga 840agtctttcac
ttttgacacc ttcatgatga ttatctttga aacgtgcaga ttctactctc 900cgcacattta
gctccagtat ttgcaactgg agcattcatt gttccaacat ctctttactt 960tttgttaaag
gtgagtgatt ggaccctcta aatataatct acttttggtc tattgttata 1020agctgtttac
cttattaaac attttcactg ttccacgcag aaatttgtgg tgaagccata 1080tttgcttaaa
agagaaaaac aaaaggcctt ggagaatatg gagaaaactt ggggccaggt 1140gattgttact
tccgagtttg gtagccaagc gagattcctt gtaattgtag atgatc
1196100692DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A16 100gatcgctttc
agtctatcat gttttgagcc ttattttggg agcgatgtat taatattttg 60cctgttcttt
attttttgtg ttgcagacat acaatgaagt gcagcggtgt tttctgactg 120ttggcttggt
ttaccctgag gatttgttta catttcttct taacgtaagg acatcttttg 180ttttatgatt
atggctctag ttattctttg tatatgtaac gcaaaacggt ggcaatacct 240agcactcata
ttagactcaa gaactattcc ttgccacaca tctgtgtgat atttatatgg 300gctttttatc
ttacatattt gaaatccctg tcttccttgt atactttcac cagaaatgca 360agttgaaaga
agaccctttg acgtttggtg ctctttgcat cttgaaacat ctgcttccga 420ggtgtattct
tttatccttc atcagtataa cttatcattc agagttaatt taccatccta 480acttaatgat
gttgcattgt gttcgaaggt tgtttgaagc atggcactca aaacggcctc 540ttttggtgga
tactgcaagt tctttgttag atgagcaaag tttagctgtt cgaaaagccc 600tttcagaggt
actgagctgg cgtagatttt cttatttact actaaaatat gcatgcttta 660gcatagtgct
tctactttaa tgacagttga tc
6921011826DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A17 101gatcacgata
attttcctta attatctaat tctaagatag tctaaccatg aatattctta 60taatatctta
actgtatagg agattctatt ttcatcccta aattatattc gtaattttat 120tcggatatac
ttgcttttat tttcgtcaac agatatatat atatatatat atatatatta 180tttattttta
attttcatta aaattagtga tttaattctc tattatttgt gtactatata 240aaacaaacaa
atgaatctta taatgtttgc tttttcgtcc ataaatattt ccgggaaaaa 300tcgttagata
taaatcgaac ctagtggtga gtgactcaca cacatgtgac aattcccaaa 360ataagtcccc
cacgtacgct atgtctgttt tagtgtgcat gtagtaacta ttatttactg 420atttagaata
taactagcat ttggccccta tttagggata acattgtttt agattatatc 480tgttacaact
tttaactaaa aattttaaaa taaagcagac agtattaata tacaacaaat 540ttattatcat
tgatcgaaga atatacaaag attaagaaaa agatataaag aaggtacaac 600ttttctaccc
aatgaatcaa ttgcgatagg caataactaa caaatcaaga gtttagaaat 660ataagagagt
ataagtacga aaattatgct gggtatatac atgtccgctt atttcatcat 720tagctccaac
caattgtaat gtgttcttct tctcatcatc agtaattcag tttacaaaca 780ttcgttgaca
cccaaagctt ggaagtctaa aaaaaaatgt aaaatgtgca caaataagta 840actacatgac
gcagacgctg cctttgaaac aatatcaaag atattgcaga tataaagaag 900taaaataaga
gatgacttta aaattgaagt atttgtatta atacaaaaat cttgcgtgaa 960aatacaattg
cagtttaata caaaaaagaa attgcagata taaagaagta aaataagaga 1020tgaaagaaga
atagtaaaaa gtatgagaat taatttacca tcaaaaaaac acttgagctt 1080cgattaagat
attaaactca cccttgtttt aaggcaactg ttcagatgag aagccaaaat 1140ttgtcgttgt
tccttgagtg tttgtgagac gggagaatca taggcattga ttgtattaaa 1200gaataatcct
atggaaaaat ggagatgtat gagagaaatc gaattcagtc aaataaagca 1260gaaacaaagc
aaaaaaaaaa aaaaaccata gaaatctaga agaaggatat atgattttcg 1320gatctatgga
aaatttctat atatataaaa caaaattaca aacagaaata gaagatggta 1380aattggttca
ttgagatgaa caaagtacct gatttctgag taatcgatta atgatgttga 1440gaaacccatt
tttgagattt tacacagtag tcatggagtt tttggaagag agaaagtgga 1500gatgtggaga
tcgtggggat gaaagagaaa atcatttgag aaagaaacaa agttaaataa 1560aaacgacaca
tactatgcgt aaaaatgaaa aaataaaaaa tagtactaag ctgatgtgtc 1620aatcactgaa
tgcattagtt attggaaaag tgactgctga tttagtatat ttagattaga 1680gaaaataaat
acttgtaatc atttttctta ttagcaatgt tgaagtgaaa aaaaaaagaa 1740gaaaaaagtg
tatatttatc atactcatag tgggaaattg ataattcaaa attgctgata 1800aacgttatga
aagaaggtgg aggatc
18261021590DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A18 102gatctgttga
ttggttaaat cgacgatctc aacggcggag gaagtgacga tgaaggcgcg 60gcagagagga
caattagagt gagatttcaa ccaagtatca atacaaggaa cgtgaaacgc 120gtggttgcat
ttaggtaaca atctcaagct ctcgttctct tgaaactcgc ttaaacaaac 180agagcaatct
gaagattcaa caaatccatc catctttctg tatttgtaaa cagttatcga 240tttaatcaga
gattcatcga gtccatcgcc accaccacca ccaatcgttt gattcggatt 300cgtagctccg
ttgttgttgt tgttgttggt tccttgccag gtgtaatctg atgagattct 360gtttatagct
gcggcggagg tagaggagga gttgtggcga cggcggtggc agtatttgga 420gatgagagtg
tagtagctga cgaggatgaa ggcgctagcg aggattccga tgagagcgat 480gaggagagga
gagaaatcag aggaggaaga gtcgtcttcg tcgtcgagat agaaggaagg 540aggaggaggg
aagatgacgt aacaccattg agggcaatag acactgcata ctccttgaga 600acagtctctg
tatgaatcgt atgttgtacc ccatggatta gggtttcctg ttgaacccat 660tatttgattg
ttggagaaag atagagagag agagcaagga agaagatgga ggtgtcaagt 720gtctctctcc
tttttctttg ggctctgctt ttgtctggta agtgtctatt tttttatttc 780gagttaattg
gtattattag aggagataat gaataaatat atatgttcat gaaagctttt 840gcatgatggt
gttaatacta attgaatgat gtttatagtg aatgttctac tttatcaaat 900ttttatttct
agtatgaata aaggtgtaga atttgcttta ttcattttta ttctttagct 960ttctctttat
gcttccattt tttttaaaga taaattaata cattagtaaa ataaatggag 1020ttcatttttt
ttttttttga ttttattttg agaaatgaga acgtaacata agaagtgttt 1080tagtgttgac
gaaataaaaa gagagagagg gtttagtcta tttcaaggca taaaaaaatg 1140gttggtgaag
tgttgacgaa ggtggaatac tataacatgg gccacgtgga tgacaaattt 1200actcctcgac
gtatctatta aagttgtggt cagaaataca gtacaattta ccgactacct 1260acatggaaga
agaatatttt catttcattt caactacagt agtataacat tcacgttata 1320cgatttttca
tttttgtttt gtaatcaaag taatgatttt ccaaaaaaat cattgctatg 1380attcgaatac
atacagtttt atattagttt acatatttat gacaactata atacaaaatt 1440ttaatagttg
ttcaagggac gattgatgtg aactcgccaa ccatatgccc tacgtacaaa 1500ataacatatt
tacatgtaga agttgaaaat aataataata aagtgtgatt aaaaacaatt 1560atacaaatgc
taacaatagg ctacgagatc
1590103706DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A19 103gatcttgatg
tgtgttttgt gtttttgtta ttgcaggatg tatgtttcat agtgagacag 60ggcttaagag
ctttgaccat ccgactaata tgatgaaggc aatgccgagg attgatagtg 120aaggtgttct
ttgtggagct agtttcaaag ttgatgcttg ttctaagatc aatagtatcc 180ctagaagagg
aagtgaagct aactgggcgc tggctaattc tcgttgattt tgcttctagt 240ttcgttaact
cttgcttctt tgttgcgttt tctttttatg tactcttgtt tatgtaaata 300tagccttatg
aagacgataa agaaataaaa ttgatttgct tcttcgtgac atagcagtct 360ttacttagac
aactgtgtga taaattcgca atctcactct ttgatagata agagggaggg 420aagaaagcag
tggtaaagac aaaactgtgt tgattttgtg aatttagaag tttacaatag 480caaaaaagaa
actttggtcg acttttatca ttcatcgttc cacatgtctg taaattcatc 540aggctccaat
gggtttgaga gttcatgcat ctttcttctt gtttttgcct ttattttctt 600agcaaatttc
ccagctttat ttcttttctc caaagctcga atctaaaagg caggaaattg 660gaatatatga
gaactctgac agataatcat atatagcaat gtgatc
7061042064DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A20 104atcgtttcaa
agcatggtct aatgatgatc ctgatctccg actgatccaa taacggttaa 60gcaacgctgt
ttttgatcct ccattgttgt ttgccatcga tcaacactca gaaataaggt 120aattaacgca
tctcgagact cattgtttta acaatctttg ttttgtttct tccaaattat 180tctcgtgaat
atccgtaatc tctccgtctt ttaatgaaca acacatatca tatgcttttg 240tttgttttgt
tttgtttttt caacatttca ataattttgt ctttttttct tcgatttaat 300ttgtttattt
cctgctataa taaacgaaaa ctataattcc atgtaatgtt cgttgttgtt 360catagtgatt
tatcataacg agcaacaaca taaaaatcaa gagaataaga aattagagtt 420atgctgctta
tttgaattag acaaaaccta cttttacttg ttaaggaaat gaaaagatgt 480taataaagat
gagcacatcg tacgtggcgc acgtggaagc acttctgtac gacggaccca 540gtccaactcg
aaccccacac acatagcaaa ggttgttaag ttggctcgta ggtgaattta 600atacctgtta
tttcctttat agctggctaa ttacctaaat tcgatccata ataacacatt 660cctactatgc
caacatttaa ccctagtcaa actaattaaa acgtttctta ctttttggcc 720tattaaaacg
tttcattatg ttccgcaaat agtatgaaat atataaagat tttctaacaa 780aaaattacta
agaacagtta gactgattga gattgttttt atttcctttt atttaatttt 840cttttattat
actctgttta tttgtgttta ataattagga ttctatttgt cttgtcttgt 900ttgctatagt
tggagttttg ttcataaaga atggcgttta atacggctat ggcgtctaca 960tctccagcgg
cggcaaatga cgttttaaga gaacatattg gcctccgtag atcgttgtcc 1020ggtcaagatc
tcgtcttaaa aggcggtggt atacggagat cgagttccga caatcacttg 1080tgttgtcgct
ccggtaataa taataatcgc attcttgctg tgtctgttcg tccggggatg 1140aaaacgagtc
gatctgtggg agtgttctcg tttcagatat cgagttctat aatcccaagt 1200ccgataaaaa
cgttgctatt tgaaacggac acgtctcaag acgagcaaga gagcgatgag 1260attgagattg
agacagagcc aaatctagat ggagccaaga aggcaaattg ggtcgagagg 1320ctgcttgaga
taaggagaca gtggaagaga gagcaaaaaa cagagagtgg aaacagtgac 1380gttgcagagg
aaagtgttga cgttacgtgt ggttgtgaag aagaagaagg ttgcattgcg 1440aattacggat
ctgtaaatgg tgattgggga cgagaatcgt tctctagatt gcttgtgaag 1500gtttcttggt
ctgaggctaa aaagctttct cagttagctt atttgtgtaa cttggcttac 1560acgatacctg
agatcaaggg tgaggatttg agaagaaact atgggttaaa gtttgtgaca 1620tcttcattgg
aaaagaaagc taaagcagcg atacttagag agaaactaga gcaagatcca 1680acacatgtcc
ctgttattac atccccggat ttagaatccg agaagcagtc tcaacgatca 1740gcttcatctt
ctgcttctgc ttacaagatt gctgcttcag ctgcgtctta cattcactct 1800tgcaaagagt
atgatctttc agaaccaatt tataaatcag ctgctgctgc tcaggctgca 1860gcgtctacca
tgaccgcggt ggttgctgcg ggtgaggagg agaagctaga agcggcaagg 1920gagttacagt
cgctacaatc atctccttgt gagtggtttg tttgtgatga tccaaacaca 1980tacactaggt
gctttgtgat tcaggtaata tgtgttcaaa gttactactt tcaagcaaat 2040cctctgtttc
ctcacatcat gatc
20641051834DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A21 105gatcttcttc
tatatatacc ggtataagtc aactggcggc tgaacaaagg tcgtgaggta 60acaaaatatg
agacaaatct acaggtcaga ttgggttctg aattctgata aggtcttaaa 120aaggagctca
ccaacccaca aaaccatgga ttgaacaagt acaggtcatt gccttcattt 180tattctttac
ttttctaagg ctcaagcttc ctttattgcc tttaataaca atatactaat 240gagtattttg
cactcagtaa caaaattcag gagagtaatt ttttgcccta acatgttact 300tttatgtgtt
aagagtttag aattttggat ctatgatttt agtttttgtt agggaatcat 360attcatataa
ataaaatatt gccattgact taattgttgt tattcaccta atttctctcc 420aaatttggtc
atttacctca gttgattcta tattatactt gctaagtgtt ctttgtctaa 480ttctctatca
ttgtttgatt taataataac caaaccttaa gacttggaag caaagaagag 540agaaaatccc
aattaatttt taataattca aagagagata ttgagtgact tccactaata 600caaagaaagc
ttggtttgtg caatattttg cggttaagct attaattgct gaggcaacac 660cttttcacac
tttgctttcc ttcttccaag ttttcaactt ttctttctta ctctttctat 720taatcaaact
gcaacacaaa aatcatttgg ataatacatg tttagaagat gattaagctt 780tagttttatt
tcaagattat cataattgtt atctgttgtt acctacattc atataatctt 840atcaaaaacg
ataaagacaa aaaggggata caatataggt ttttattata aagaaacagg 900aaagaaagaa
aagggttttc accaaacgaa attagttcaa tcatttaaat tatctttatc 960cttatgatta
gtgtctttat atctgtcata tgctgcttct ccttccaact tcctttggat 1020tatattctct
tctctttatt ttaatttcca tttgtggtag ctgttttatt ttttgtattt 1080tcacgccgtg
tccctttaaa ataatattaa ctacaccact aatgttggaa catgaaaaac 1140atgaatgagg
taattatgat gatgaaccaa atgttaagga caagctcggt gtaactaaga 1200agataattag
tgaaacagaa caagtcaata acttgtaagc atttcagaat tgaaaataaa 1260gataagggag
gatgaatatg aatttagtaa atgggtaatg aaagtgaaag aagaagaggg 1320aagggttggt
tactgtctca agggtttgaa atggagacgg ttgcttgaga atgaggaaaa 1380agagttagta
agtttttaac tctctctttc tctctccctc tctctttttc aacgtcaatt 1440cctttaagga
atggcctctc tctctctctg aaagtgtgtg tgtatatatt aaacgactcc 1500atttctcctc
tgcttagacc aaaactcatc ttctatactg caacaaagaa ggaggagccg 1560ttgagactac
aaaatgactg cagcagaaaa cccttttgta tctgacacct cttctctgca 1620aagccagctt
aaaggttctt atttttcttt ctgtttattg ttcatcaacc cttatgagta 1680atttgcttga
tgttgaggtt gttctgcttt cttttaattc cactctgcag aaaaagagaa 1740agagcttttg
gctgctaaag ctgaagttga ggctttgaga acaaatgaag agctcaaaga 1800cagagtcttt
aaggaggtaa catgcatgat gatc
1834106751DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A22 106gatccattaa
gaagcagccg caaaatcgga ttgagaacag gaaaagaggc ggttaaggct 60tatgatgaag
tcgttgatgg gatggttgaa aaccattgtg cccttagcta ttgttcaact 120aaggagcact
cggagactcg tggtttgcgt gggagtgaag aaacttggtt cgatttaaga 180aagagacgaa
ggagtaatga agattctatg tgtcaagaag ttgaaatgca gaagacggtt 240actggagaag
agacagtatg tgatgtgttt ggtttgtttg agtttgagga tttgggaagt 300gattatttgg
agacgttatt atcttctttt tgacagaaat acattgaaaa ctaccgttgc 360taatttgata
ggtatacata tatagacatg tatatattgt ataattatat gtcaagatta 420tttatttatt
ttacattttt cacaaaaaaa aacgttaatc tatttttctg tcacaagtgt 480gtttttattc
atactacata ctacaacgcc aatttaacat gccaaatata aaacatacat 540gggcaaaggc
ccaacagcca gtttaaagaa ctttgtctga agagaaagtt gttgtatata 600tcacaaggga
tatgtggtaa ttgggaaaca tgttgggttg acacgtggga aattgaagga 660gatggagttt
ccgtcactgg tagaatcttc taacactaga gagcttcaat tcaggttgaa 720atcgtcagaa
aactaatgca gacggtagat c
751107653DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A23 107gatcaaaact
tagtcaaatc gttccttcca ttttctttca gtttgattcc actttaatgg 60cgtcataatc
atctcttaaa tcaaacaatg actccactat ctcgtttccg atctcttgtt 120acataaagtt
ttctgtagca ttgagattgt ccttttcgga attgctttta tttgcgcagc 180ttgatggaaa
caacaaacag tgtagtagtt tagtagaaag actgagagat aaaacgaaga 240gtcaagttcc
taagtccatt acttgcatta accgcttaga gatatcgcgt atagcaccat 300tacacgcaac
gatgaatagc ccgaaaggat ttggacctcc tcctaagaaa accaagaagt 360cgaaaaagcc
aaaacccgga aaccaaagtg atgaagacga cgacgatgaa gacgaagatg 420atgatgatga
agaagatgaa cgtgagagag gtgtaattcc agagatagtg accaacagaa 480tgataagcag
aatgggattt acagtggggt taccactctt cattggtctt ttgttcttcc 540cattctttta
ctatctcaaa gtgggattga aagttgatgt gcctacatgg gttccgttta 600ttgtttcgtt
cgtcttcttt ggtacggctt tagctggtgt gagctatggg atc
653108548DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A24 108gatcagactg
aactcgtgta ctctgagcct tgcttcttgt agctctttta gctttcacat 60tttcatcagt
attcacatca ttcctgataa ttgtgccaga agtcccacga ctatcttgtt 120gctcactaat
ggttgctgct gcagatgatt ccatgttgtc ctcttgtgaa accccaatgc 180ttcgtctagc
aactgtattt cttgcacttc ctgctttgcg gtttttacat ttggatgatg 240caactttaac
tttaggtagc ttcttttgag taagatcaat ctcatctcta cctaggacct 300gcaaatcgat
gaaatttgag ttcatttcaa cacacttgat gacactatca tagaaaacaa 360aaagaccttg
ctgtaccaga gtgaagaaca gcctttacct tggccttcac aggactaggt 420agaatctccg
gagaacaagg cctctgagtc cattcaaaca tttcgctatc aaacatgtca 480cctggattgg
gcttttgttg ctcgtcttcc tgaaacattc atcggaaaaa aagtaagatc 540aaaggatc
5481091000DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A25 109gatccaaact
ctgcaatgta tattacgaag tcgtttgata taacacctct cttgataaaa 60gatgattaga
acctaaagta attttaaaat atggtgaaaa attagactct tggagtatat 120aaatggctca
atctgtattg cccgcaccgc ccaaactccc atggcaaatc cattgacgaa 180accaaggtaa
aaatcacatg ctttgagcgt ttttttaaaa cagaagtgta agcttaaatt 240ttttagttta
atagtagtaa caaattcaac cttgtgaaga gatttattaa taatattaaa 300atcattcccc
taattatttg ccttgagttt cgagccttct actgtaccac tcacacatta 360aaaatcatca
gactattcaa actttcttac atggttgatt agttcatctc atatatgctc 420agtatcatac
tcttgcagat taatttttca ttttaattat caacgaattt tttatttaat 480tattcatgac
caaaatacat ttattttttt taaataaaac aaataataaa tttggaagtc 540aaaaatacaa
tcaatagaaa aaaaagtatg acagtgatag ataatatttg cagaatatta 600tgtgaaagct
attttctctg taacaataaa tgagaaaatc tttattattt tacatgaaag 660aaaaagaaaa
caaaacagag atatttttcc agctgaaaag aacaaacatc tctcattgat 720gttcagtgaa
cttgcaccaa acttcacttc ttctatactt cttcatagcc acaaactcag 780ttctttgcaa
gaaacacaaa cttaagtatt caaaatatcg tcatcatgtt ctcaagattc 840catgctctgt
ttcttctcct tgttctttca gtaagaacat ataaatgtgt atcttcatct 900tcttcttctt
cttcttcttt ctcattctct tcattttctt cttcgtcttc ttctcaaact 960cttgtcttgc
ctctaaagac ccgaataacc ccaacggatc
10001101926DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A26 110gatcctcgat
tcttatctgg atacagaaga aaacaccttt ttgtctttta agtactcgga 60gaaatctgag
ggtatctttt tcttgagcag atggaggtga agtcctgagt tggggaggag 120ggggctctgg
aagacttggc cacggtcacc agtccagtct ttttggcatc ttaagaagta 180acaggtttgt
tttacttaat ttcaatatcg ttttgtctct ttctcatgca ttttttgctc 240acaagaattt
tcccatttcc tcctttactt tatcatgatt ccttcataat tttcttgtat 300tgcactgtaa
agtatccccc tgattgcagt gagtttactc caaggcttat caaggaactt 360gaggggatca
aggtaatcta gtggtgaaga atatccacct tggatgaaga gtttctagtt 420acctagtggt
ggttttaatc tttagacttt catgcttatg tttttccatt ctttctgtcg 480agcactaggt
cacaaatgtt gctgctggtc tgctgcattc agcatgcact gatggtattg 540atttactttc
ttaaaagtat gaatgttgtg ccatttaccg aactttatga ggtttgtttg 600caaatgcaga
gaatggctct gctttcatgt tcggagagaa atctataaac aagatggtaa 660gaaaatgtct
ttttctttga tttctgtggt catatatgtg aagctatctg atgggaaaat 720acagggcttt
ggaggagtaa gaaatgccac aacaccatcg attatcagtg aagtaccata 780tgcagaagaa
gttgcatgtg gtggctacca cacatgtgta gttacaagta atactctctt 840attatatcgt
tctttctttg atattgagtt tgcttgtata ctgcaaatgc ctgtcctgct 900caaatttctt
tttgttattc tttatagagg cccaaaactg ctctttagtt tctgctaaat 960ttatgaacat
attgtgtttg taagatggtc gataacaact catcgtttga tgtttccttc 1020gtttttggaa
ggaggtgggg agctttacac ctggggctca aacgaaaatg ggtgccttgg 1080aacagagtaa
gttacatacc ccgaaaaaat agaatgtttc cccataagat gaaaacaagg 1140ttcttgaact
gtacctatac tcttatttca aaaaattcag ttcaacgtat gtctcacact 1200cccctgtgag
agttgaaggt cctttcttgg agtctactgt atctcaggta tcttgtgggt 1260ggaagcacac
tgcagctatt tcaggtagca tctcttttga gtaaaacata tttgtttcct 1320ctctcattgt
ataagttaat tcaactcaat ttctgaaact tgtttgcaga taacaatgtc 1380ttcacctggg
gctggggagg atctcacggc acattctctg ttgatggaca ttcctctggt 1440ggacaattgg
tttgtttcat catcttatct tattgatcaa atctctgaaa caacattttc 1500aagtgtcgaa
gagaataaat atggtatgct taatatgtag ggccatggta gtgatgtaga 1560ctatgcaaga
ccagcaatgg tggacttggg aaagaatgta agagcagtgc atatatcttg 1620tggcttcaat
catacagcag cagttcttga acatttttga agactcggtc tcaagttaat 1680atcatataca
gatgtttagt ttattcttgc ttaaacatct atagactaaa aaaataataa 1740gaaatttaca
ctattgaata gcgatcaatt acaccattgg ttctaacttg aacaatttag 1800taaataggtg
gaatattctt gtcgtgtaaa ttattgattt tatttattta tttttgaaaa 1860ctacaacaaa
cgatagaaga gttgaggaaa tctctttgta atcataatta tgagaaaatt 1920aagatc
19261111109DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A27 111gatcggaatc
attttgggag tttgaaggaa ctaaacataa tatgcatgtc gaagtcaact 60tattgcaaat
aattttgaaa tgattctgaa ttggaaattc atgaagctta attattttat 120ctaaataagt
ttaatatagg tttgagtgag atatcgagat taaatgataa gagtctttct 180tcgaggagac
attagaattc tacacaaaaa tcgaaattaa tctagtcctt gacaatcagt 240tttcaattaa
tcaaaaacct ataaaattca actcaaaacc aatcgtatga aacttcatta 300taccatataa
tctggttact tagcttaaat ctctacccgg cgatgtttca tgcttgagag 360actaggtaca
taggacacta ggagtactgc atatatggtt acctcatgag ttctcatcgt 420aaaatcatcc
aataaaaaat ggtttcctgc ttaggtatac ggtataccat cttgtatcgt 480taaaatttat
agctcagttc gttgctaaca gtcaaatacg tctttccagg gtaaaaaatg 540tggaaatttg
ttccactgta aaaacctaat aatttttgac attaataatt aaaagggatt 600ataatgtaat
atatacaaag ataggggaga cagagacgaa ggcccacaca tctttaacaa 660aagaacaaca
agcccgtgac cccaaaataa aactagcttt cagatttatt atttttcatc 720tgacataatt
gcaaccgtta gatttcattt ctcaggtccc attctgactc agatccaacc 780gtccatattc
ctctagtgtc ttcaatagtt gggccccttt tctttttcct ctcgccgtac 840actctccttc
cagcgccaac gccaccgccc gagccacttc ttccgccggc gccaccgcga 900tttcctcgcc
ggaatcccct ccttcgccgc ctttcccgta gaccacggaa aggatgctta 960tggcgtattc
tctccctcta ccagccaatc tcgccatcac cgctaccatc gccggcaccg 1020tcatcgcgtg
agcgcgaacc tccgccgctc cttctgccgt tgtacacatt agctcaagag 1080cagctaaggc
tcgctccacc gctgagatc
11091121659DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A28 112gatcgaactt
tggtaacatg cttgcttact gctttctatt gtctgcaaaa cctctgttct 60gggtgacctt
ctggcccctc tctctcgaag cttcagaact atggaggaga gattggataa 120aggagacaaa
aggtgtggtg tggcgaaatg ttagggtacc ggcaattgtg tatgtatgag 180ttgattttgt
tcttttctca taaagaggat ttaacaaagg atgagaaaac aaatccaact 240tgagtactac
gaggagataa aagcttttat tgggtattga gtattgacac gttgttgaaa 300gtctgataca
ttttagactt ttactgcata tgtccaaata tttagatttt tttttcgttt 360ctcaaaaaag
taacttgttt aacaaaaaaa aatcgttatt gggcttttcg tttcttttat 420attgggcctt
gagccttttt agcttttgta tttttagtcc ttttcgggtt tatttattta 480ttaataagat
accaaaaaca taacaaaaat gtagttttgt atttttaacc tagtctttta 540aatatttaaa
cttaattaga aaaattctat ttaaaatatt ataaaaaaaa catgattttg 600tgattttccc
atattttgtg taactatttt tgacaagctt ttgaaacaac aaagacaaaa 660tccatgtgat
aaggtcggtc aaaaatcttg cgtagtagag gagttaaaga tttttggatg 720gttacaatgg
tatactctta tttgatatcc catcaatggt atatagcttt gaatggtagg 780acaagtgaga
gtaaaatttt ctcatcattg ctaagtttta ttttaggttc tacattgttt 840cacccttctt
aagtatccta ctctcaacta gaaaaaaaaa ttgtgagggc ggttttatcg 900gctggaatgc
agctcatgta gctcccacga cggagttttc tggctaagaa actcggacac 960aacgttggcc
tccaatatct tcaaggcttc ttcattcgtc accgacctcg gtgtcttata 1020ctgactcaca
gaagagcctc tagacagaaa gaagttcatg agcttgtcga aagcgccagg 1080cttaacaacc
ttaatctcaa gtggtccaat gttcttatca ttctttcgtc cttttctgta 1140aaccgcgtcc
agagactcct caatggtgaa gcagcattcc tccaaaacat tctggtcaag 1200ctcaagcttg
gcgtccttga cttttctccc gagttcccag tagagcacgt agtgacctgg 1260atacgaggag
gaatccacac ggctagtgaa atccatgagc attaggtcat gtggctcaag 1320caggagactc
gcgttagtca ctgccttgag gaggtcttcg tcgtaggtct tgtccatgtc 1380gatgctcaga
acaactttct gtcttcccac gaaatgaaac tgtggcgcat tgttgtagaa 1440accagtcact
cttaaaacgt cccctaaacg gtacctatac aaacctgtat aaagaatttt 1500gatacacatt
aagaaaatta ttaacatgtc atttagtttt gaaattgaga gagtaaacaa 1560gaaaaaacac
ttaccagcaa acgttgtgac aacaggttca taatcatgac cgattttaac 1620atcgacaaga
tcgactacaa caggattctc tgcgggatc
1659113874DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A29 113gatcagagtc
acaaccatag gagtcggaga cggccatgca tgtgtcttga tagaagaatt 60aaccggttct
aaatctgaaa acgaatccgg tcgtctcgaa ccgaaatcaa taaccggtcc 120ggtcaaagaa
acggttgcac gagtgaagga aacggttacg aaaacggagc cgttaatatg 180cgatgacgga
gtgacaaagg ggaagctgac gatgtgctac gaggtagacg ttgacgttga 240cggtgggagg
tgtgttaacg gagatttaac ggcagttagc tacggaggag gtttgggtaa 300ttgtggcggg
gattggtggg agaaatggga tggagtggtg aggatgagaa atggtgatga 360cagttggtac
cgttacgtgg atttaacggt gattaatgga aatgtggtaa ggttatggga 420tgacaacaaa
acactagtaa cggcggcatg tgtctaaatt agagaagttt catatttcgg 480aaagttttta
aatcttgaga agctttcttg gtttgaagtg tttttttttt gttggttgat 540taagttgtaa
tttgtaaata attttcacac aagagaccaa gaaggaacgc ttaaatcaat 600atcaattggt
gttgattccc agctttttct agtcgaactt aggtaacacg tccattgcga 660tgatgaattc
gtgacaaggg gtcaactatt tgaacacaac aaacaagtgc gttttcttgt 720taaggcccat
ctaaaattga ctacacacat ttacttttag gcccatttta aacttgactg 780tagcctgtag
gcatgtattt gttcgtgtta ctcccagcct caaacccgca aaatccacga 840attcttctta
cttagtctag actctggtct gatc
8741142138DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A30 114gatctggcta
atccgtttag cacacaacca gatgtaacat tggttgcaaa gattattgaa 60gagtctcgat
ctaatgtaac acacctctgc gcattcagga gtgcttacgt caacacattc 120cgggaacgaa
aaactgttag cgtatgtgta ttttaaagta ttaccatatt tctttatatc 180ttctagcacc
tcctcacaaa tgtcacgtgc gtcctccgat tccaaagcat aatggttgct 240tccgaagagc
cgaaggtaga caccacccat gtgagcatta ccagcacata tgtaaagaat 300tgcgcatgca
agggttgcag cggcgttcct tggggcgatt cgctctaagt gtaggatagc 360tccctggatg
tcagactcat gtgtaacgag acgcagtcct tcatggtaaa tagccgtggg 420gttaccagct
tgtaagcacc gtttgaagaa gggtctatag cgaccttcgg agttgatgtc 480atttggatcg
tggcctgccg cgtagaagtc atcgggatcg tcgcacatgc tgaaaatgtt 540tgcatttttg
aggacatccg gacagtagac aatgtctctt ccacgaggac cggatttcaa 600cataggtccg
aggtaccacc aacatttgtc agccattttc ttggctatct tcgcaagcaa 660atcgtcagga
atatttgggt ttgtcatatt taggagtaag gtgtttcgag aaaatgaaat 720ttgaacactt
aaataagcat cattgaagat atggttgggt aagttatggt tgtatttatt 780gcaaaggtat
taagtgatga tgtgtattca tattgtcaaa tcaaagtaat agtattccat 840atataatttg
ttatcgttgt tatgagcaac ctctttttat taacagctta aaactagacg 900tgtacgtttt
actgacggtc ttagtgtacg tccacattta catttctaca tttactcaac 960aaacagtgta
cgttgtagtg tatgttttag tgaacgtcca catttacatt tctacatttg 1020cccaacaaac
agtgtacgtt gtagtgtacg tccacattta catttctaca tttgcccaac 1080aaacagtgta
cgttgtagtg tacgtttaag tgtacgtcca catttacatt tctacatttg 1140cccaacaaac
agtgtacgtt gtagtgtacg ttttagtgta cgtccatatt tacatttcta 1200catttactca
acagacagtg tacgctgtag tgtactatta gtgtacgtcc attcataaat 1260atcaccattt
atgagacaaa ccaaagacct catacgtttg catgtgttat tttttagtgt 1320acgttagagt
tgatatctca tgctagtgaa cgtccatatc tagttttccg agacaaagaa 1380aaaacctcta
agtattattt ggtagatgca cgtgtacgga gttgtggacg cttagatttt 1440aatatccaaa
tttacattta ctgcagtgtc taaatatcat atgtgaattt ggctgaaaaa 1500tattcaactt
gagaaacata acacaccttg caaatttctt aagcaataat ataatttcaa 1560cataaacata
aacaacatag tagaaggctt atcataattt gaaacatgac atagcggata 1620acataaacaa
acatataaag tagaatggaa taactatagc atttgactaa cacgcctggc 1680acacgaccag
aggtaacagc ggttgcaaac gttttggaaa gctcctgata ccatgtaaca 1740atataaggcg
caaggaggca tactaattcc atggctggta ggataagaga acgtaggacc 1800atatgtattg
ctgtatggag ggtcaaactt ctttatttcc tcgatgaact catcacccaa 1860aactcgagtg
gcaaccgagt ccaatggata atggttgcgg gtgaagagct gtagaaacaa 1920gccgcccata
taatcatacc cagcacatat gaatacaatg gcgcatgcaa gtgttgcatt 1980tgctcgtact
ggagcatgac gctgtaagag cctgatggct ccattgatgt ttcgttcatg 2040cgttagaaca
cgaatacctt cgtaatacac ggccgtggga ttattagctg caaaacacct 2100taagaaaaat
gttcgatgtc ggccttcatc agcggatc
21381152092DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A31 115gatcaaaaga
atcgtacttg aaatatttag tggaacgcat atgtcagagt tacagatatg 60gtttaactct
ttttatctcc tttttttaat ggtgtttctc tttttatctc ctataatctt 120ttgggaattt
tttattatta aatattaatt aaaaagataa attcttagag aaaatcccaa 180ctgacttgtt
aactagtgag acatatctta tttattctct gcttatctaa aaagaaaatg 240aaaaagaaaa
aaaaagtata tattagaaga ttaatataag tttaggggga aaatgattat 300tattactatt
tataaaatta gtatatttca aaattgtaca attaattact aagccttaaa 360ataaaaatgt
aaaagaagat tatcatcaag aatagtatac catctttgtt tcaaaagaaa 420agtttactaa
aagaaaaaac ttttgtttaa tttctactaa agctgaaagg aaaatgattg 480tcaatttgtt
attattatta tttatatgat agatttctta agaaacgtat agagttagtt 540acaaattcta
aattaaaaat tgtatgataa gattatctta agaaagttat acaatatatt 600cctaattcta
aaagaaaatg gttatttttt tggaatagat atacacaaca aaacaaattt 660agtataagaa
gatatgttag attaactaaa taaacatctc aggcatgaaa ctggattagg 720ttaaccagag
gtccagagac ctatatatct ctaggcatta gggtttaact acggagcaaa 780gcctcataat
caagtttata tcttgcgcat ctttagcaac caatcaatta tctaagaagc 840catgactaat
actaatgttg ctgctacaaa gcctctttct actatggtcg atgaatctcc 900tagccttctc
cgtgattggt ggtgagactc tagatcaatg atttttctta cttttttccc 960attactatgt
tatgttacgt aacataagat ggattaaact gaatctgatc ctcttaaatt 1020atattggttg
cagtatgaac aagaacctac aatacaactt tgcgatgaac ttcgtcatga 1080taatcatcaa
cattgaagca atcttgtcta tcagaaacca cgaaaatcac gtaaggaaag 1140attattcaac
gattttgata atttccggta tgttcttgcc tttcgcctat taagttgcgt 1200ttgttgggtt
ggcgcaatca gggatgtgac attatgtgaa ctcgcctaca tcttcggacg 1260catcagtcac
aacataggct ttattttctt cctagaactc ctctattgta tttctcccta 1320cttggctcta
ctcgttggtc tacatgtagg ccaatggtat ctaacttcca tgattggact 1380gtctctatgg
gaaggaatgc aagcattacg aactgatatt taacctcgtt taatagtaaa 1440atctaaactt
atttagctgc atattttggt ttaaggcaat cgagaatgtc ttagcatcta 1500aagcttactt
cgtgggacgc atctgtcaca cgttcggctt ttgtattttc gtccacctcc 1560tctattcggt
ttctcctcac ttggctctat acttcggtct cccttgtttg ctaggtttcg 1620tagccgtcat
gattgcacca agttgtccgt atcaatggaa aggcctatgc aacaaagtgc 1680aagagttacg
agactggtgg aagcatgtga atcgaccaca atcctcggtt gttattgttc 1740aaggatctcc
atttctaaga tgtgaatttt aggactcttt tatccctttt gccttttaaa 1800ttggaatacc
aacgtttatt atgtgggtta gttatgtgtg tatatgatat acaaatcaaa 1860caacatatat
aaggagaaga gatattgaat gttgattctt aatttacagg aacatgaagc 1920tcgggtcttt
ccggcaatgc catcaatatc cgaggcggtg cagtttcttc gtcagacgag 1980aaaccagaga
gtctagtatc ctaattttga acaaatagag cataaaggaa caagttatat 2040agcttcacat
aacccgaaac atgttttaag tttcaatatc aaagacaaga tc
20921161290DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A32 116gatctagaca
tatgtgtgag acgtttcatt gtaggtatct gaatgtaaag ctcaaagctt 60taacctttga
accgataaac ctctaaagct ctctcttttc cttggatgag tctcacaagt 120taagaacttc
agtgaaataa tctgacttta ttgaacccaa acttgggtat cactgtttat 180cttagcatta
cagagttttg tttttgttat gtacattgga tttgaagtct acaatgtttt 240tccaggttta
taaaccggaa gaatatagcc gggttctagc tatctgtggt cctgggaaca 300atggtggtga
tggtttggtg gcggcgaggc atttgcacca ctttggatat aaaccgttta 360tttgttatcc
caaacgtaca gccaagccac tttatactgg actggtcact caggtttgtg 420taaccagtgc
ttaatttatg ggggatcttt gttagctttc tccgtttctt tactgcctgc 480tgaatttgcc
tgtttttgta gttggattca ctctcagtcc cttttgtttc cgttgaggat 540ctgccggatg
acttgtcaaa ggactttgat gttattgtag atgcaatgtt tgggttttca 600ttccatggta
actatttttg tgcatgaatc gttagaattc ttcaaagcat gaaacaatta 660taagaagtaa
attcatcaaa cttttgaaca gcaagttttg gaatcaaagt ctcagagatg 720caccttattc
atttgcatca tgtttcagtt ggcctttgaa aatccatttt ttgcacatgt 780aggagctccc
aggcctcctt ttgatgacct catccggcga ttagtatcgt tacagaacta 840tgagcagact
cttcaaaaac acccagtcat tgtctctgtg gatattccct ctggttggca 900cgttgaagaa
ggagaccatg aagatggagg aattaagcct gatatgttgg taagtcttag 960ccgaaatgct
tgtgtttctc tttttctctt gtactcattt gttactatct gatataatga 1020aaactacttt
ataaattgaa catatttact ctttttaggt atctttgact gccccaaaat 1080tatgtgcaaa
gagattccgt ggccctcatc actttttagg tgggagattt gtaccacctt 1140ctgttgcaga
aaagtataag ctggagctcc ctagttaccc agggacatct atgtgtgtta 1200gaattggtaa
acctcccaaa gttgacatat ctgctatgag agtgaactat gtctctccag 1260aattgcttga
ggagcaggtt gaaactgatc
1290117869DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A33 117gatcccgttc
atgtattttt gccagttcga gttggggttg gttctgttta ctttttctag 60tccatgtatt
ttgcagacct attaaaacca ttctgttttt tttttggacc aacaaaaccc 120atccgttttt
agatacgaaa ataaaatttt attaaaacca ttatttttct tggaccatca 180aaacccatcc
gtttaaagat acgaaatgaa attcgattga taaatacaaa ataaagttca 240ccaaacttaa
ataaaaaggc atagatggga ccaatgagaa agaaatttct tttctcctca 300atttccccaa
aaatatataa accttaagtt tacttttttg ttgcaaggaa aaacattaat 360ctttttcaac
tttctaaaaa caatcatttc aaacgttaaa ggaacctcct cctttcttta 420cgcgtttgca
atataaccca agaagaccgc ttgtttgtac aactttccaa aaaccaaaca 480gtagtgtaat
aaacctctga cttctttttt cttctctatt tttgtgggtg ataatcaatt 540cactcggttt
gaaatttcgt ccacttttca aagatgagtg aatgaaaaag ccacgaaact 600ttccatttct
tcctctgtgt ataactctca ctgagtacga cttgccattt tctcatccaa 660aaaaaatgtt
tatccaaata catatttgtg aactttgctt ttaaaccact caagattctt 720ccccatggct
tcttcgtctt cttcttctcg gtctcgcacc tggagatacc gcgtcttcac 780gaacttccat
ggacctgacg tccgtaaaac attcctcagc catttacgta aacagtttag 840ctacaacggg
atttcgatgt ttaatgatc
869118921DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A34 118gatccatgct
tttgagttta agtgatttat ttaagatcct ctaaactttt ttttcttcac 60ttagtggtgg
ttccagtcaa tttagcaagt aagatgttgt atgtgtcaat gctataactg 120tgaattttca
gctattgtag tttgattttt gtctttgtta gcttcaggtg tcttgaatct 180gaatctgtgg
ctatatttgg tgctcggtgg tgagcaggaa gggaggggga tattgtcagg 240gttttaatgt
acgtcagatg aatagagcaa ctaatgttac tggcagtaga aggagggggt 300ttattctcag
cgtccgcgtc tgggtatagt aagggattga cccttctttt ctctggtgat 360aaagacgtag
ataggcccat gagagttgtc ccgtggaatc actaccaggt ggttgaccaa 420gagcctgagg
ctgaccctgt tcttcagctg gattctatta agaaccgagt ttcccgcggt 480tgcgctgctt
ccttcagttg ttttggtggc gcttccgcgg gacttgagac cccttctcct 540cttaaagttg
aacctgtgca gcagcagcat cgtgaaatat catcaccaga gtctgttgtt 600gttgtttctg
aaaagggtaa agaccaaata agtgaagctg ataatggcag cagcaaagaa 660gctttcaaac
tctcgttgag gagtagcttg aagaggccct ctgttgcgga atcacgctct 720ctagaagata
taaaagaata cgagacgttg agtgtggatg gtagcgatct cactggtgac 780atggcaaggc
ggaaagttca gtggcctgat gcttgtggta gtgaactcac tcaagttaga 840gaatttgagc
cgaggtacgt gtgatatgtt ttcctcttat tgagttgctt aaatcccaat 900acgagttaat
ttaagtagat c
9211191140DNAArtificial Sequencesequence of STAR A35 119gatccatttc
atatacatat taccaatttt ggcttttata ggtttgtatc cagaaggcct 60tttcgtggct
acgattaagg aaaatacgaa aacaaaagtg aattttacta cttttgtagc 120atggtttatt
ctactttata tacctaagaa atatgagcaa caattacttc tgtaatgact 180ttttactact
tcgtagttgg tacaaactac aaaagattgt gttgttttta catgatactt 240tataatatct
atattaatat atttagtcgt gtttaatcaa aaaagcacca gtggtctagt 300ggtagaatag
taccctgcca cggtacagac ccgggttcga ttcccggctg gtgcattgag 360ctatgatgat
ataggcttca gcattggttg ggtccattgc attcttctga actatcagtt 420gatgtatgcc
acacctctga gctcttcttt ttttttcctc gtcaattaat tttttaaagt 480tttgtctgcc
taaaaacttt cttctttttg attaatcata ttaagcatct cggctataaa 540aaccacggtc
tactaactta acatgcattg gactagtttt agtggagagt gttcgagtta 600aaatgagaag
ctcacgattg cataacggaa catttgattc gctaggcatc tccatttgta 660aaagtagcca
ctccaataca aaatggtcga tgatggtgag tgggtgagac aaacccacca 720ccacctcaag
aagatatatt tctctggtta agaatttgaa tggttgacaa agaaacggtc 780actctatata
cttagaaaat atagtcatac atagacacca tcggtctagt tataataata 840accactggat
taatgcccag tgaaaataat tgagtagcca aaacatgaat ataacaatat 900cccaatttac
atacaacaac acaaaggagg ttttacacga ttctatagta caaactcata 960acaacaaaaa
atcacacttt tgtttaacag ttgcctttat ggctttacta cagtatcttg 1020tccagggttt
tcacacataa caatcacagt aaatcgtttc cttttctttg catcttccat 1080tccttttgta
cacgtaacat ctccggcttc ccgaccatca gctaagaacc agatgcgatc
11401206DNAArtificial Sequencepalindromic DNA sequence 120canntg
61216DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide 121aaaaaa
61226DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
122tttttt
61236DNAArtificial Sequencehexamer 123acgtga
612426DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide 124gtacggatat cagatcttta attaag
2612526DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
125gtaccttaat taaagatctg atatcc
2612651DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer 126atcagatctg gcgcgccatt taaatcgtct
cgcgcgtttc ggtgatgacg g 5112741DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer
127aggcggatcc gaatgtattt agaaaaataa acaaataggg g
4112836DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer 128gatcggatcc ttcgaaatgg ccaagttgac
cagtgc 3612932DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer
129aggcgcggcc gcaattctca gtcctgctcc tc
3213031DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer 130gatcgaattc tcgcgacttc gcccaccatg c
3113147DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer
131aggcgaattc accggtgttt aaactcatgt ctgctcgaag cggccgg
4713231DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer 132gatcgaattc atggtgagca agggcgagga g
3113340DNAArtificial Sequenceprimer
133aggcacgcgt gttaacctac acattgatcc tagcagaagc
4013448DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide C65 134aacaagcttg atatcagatc
tgctagcttg gtcgagctga tacttccc 4813554DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide C66 135aaactcgagc ggccgcgaat tcgtcgactt
taccactccc tatcagtgat agag 5413639DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide C67 136aaaccgcggc atggaagacg ccaaaaacat aaagaaagg
3913732DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
C68 137tatggatcct agaattacac ggcgatcttt cc
3213833DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide C81 138aaaccatggc
cgagtacaag cccacggtgc gcc
3313935DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide C82 139aaatctagat caggcaccgg
gcttgcgggt catgc 3514022DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide C85 140catttccccg aaaagtgcca cc
2214124DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
D30 141tcactgctag cgagtggtaa actc
2414228DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D41 142gaagtcgacg
aggcaggcag aagtatgc
2814329DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D42 143gagccgcggt ttagttcctc
accttgtcg 2914423DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide D51 144tctggaagct ttgctgaaga aac
2314517DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
D58 145ccaagttgac cagtgcc
1714619DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D70 146tacaagccaa
ccacggcct
1914720DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D71 147cggaagtgct tgacattggg
2014820DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide D80 148gttcgtggac acgacctccg
2014921DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
D89 149gggcaagatg tcgtagtcag g
2115030DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D90 150aggcccatgg
tcacctccat cgctactgtg
3015120DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D91 151ctaatcactc actgtgtaat
2015215DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide D93 152aattacaggc gcgcc
1515315DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
D94 153aattggcgcg cctgt
1515425DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide D95 154tgctttgcat
acttctgcct gcctc
2515520DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E12 155taggggggat ccaaatgttc
2015620DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide E13 156cctaaaagaa gatctttagc
2015720DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
E14 157aagtgttgga tccactttgg
2015820DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E15 158tttgaagatc
taccaaatgg
2015920DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E16 159gttcgggatc cacctggccg
2016020DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide E17 160taggcaagat cttggccctc
2016120DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
E18 161cctctctagg gatccgaccc
2016220DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E19 162ctagagagat
cttccagtat
2016320DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E20 163agagttccgg atccgcctgg
2016420DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide E21 164ccaggcagac tcggaactct
2016520DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
E22 165tggtgaaacc ggatccctac
2016620DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E23 166aggtcaggag
atctagacca
2016722DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E25 167ccattttcgc ttccttagct
cc 2216822DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide E42 168cgatgtaacc cactcgtgca cc
2216920DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
E57 169agagatctag gataatttcg
2017036DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E92 170aggcgctagc
acgcgttcta ctcttttcct actctg
3617135DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E93 171gatcaagctt acgcgtctaa
aggcatttta tatag 3517235DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide E94 172aggcgctagc acgcgttcag agttagtgat ccagg
3517335DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
E95 173gatcaagctt acgcgtcagt aaaggtttcg tatgg
3517436DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E96 174aggcgctagc
acgcgttcta ctctttcatt actctg
3617526DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide E97 175cgaggaagct ggagaaggag
aagctg 2617625DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide E98 176caagggccgc agcttacaca tgttc
251776DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 177ccccac
61786DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
178cagcgg
61796DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 179ggcccc
61806DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 180cagccc
61816DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
181gccccc
61826DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 182cggggc
61836DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 183ccccgc
61846DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
184cggcag
61856DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 185agcccc
61866DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 186ccaggg
61876DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
187ggaccc
61886DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 188gcggac
61896DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 189ccagcg
61906DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
190gcagcc
61916DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 191ccggca
61926DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 192agcggc
61936DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
193cagggg
61946DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 194ccgccc
61956DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 195cccccg
61966DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
196gccgcc
61976DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 197gccggc
61986DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 198cggacc
61996DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
199cgcccc
62006DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 200cgccag
62016DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 201cgcagc
62026DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
202cagccg
62036DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 203cccacg
62046DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 204gctgcc
62056DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
205ccctcc
62066DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 206ccctgc
62076DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 207cacccc
62086DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
208gcgcca
62096DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 209aggggc
62106DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 210gagggc
62116DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
211gcgaac
62126DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 212ccggcg
62136DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 213agccgg
62146DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
214ggagcc
62156DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 215ccccag
62166DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 216ccgctc
62176DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
217cccctc
62186DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 218caccgc
62196DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 219ctgccc
62206DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
220gggcca
62216DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 221cgctgc
62226DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 222cagcgc
62236DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
223cggccc
62246DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 224ccgccg
62256DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 225ccccgg
62266DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
226agccgc
62276DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 227gcaccc
62286DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 228aggacc
62296DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
229agggcg
62306DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 230cagggc
62316DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 231cccgcc
62326DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
232gccagc
62336DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 233agcgcc
62346DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 234aggccc
62356DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
235cccacc
62366DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 236cgctca
62376DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 237aacgcg
62386DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
238gcggca
62396DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 239aggtcc
62406DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 240ccgtca
62416DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
241cagagg
62426DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 242cccgag
62436DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 243ccgagg
62446DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
244cgcgga
62456DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 245ccaccc
62466DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 246cctcgc
62476DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
247caagcc
62486DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 248tccgca
62496DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 249cgccgc
62506DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
250gggaac
62516DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 251ccagag
62526DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 252cgttcc
62536DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
253cgagga
62546DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 254gggacc
62556DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 255ccgcga
62566DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
256cctgcg
62576DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 257ctgcgc
62586DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 258gacccc
62596DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
259gctcca
62606DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 260cgccac
62616DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 261gcggga
62626DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
262ctgcga
62636DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 263ctgctc
62646DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 264cagacg
62656DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
265cgagag
62666DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 266cggtgc
62676DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 267ctcccc
62686DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
268gcggcc
62696DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 269cggcgc
62706DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 270aagccc
62716DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
271ccgcag
62726DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 272gcccac
62736DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 273caccca
62746DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
274gcgccc
62756DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 275accggc
62766DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 276ctcgca
62776DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
277acgctc
62786DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 278ctggac
62796DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 279gcccca
62806DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
280accgtc
62816DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 281ccctcg
62826DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 282agcccg
62836DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
283acccga
62846DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 284agcagc
62856DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 285accgcg
62866DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
286cgaggc
62876DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 287agctgc
62886DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 288ggggac
62896DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
289ccgcaa
62906DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 290cgtcgc
62916DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 291cgtgac
62926DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
292cgccca
62936DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 293ctctgc
62946DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 294agcggg
62956DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
295accgct
62966DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 296cccagg
62976DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 297ccctca
62986DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
298ccccca
62996DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 299ggcgaa
63006DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 300cggctc
63016DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
301ctcgcc
63026DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 302cggaga
63036DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 303tcccca
63046DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
304gacacc
63056DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 305ctccga
63066DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 306ctcgtc
63076DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
307cgacca
63086DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 308atgacg
63096DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 309ccatcg
63106DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
310agggga
63116DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 311gctgca
63126DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 312acccca
63136DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
313cggagc
63146DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 314cctccg
63156DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 315cgggac
63166DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
316cctgga
63176DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 317aggcga
63186DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 318acccct
63196DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
319gctccc
63206DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 320cgtcac
63216DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 321agcgca
63226DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
322gaagcc
63236DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 323gaggcc
63246DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 324accctc
63256DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
325cccggc
63266DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 326cgagaa
63276DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 327ccaccg
63286DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
328acttcg
63296DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 329gatgac
63306DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 330acgagg
63316DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
331ccggag
63326DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 332acccac
63336DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 333ctgggc
63346DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
334ccacgg
63356DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 335cggtcc
63366DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 336agcacc
63376DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
337acaccc
63386DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 338agggcc
63396DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 339cgcgaa
63406DNAArtificial
Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in STAR elements
340gagccc
63416DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 341ctgagc
63426DNAArtificial Sequenceoligonucleotide patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 342aatcgg
63438DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 343cccnncgg
834412DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 344ccgnnnnnnc cc
123456DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 345cagcgg
634621DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 346cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc c
2134715DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 347cggnnnnnnn nngcc
1534815DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 348cccnnnnnnn nncgc
153497DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 349cccngcg
73506DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 350ccccac
635122DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 351agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc cg
2235210DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 352cccnnnncgc
1035319DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 353cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnngga
1935422DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 354gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc cc
2235511DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 355cgcnnnnngc a
1135620DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 356cccnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnccc
2035710DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 357ctgnnnncgc
1035818DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 358ccannnnnnn nnnnngcg
1835917DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 359cggnnnnnnn nnnncag
1736011DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 360cccnnnnngc c
113616DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 361gccccc
636210DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 362cgcnnnngac
103636DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 363cggcag
63649DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 364cccnnncgc
93657DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 365cgcngac
73668DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 366gcgnngcc
836710DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 367cccnnnngcc
103687DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 368cccnccc
736919DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 369ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnncag
1937010DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 370gccnnnngga
103719DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 371ccgnnngga
93728DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 372aggnnggg
837311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 373cacnnnnngc g
1137423DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 374cgcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn cca
2337515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 375cccnnnnnnn nnggc
1537611DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 376cctnnnnngc g
113776DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 377gcggac
63786DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 378gccggc
63798DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 379gcgnnccc
838017DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 380ccgnnnnnnn
nnnnccc
1738114DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 381cccnnnnnnn ntcg
1438223DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 382ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn gcc
2338311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 383gggnnnnngg a
1138412DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 384ggcnnnnnng ga
1238510DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 385ccannnnccc
1038620DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 386cctnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnccg
2038718DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 387gacnnnnnnn nnnnnggc
1838819DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 388cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnccc
1938922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 389cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc cc
2239016DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 390agcnnnnnnn nnnggg
1639119DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 391cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnggc
193927DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 392cggngcc
73936DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 393agcggc
639422DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 394cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng gc
2239525DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 395gctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccc
2539622DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 396cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng gg
2239715DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 397cccnnnnnnn nncgg
1539816DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 398cccnnnnnnn
nnncgg
163996DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 399ccagcg
640023DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 400gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cgc
2340112DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 401cctnnnnnnc gc
124027DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 402gganccc
740324DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 403cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncac
2440426DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 404cgcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn nnnccg
264056DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 405ccggca
640626DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 406cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnccc
2640721DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 407agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc c
2140813DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 408cctnnnnnnn ggc
1340911DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 409gccnnnnncg c
1141020DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 410gccnnnnnnn
nnnnnnncgc
2041117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 411cagnnnnnnn nnnnccc
1741222DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 412gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng ac
2241321DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 413cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngc g
214146DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 414ccccgc
641522DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 415cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnna gc
2241615DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 416aggnnnnnnn
nnggg
1541718DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 417cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnctc
1841814DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 418cacnnnnnnn ncgc
1441913DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 419ccannnnnnn ccg
134207DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 420cggngca
742120DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 421cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnccc
204226DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 422agcccc
642319DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 423cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnngtc
194249DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 424gcgnnngca
94256DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 425cggggc
642620DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 426gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnccc
2042713DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 427accnnnnnnn cgc
1342813DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 428aggnnnnnnn cgg
1342922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 429cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc ga
2243012DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 430cgcnnnnnnc ag
1243117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 431cagnnnnnnn nnnngcg
1743218DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 432ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnccg
1843324DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 433cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncag
244347DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 434cagnggg
74356DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 435cgcccc
643624DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 436gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ngcc
2443721DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 437cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngg c
2143821DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 438cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnag g
2143926DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 439aggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn
nnngcg 2644011DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 440cggnnnnnct c
1144123DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 441tccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cga
2344210DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 442gcgnnnnccc
104438DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 443cccnncgc
84449DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 444cgtnnncag
944519DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 445ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnngag
1944612DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 446ctcnnnnnnc gc
1244710DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 447cgcnnnngag
1044811DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 448gcgnnnnngg a
114497DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 449ccgncag
745017DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 450cgcnnnnnnn nnnnccg
1745125DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 451gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccc
2545224DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 452cgcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn ngaa
2445325DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 453gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngga
254547DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 454ccancgg
745513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 455cccnnnnnnn gcg
1345616DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 456aggnnnnnnn nnnccc
164576DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 457ccaggg
645816DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 458cagnnnnnnn
nnnccc
1645924DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 459ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccg
2446024DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 460ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nggc
244618DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 461cccnngcg
84627DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 462cgcnggc
746311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 463ccgnnnnnga c
114646DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 464ggaccc
64657DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 465cccnccg
746621DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 466cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnac g
2146714DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 467agcnnnnnnn nccc
144689DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 468cccnnnggc
946915DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 469aggnnnnnnn nncgg
1547020DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 470cccnnnnnnn
nnnnnnncgc
204716DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 471ccgccg
647214DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 472cgcnnnnnnn nagc
1447325DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 473cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnacc
2547423DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 474gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn gac
234757DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 475agcngcg
747617DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 476ccgnnnnnnn
nnnnggc
1747710DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 477cggnnnnaga
1047820DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 478cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnccg
2047926DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 479cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnngcg
2648016DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 480ccannnnnnn nnncgc
1648126DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 481cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn
nnncac 2648217DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 482ccgnnnnnnn
nnnngcc
1748324DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 483cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccc
2448421DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 484cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncg c
2148522DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 485cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng cc
2248626DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 486cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnggc
2648725DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 487cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccg
2548816DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 488cggnnnnnnn
nnncca
1648923DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 489cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ccc
2349017DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 490cgcnnnnnnn nnnnaca
174916DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 491cggacc
649216DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 492gcgnnnnnnn nnngcc
1649314DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 493gcgnnnnnnn ngac
1449421DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 494cccnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnngg g
2149522DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 495cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng gc
2249622DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 496cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc ca
224979DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 497gccnnnccc
949810DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 498cagnnnnggg
1049912DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 499cccnnnnnng cg
1250022DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 500ccgnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnc gc
2250123DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 501cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn gca
2350219DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 502cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnntcc
195037DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 503gccncgc
750425DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 504ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngag
2550516DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 505gggnnnnnnn nnngga
1650611DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 506cagnnnnncc g
115079DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 507cgcnnnaga
95086DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 508gccgcc
650914DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 509cccnnnnnnn nggc
1451012DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 510cctnnnnnng cg
1251112DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 511gacnnnnnnc cc
125127DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 512cggnccc
751321DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 513cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc g
2151415DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 514cagnnnnnnn nnccc
1551516DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 515cggnnnnnnn nnnggc
1651616DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 516cgannnnnnn nnnacg
165179DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 517gcgnnntcc
95189DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 518cccnnngcc
95197DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 519gcgnacc
752015DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 520ccgnnnnnnn nnagg
1552122DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 521cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc ag
225226DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 522ggcccc
652318DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 523aggnnnnnnn nnnnnccg
185246DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 524ccggcg
65258DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 525ccgnngcc
852617DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 526ccgnnnnnnn nnnngtc
175276DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 527cagccc
652811DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 528cccnnnnncc g
1152926DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 529gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn
nnnccc 265308DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 530gacnncgc
853112DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 531cgcnnnnnnc ac
1253220DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 532aggnnnnnnn nnnnnnngcg
2053311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 533gacnnnnncg c
1153425DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 534cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccg
2553518DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 535ccgnnnnnnn nnnnngga
1853615DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 536ggcnnnnnnn
nngac
1553716DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 537aggnnnnnnn nnnggg
1653816DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 538ccgnnnnnnn nnngag
1653912DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 539cgcnnnnnng ga
1254013DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 540cgcnnnnnnn agc
1354119DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 541ccannnnnnn nnnnnncgg
1954212DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 542cggnnnnnng ga
1254325DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 543cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngcc
2554418DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 544ccannnnnnn nnnnncgc
185457DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 545cggnggc
75469DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 546gcgnnncca
95477DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 547aggncgc
754811DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 548ctcnnnnncg c
115496DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 549cccacg
655023DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 550cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ccg
2355110DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 551ggcnnnnccc
1055214DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 552aggnnnnnnn ngcg
145537DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 553ctgnccc
755422DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 554cccnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnc ag
2255515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 555cgcnnnnnnn nngac
1555612DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 556cagnnnnnnc cg
1255718DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 557cgtnnnnnnn nnnnncgc
1855813DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 558ctcnnnnnnn gcc
1355925DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 559cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nntcc
2556013DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 560cccnnnnnnn gcc
1356119DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 561cagnnnnnnn nnnnnncgg
195627DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 562cgcngcc
756323DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 563cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ccg
2356410DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 564aggnnnnccc
1056516DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 565agcnnnnnnn nnncgc
1656617DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 566cccnnnnnnn
nnnncgg
1756714DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 567cccnnnnnnn ngcc
145687DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 568ccgncgg
75697DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 569cccnacc
75706DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 570cgccag
657125DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 571ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nntgc
2557210DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 572gcgnnnncga
1057325DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 573ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngcc
2557416DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 574ccannnnnnn nnnccc
1657519DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 575cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnggg
1957624DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 576agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncgg
2457714DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 577cgannnnnnn ncgc
1457810DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 578agcnnnnccc
1057912DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 579ggannnnnnc cc
1258019DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 580cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnaag
1958117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 581accnnnnnnn nnnncgc
1758218DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 582ccgnnnnnnn nnnnncag
1858318DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 583cccnnnnnnn nnnnnggg
1858423DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 584cacnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn acg
2358524DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 585cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccc
2458616DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 586cgtnnnnnnn nnngtc
1658719DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 587cccnnnnnnn nnnnnngcg
195887DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 588gcancgc
758910DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 589agannnnccg
1059016DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 590gcgnnnnnnn
nnnagc
165916DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 591cgcgga
659210DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 592cggnnnngac
1059318DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 593cccnnnnnnn nnnnncgc
1859421DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 594gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc c
2159512DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 595gcgnnnnnnt cc
125969DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 596cggnnncag
95979DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 597cccnnncca
95989DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 598agcnnnccc
959922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 599gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng ca
2260014DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 600aggnnnnnnn nccg
146016DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 601cccccg
660211DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 602gcgnnnnnga c
1160315DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 603cccnnnnnnn nnacc
1560411DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 604ctgnnnnncg c
1160520DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 605cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnctc
2060620DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 606cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnngca
2060714DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 607ccgnnnnnnn ngcc
1460813DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 608ccgnnnnnnn cac
1360914DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 609agcnnnnnnn ngcg
1461022DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 610cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng ga
2261118DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 611ccannnnnnn nnnnnccg
186128DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 612cggnnccc
861319DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 613ccannnnnnn nnnnnnggg
1961421DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 614cggnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnngc a
2161515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 615cgcnnnnnnn nngca
1561625DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 616cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nncca
2561721DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 617gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncg a
2161816DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 618cccnnnnnnn nnncgc
1661920DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 619ctcnnnnnnn nnnnnnncgc
2062017DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 620cacnnnnnnn
nnnngcg
176218DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 621ccgnnggc
862224DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 622ctgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccc
2462319DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 623gggnnnnnnn nnnnnncac
1962421DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 624cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngg c
2162526DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 625cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn
nnncga 2662614DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 626cccnnnnnnn
ncga
1462713DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 627gagnnnnnnn ccc
136288DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 628cgcnnccg
86296DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 629ccctcc
66306DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 630agcgcc
66318DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 631cccnntcc
863211DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 632ccgnnnnncc c
1163319DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 633cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnncgc
196347DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 634cccncgc
763522DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 635gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng ca
2263622DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 636cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc ca
2263719DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 637ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnncgc
1963823DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 638ccgnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn cag
2363924DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 639cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nggc
2464020DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 640ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnagg
2064111DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 641cccnnnnncg g
1164212DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 642cccnnnnnng ga
126438DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 643acgnnccc
864415DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 644ccannnnnnn
nnccg
1564525DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 645cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nncca
256466DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 646cagggg
66477DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 647agcnccc
764813DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 648gcgnnnnnnn tcc
1364924DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 649acgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncca
2465020DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 650gctnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnccc
2065120DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 651gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnccc
2065225DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 652gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnagc
2565314DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 653ccgnnnnnnn ncag
1465412DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 654gcgnnnnnng cc
1265516DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 655gcgnnnnnnn nnngca
1665613DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 656cctnnnnnnn gcc
1365719DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 657gccnnnnnnn nnnnnngcc
1965820DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 658cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnngcc
2065921DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 659cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncg g
2166019DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 660ccannnnnnn nnnnnncgc
1966117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 661agcnnnnnnn nnnnggg
176626DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 662ggagcc
66639DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 663gccnnntcc
966411DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 664cctnnnnngc c
1166524DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 665cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccc
246669DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 666cctnnnggc
96676DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 667ccgctc
666823DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 668agcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn gcg
2366920DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 669acgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnggg
2067018DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 670cgannnnnnn nnnnnggc
1867126DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 671cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnncgc
2667218DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 672acgnnnnnnn nnnnnctg
186736DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 673ccgccc
667416DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 674ccgnnnnnnn
nnngga
166759DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 675cccnnngcg
967620DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 676gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnncgc
2067714DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 677ccgnnnnnnn ncgc
1467816DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 678cgcnnnnnnn nnnaca
1667925DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 679cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccg
2568020DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 680cacnnnnnnn
nnnnnnncgc
206819DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 681gacnnnggc
968213DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 682gaannnnnnn cgc
1368322DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 683cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng gc
2268415DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 684ggcnnnnnnn nnccc
1568515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 685cccnnnnnnn nngcc
156866DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 686cgctgc
668714DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 687cctnnnnnnn nggc
1468814DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 688ccannnnnnn nccc
146898DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 689gacnnccc
86907DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 690ggcnccc
76916DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 691cgcagc
669210DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 692aggnnnngcg
1069312DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 693cggnnnnnnt cc
1269425DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 694acgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnggc
2569514DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 695cccnnnnnnn nacg
1469624DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 696cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ngcc
246978DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 697gccnncga
869814DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 698cccnnnnnnn
ngcg
146996DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 699cccctc
670017DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 700gccnnnnnnn nnnncgc
1770115DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 701agcnnnnnnn nnccc
157026DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 702gctgcc
67039DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 703cgcnnnccc
97048DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 704cccnnccc
870515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 705gccnnnnnnn nncgc
1570625DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 706gcannnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nncgc
2570710DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 707cagnnnncgg
107088DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 708cagnnggg
870922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 709gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc cc
2271011DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 710gagnnnnncc c
1171122DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 711cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnt cg
227129DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 712cccnnnggc
971319DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 713gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnngga
1971423DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 714gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ggc
2371520DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 715cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnggc
207169DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 716aggnnnccg
97176DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 717caccgc
671824DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 718cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncag
247197DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 719agcngcc
772024DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 720cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nggc
2472111DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 721cccnnnnnag g
117226DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 722aacgcg
672316DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 723cccnnnnnnn nnncca
1672419DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 724cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnngag
1972513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 725cgcnnnnnnn gcc
1372615DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 726cccnnnnnnn nnccg
1572722DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 727cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc cc
2272819DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 728gaannnnnnn
nnnnnncgc
197299DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 729ggcnnnccc
973017DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 730tccnnnnnnn nnnncca
177316DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 731cacccc
673222DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 732cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc cg
2273321DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 733cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnag c
2173418DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 734cccnnnnnnn
nnnnngcg
1873515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 735cccnnnnnnn nngag
1573626DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 736ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnntcc
267376DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 737cgccgc
673813DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 738atgnnnnnnn cgg
1373926DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 739gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn
nnngca 2674010DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 740cggnnnnggc
1074122DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 741cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnna gc
2274211DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 742cggnnnnngg c
117436DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 743gcggga
674426DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 744ggcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnncac
2674515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 745cccnnnnnnn nnccc
1574623DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 746accnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn ggc
2374712DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 747cccnnnnnnc ga
1274816DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 748aagnnnnnnn nnncgg
1674923DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 749cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cac
2375022DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 750cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc gg
2275124DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 751gacnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nggc
2475221DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 752gggnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnga c
2175310DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 753gccnnnntcc
1075421DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 754ggcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc c
2175518DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 755cagnnnnnnn nnnnncgc
187569DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 756ccannngcg
975722DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 757ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng ag
227588DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 758agcnncgc
875910DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 759gagnnnnccc
107609DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 760aggnnncgc
976119DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 761cacnnnnnnn nnnnnnagg
1976210DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 762cccnnnncag
107638DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 763cccnngaa
876425DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 764cgcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn nngag
2576524DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 765acgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nggg
2476610DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 766cccnnnnggc
1076715DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 767cggnnnnnnn nngag
157689DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 768cccnnnggg
976910DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 769gagnnnnggc
1077011DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 770cgcnnnnnga g
1177126DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 771ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnagg
2677221DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 772cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc c
2177323DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 773aggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ccg
2377412DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 774aggnnnnnng gg
1277526DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 775ggcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn
nnnccc 2677623DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 776gcannnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn cgc
2377717DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 777cgannnnnnn nnnnacg
177788DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 778cgcnngga
877911DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 779ctgnnnnncc c
1178026DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 780tccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnncca
267818DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 781ccannggg
878221DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 782ccgnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnngc g
2178311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 783ccannnnngg g
117847DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 784cggntgc
778520DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 785cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnngcg
207866DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 786cagccg
678715DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 787gccnnnnnnn nntcc
1578826DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 788aggnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn nnncgc
2678912DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 789cccnnnnnng ac
1279017DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 790cggnnnnnnn nnnncca
1779120DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 791gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnncac
2079221DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 792gcannnnnnn nnnnnnnncg c
217938DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 793cgcnnaca
879415DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 794accnnnnnnn
nnccc
1579515DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 795gcgnnnnnnn nncgc
1579621DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 796cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngc g
2179724DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 797cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ngtc
247989DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 798gcgnnnccc
979917DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 799cggnnnnnnn nnnngcc
178007DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 800cccncgg
780110DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 801gccnnnncca
1080210DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 802cccnnnnccg
108038DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 803cgtnngca
880413DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 804agcnnnnnnn tcg
1380521DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 805ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnga a
2180611DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 806accnnnnncc c
1180720DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 807cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnngag
2080813DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 808cccnnnnnnn cgc
1380918DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 809gagnnnnnnn nnnnncgc
1881023DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 810ggcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ccc
2381117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 811acgnnnnnnn nnnnctc
1781215DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 812acannnnnnn
nncgg
1581313DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 813ctgnnnnnnn ccc
138148DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 814cccnngcc
88158DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 815cggnngca
88166DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 816ccctgc
681713DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 817cgcnnnnnnn acc
138188DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 818gcanngcc
881914DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 819gcgnnnnnnn ncca
148206DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 820agccgc
68218DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 821gcgnngca
88228DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 822ccgnngtc
88239DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 823ccgnnnaca
982419DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 824acgnnnnnnn
nnnnnntgg
1982514DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 825ccannnnnnn ncgc
1482615DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 826ccgnnnnnnn nnggc
1582711DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 827ccannnnncc g
118289DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 828aggnnnggg
98298DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 829cagnnggc
883014DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 830cccnnnnnnn
ncag
1483111DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 831agcnnnnnca g
1183222DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 832cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng cc
2283321DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 833gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc c
2183417DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 834cccnnnnnnn nnnngcc
178358DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 835cgannacg
883610DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 836cggnnnngcc
1083712DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 837cacnnnnnnc gc
1283811DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 838cggnnnnnac g
1183910DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 839ctgnnnngcc
1084024DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 840gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncga
2484114DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 841cctnnnnnnn ncgc
1484210DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 842gccnnnnccc
1084316DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 843cggnnnnnnn nnngcc
1684411DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 844gccnnnnngg a
1184513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 845accnnnnnnn gcg
1384614DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 846cccnnnnnnn ncgc
1484711DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 847cagnnnnncc c
1184820DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 848cacnnnnnnn
nnnnnnngga
208497DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 849cccngcc
785011DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 850cccnnnnnag c
1185111DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 851ggcnnnnngg a
1185223DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 852cgannnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn gag
2385313DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 853cgcnnnnnnn aca
1385419DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 854ccannnnnnn
nnnnnnccc
1985526DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 855cggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnggc
2685623DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 856cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn gcc
2385716DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 857cctnnnnnnn nnnccg
1685814DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 858cccnnnnnnn nccg
148599DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 859cgcnnngag
986013DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 860cgcnnnnnnn aag
1386117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 861cggnnnnnnn nnnngga
1786221DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 862ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncc g
218639DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 863cccnnngca
98648DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 864cggnncag
88658DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 865aggnnccg
886610DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 866cccnnnncac
1086725DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 867ggannnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccc
2586814DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 868cccnnnnnnn ncac
1486912DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 869accnnnnnnc cg
1287012DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 870cccnnnnnng gc
1287112DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 871cccnnnnnnc cg
1287220DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 872cgcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnngcc
2087311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 873ccgnnnnntc c
1187412DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 874gccnnnnnng cc
1287513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 875cggnnnnnnn gga
1387612DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 876gggnnnnnng ga
1287718DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 877gccnnnnnnn nnnnntcc
1887822DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 878agtnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnc cg
2287925DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 879ggcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngcc
258809DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 880ccgnnnccg
988114DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 881cccnnnnnnn nacc
1488221DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 882cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngc c
2188323DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 883cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cgg
238847DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 884gcgncca
788520DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 885cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnncag
2088614DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 886cccnnnnnnn nccc
1488718DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 887acannnnnnn nnnnngcg
1888810DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 888aggnnnnccg
1088919DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 889cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnngcc
198908DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 890gagnncgc
889115DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 891cccnnnnnnn nngcg
1589223DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 892cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn aca
2389323DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 893gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cca
2389424DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 894aagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccg
248957DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 895cgcngga
78967DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 896ccanccc
789724DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 897cgtnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ntgc
2489820DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 898tccnnnnnnn nnnnnnncga
2089911DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 899cacnnnnngg g
1190018DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 900ccgnnnnnnn nnnnngca
1890112DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 901ctgnnnnnnc cc
1290214DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 902cggnnnnnnn
nggc
1490317DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 903ccannnnnnn nnnnggg
1790425DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 904acgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nncaa
2590526DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 905gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnccc
2690610DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 906cgcnnnncag
1090723DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 907agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ggg
2390826DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 908cacnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn nnnccg
2690923DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 909acgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cag
239107DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 910aggnccc
791118DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 911cgtnnnnnnn nnnnncac
1891215DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 912cggnnnnnnn nnggc
1591316DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 913cgcnnnnnnn nnngcg
1691412DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 914cccnnnnnnc tc
1291516DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 915ccgnnnnnnn nnnagg
1691624DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 916cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncag
2491723DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 917agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ccg
2391815DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 918agcnnnnnnn nngcg
159199DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 919ccannnggc
992017DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 920cccnnnnnnn
nnnnggc
1792111DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 921acgnnnnngc a
1192220DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 922cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnncgg
2092311DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 923cccnnnnncc a
119247DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 924ccgnagg
792516DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 925gggnnnnnnn nnngac
1692621DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 926cgcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnncc a
2192725DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 927cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nncgc
259289DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 928cgtnnncgc
992920DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 929agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnccg
209308DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 930ggcnncga
893114DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 931cagnnnnnnn nccc
149328DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 932ccgnngac
893325DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 933agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnagg
2593410DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 934cctnnnnggc
1093517DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 935ccgnnnnnnn nnnnagc
1793610DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 936cacnnnncgc
109377DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 937ccgnccc
793819DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 938ctgnnnnnnn
nnnnnnggc
1993922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 939cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnna cc
2294024DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 940cacnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncag
2494114DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 941ggcnnnnnnn ngcc
1494221DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 942gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngg a
2194322DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 943ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng cc
2294426DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 944ccgnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn nnnacc
2694513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 945cgannnnnnn ccc
1394612DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 946ccgnnnnnnc tc
1294716DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 947cggnnnnnnn nnnctc
1694822DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 948cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc gc
229499DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 949ccannnagg
995024DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 950gccnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn ngcc
2495124DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 951cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ngga
2495226DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 952ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnggc
2695316DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 953acannnnnnn nnngcg
1695411DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 954cggnnnnncc c
1195513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 955cccnnnnnnn tcc
1395616DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 956acgnnnnnnn
nnncgc
169579DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 957cccnnntcc
995814DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 958ccgnnnnnnn ncgg
1495921DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 959ccannnnnnn nnnnnnnncg g
2196012DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 960ccgnnnnnnc cg
129619DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 961cagnnngcg
99627DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 962gagnccc
796324DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 963ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ntgc
2496413DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 964cccnnnnnnn cca
139659DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 965cggnnncca
99667DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 966acgnccc
796719DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 967cggnnnnnnn nnnnnntga
1996812DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 968ctcnnnnnng gc
129698DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 969gcgnngac
897017DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 970gggnnnnnnn nnnnacc
1797110DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 971cgcnnnngga
1097217DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 972cccnnnnnnn nnnnccg
1797325DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 973ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngca
259746DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 974gcggca
697513DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 975agannnnnnn ccc
139768DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 976cggnncca
897712DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 977cccnnnnnnc cc
1297810DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 978accnnnngcg
1097921DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 979cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncg c
2198015DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 980agcnnnnnnn
nngtc
1598124DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 981cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nctc
2498224DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 982cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ncga
2498321DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 983cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngc c
2198417DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 984accnnnnnnn nnnnggc
1798521DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 985aggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnncg c
219866DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 986gcgcca
698715DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 987gcgnnnnnnn nnagc
1598824DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 988gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ngca
2498923DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 989cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cag
2399014DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 990ccannnnnnn ncgg
1499116DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 991ccgnnnnnnn nnnggc
169926DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 992gcagcc
69938DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 993cagnncgc
899414DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 994cgcnnnnnnn nggc
1499523DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 995ctgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ggc
2399620DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 996gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnacc
209977DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 997ccgntgc
799814DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 998cagnnnnnnn
ncgc
1499917DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 999aagnnnnnnn nnnncgc
17100012DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1000ccgnnnnnnt cc
12100124DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1001ccannnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nccc
2410026DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1002ccaccc
6100312DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1003gagnnnnnnc cc
12100426DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1004agcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnggc
2610056DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1005cagcgc
6100618DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1006ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnctc
18100721DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1007cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnac g
21100823DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1008ggcnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnnnn cga
23100922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1009ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnna ag
22101020DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1010cgcnnnnnnn nnnnnnntcc
20101113DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1011aggnnnnnnn cgc
13101213DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1012cggnnnnnnn ccc
13101310DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1013cgcnnnngcc
10101412DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1014cgannnnnnc cc
12101525DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1015cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nngga
25101622DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1016cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng cg
22101713DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1017ccannnnnnn cgc
13101812DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1018cccnnnnnng cc
12101920DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1019gccnnnnnnn nnnnnnntcc
20102020DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1020aggnnnnnnn nnnnnnngcc
20102117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1021cgcnnnnnnn nnnngcc
1710226DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1022tccgca
6102314DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1023gcgnnnnnnn
nccc
14102417DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1024ccannnnnnn nnnngcg
17102510DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1025cacnnnnggg
10102613DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1026cggnnnnnnn tcc
13102711DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1027gcgnnnnngc c
11102818DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1028acgnnnnnnn
nnnnncag
18102925DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1029ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nncgc
25103014DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1030cggnnnnnnn ntgc
1410317DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 1031cccngag
7103225DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1032gcgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nntga
25103321DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1033ggcnnnnnnn nnnnnnnngc c
21103413DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1034ccgnnnnnnn
ccc
13103525DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1035acannnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnccc
25103622DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1036accnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnng gg
2210377DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented
in STAR elements 1037aganggc
7103823DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1038gggnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn tga
23103911DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1039cagnnnnngg g
11104019DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1040gccnnnnnnn
nnnnnncgc
19104113DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1041gcgnnnnnnn gga
13104220DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1042cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnncca
20104310DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1043ccgnnnngtc
10104419DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1044cccnnnnnnn nnnnnncgc
19104520DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1045gcgnnnnnnn
nnnnnnnacc
20104626DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1046cagnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnnggg
26104710DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1047ccgnnnnccc
10104811DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1048cgcnnnnngg c
11104912DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1049cctnnnnnng gc
1210509DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1050aggnnnggc
9105117DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1051cggnnnnnnn nnnncgc
17105224DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1052ctgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn ngga
24105323DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1053cacnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn cca
2310549DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1054cggnnngag
9105515DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1055cccnnnnnnn
nncca
1510567DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1056cccnacg
710577DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1057cagngcc
7105812DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1058aggnnnnnnc cg
12105915DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1059agcnnnnnnn nnggg
15106013DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1060cccnnnnnnn
ggc
13106119DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1061cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnccc
19106225DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1062ccgnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn nnttc
25106313DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1063cccnnnnnnn ccg
13106412DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1064cgannnnnng gc
12106510DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1065cggnnnnctc
1010666DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1066cggcgc
6106719DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1067cctnnnnnnn nnnnnnacg
19106812DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns
over-represented in STAR elements 1068gggnnnnnnc ac
12106922DNAArtificial SequenceDyad
patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1069cccnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnc gc
22107016DNAArtificial
SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR elements 1070cccnnnnnnn
nnnctc
1610716DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in STAR
elements 1071ccccag
6107211DNAArtificial SequenceDyad patterns over-represented in
STAR elements 1072gccnnnnncc c
11
User Contributions:
Comment about this patent or add new information about this topic:
| People who visited this patent also read: | |
| Patent application number | Title |
|---|---|
| 20120227841 | BOILING WATER TAP |
| 20120227840 | CHECK VALVE OF HYDRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM |
| 20120227839 | Check Valve Assembly for Well Stimulation Operations |
| 20120227838 | PRESSURE REGULATOR WITH MANUAL SHUT-OFF VALVE |
| 20120227837 | CHECK VALVE OF HYDRAULIC BRAKE SYSTEM |